So, you've hit "send" on your latest email campaign. Now what? You might assume your job is done, but the most critical part of the journey is just beginning.
What Is Email Deliverability and Why It Matters
Let's get one thing straight: email deliverability is not the same as email delivery. They sound similar, but the difference is huge.
Think of it like sending a package. Email delivery is when the postal service confirms they've picked up your parcel from the warehouse. Success, right? Not quite. Email deliverability is the full journey—making sure that package actually gets through the right doors, past security, and lands directly in the recipient's hands, not in a back-alley dumpster or a forgotten P.O. box.
This distinction is everything. Just because a server accepts your email doesn't mean a person will ever read it. In fact, a staggering 15-20% of all legitimate emails never make it to the main inbox. For any business, that's a massive blind spot, leading to lost sales, invisible marketing, and a tarnished brand reputation. If your audience isn't seeing your messages, you're just talking to yourself.
To help clarify, here's a quick breakdown of these often-confused terms.
Deliverability vs Delivery vs Inbox Placement
| Concept | What It Means | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | The receiving server (like Gmail) accepted your email. It's the first technical handshake. | The post office accepted your letter. |
| Deliverability | The broader measure of where your email lands: the primary inbox, a promotions tab, or the spam folder. | The postal service successfully delivered your letter to the right building. |
| Inbox Placement | The ultimate goal: your email arrived in the recipient's main, high-visibility inbox. | Your letter was placed directly into the recipient's personal mailbox, not the junk mail bin. |
Getting this right means your message has the best possible chance of being seen and acted upon.
The Modern Pillars of Reaching the Inbox
Getting into the inbox today is about proving you're a trustworthy sender. It's not about gaming the system; it's about building a solid reputation with mailbox providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Apple Mail. This trust is built on three core pillars.
Mastering these is non-negotiable:
- Email Security: This is all about your technical credentials. Authentication protocols act like a digital passport, proving you are who you say you are and that your email hasn't been hijacked.
- User Privacy: This pillar is built on respect. It's about sending to people who actually want to hear from you, making it dead simple to unsubscribe, and protecting user data. These actions are huge signals to inbox providers.
- Hosted Email Platforms: Your sending infrastructure is the foundation of it all. Using a secure, privacy-focused email host like Typewire gives you the managed IP addresses and built-in security needed for consistently strong deliverability.
Your ability to land in the inbox is no longer just about clever subject lines; it's a direct reflection of your commitment to security and privacy. Mailbox providers reward senders who prove they are safe, reliable, and respectful of the end-user.
This guide will walk you through exactly how to build and maintain these pillars. By focusing on a foundation of security and user respect, you can ensure your emails aren't just sent—they're seen.
The Three Pillars of Email Authentication
Before an email can even think about landing in an inbox, it has to prove it's legit. This is where email authentication comes in. Think of it as a digital passport for your messages—a set of checks that prove to services like Gmail and Outlook that you are who you say you are, not some spammer or phisher in disguise.
This whole verification process is the absolute foundation of good deliverability. Without it, your emails are basically unsigned letters showing up from a mystery address. They look suspicious, and they’ll probably get tossed out before anyone ever sees them. In the world of email today, trust is built on three core security protocols: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
This map shows how authentication fits into the bigger picture, taking your email from simply "delivered" all the way to the primary inbox.
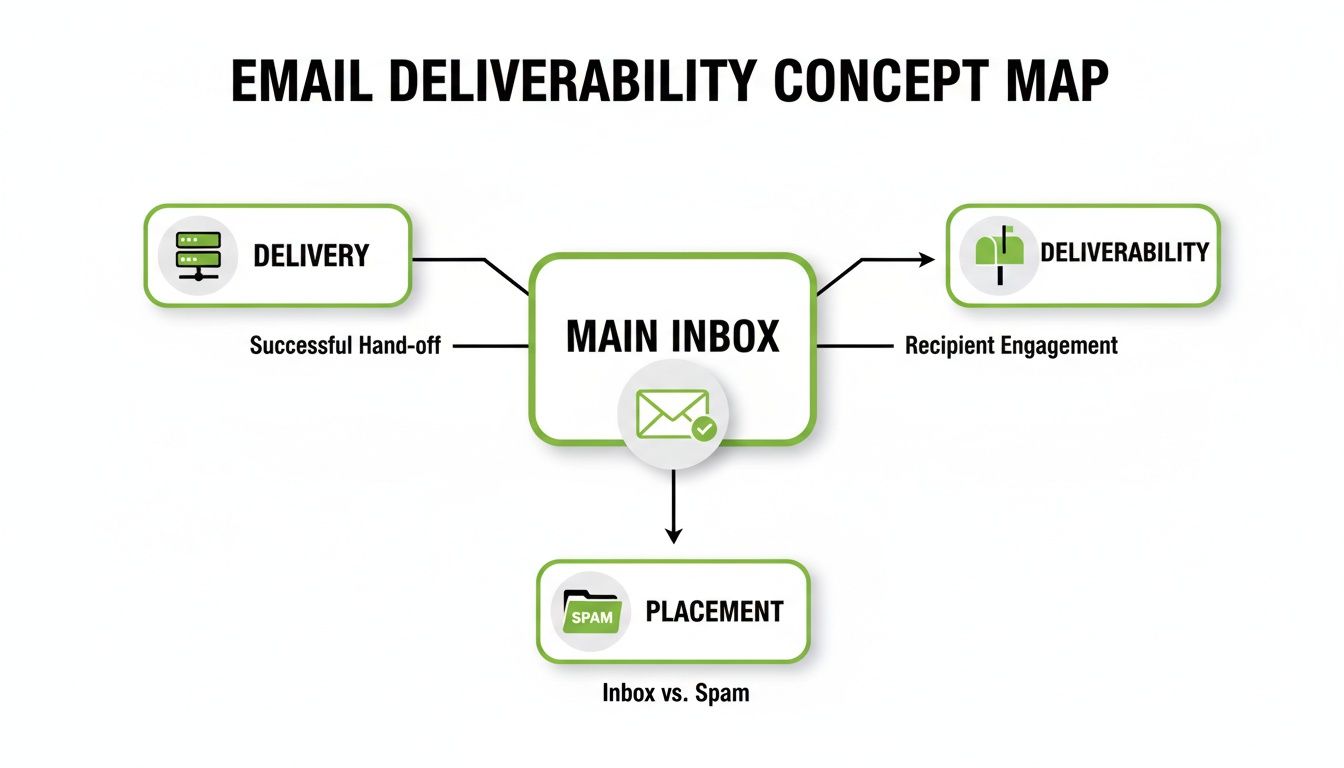
As you can see, just getting your email delivered is only the first hurdle. True deliverability is about successfully navigating spam filters to secure that prime real estate: the main inbox.
SPF: The Approved Senders List
First up is the Sender Policy Framework (SPF). Picture yourself as a business owner who only allows specific, authorized courier services to deliver your company’s mail. SPF does the same thing for your domain. It's a public record that lists all the mail servers (by their IP address) that are officially allowed to send emails on your behalf.
When an email from your domain arrives, the recipient's server glances at this list. If the sending server is on your approved list, it passes the SPF check. Simple. If it’s not, that’s a huge red flag that someone might be trying to forge your address.
DKIM: The Tamper-Proof Seal
Next is DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). While SPF confirms who can send your emails, DKIM confirms that the email itself hasn't been messed with on its way to the recipient.
Think of it like a high-tech, tamper-proof wax seal on an envelope. A unique digital signature gets attached to your email's header, and the key to unlock it is published in your domain's public records. The receiving server uses this key to check the signature. If it all matches up, the server knows the message is authentic and nothing has been altered.
DMARC: The Security Policy
Finally, Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is the glue that holds SPF and DKIM together. It also gives receiving servers clear instructions on what to do if a message fails either of those checks. It’s like telling the post office, "If a letter claiming to be from me doesn't pass verification, either quarantine it or just reject it outright."
DMARC also sends back crucial reports, giving you a window into who is trying to send email from your domain—both the good and the bad.
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC properly isn't just a "nice-to-have" anymore. It's the absolute minimum for building trust with mailbox providers and a clear signal that you take email security and user privacy seriously.
Getting these protocols in place can sound a bit technical, but a secure email host like Typewire is built to handle the heavy lifting for you. For anyone ready to get their hands dirty, our real-world guide to setting up email authentication breaks down the steps.
The difference this makes is obvious when you look at the numbers. In North America, where these protocols are widely adopted, the average inbox placement rate is a healthy 87.9%. This shows a direct link between strong authentication and getting your emails seen, especially since nearly 17% of marketing emails globally still fail to reach the inbox.
How Sender Reputation Impacts Inbox Placement
Once you’ve proven you are who you say you are with email authentication, the next big hurdle is your sender reputation. The best way to think about it is as a credit score for your email program. Every major Internet Service Provider (ISP)—think Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo—is watching what you do. They're assigning you a score that directly influences whether your emails land in the inbox or get lost in the spam folder.
This score isn't just a single number; it's a blend of your IP reputation and your domain reputation. These two work hand-in-hand to build a complete picture of you as a sender. A good score tells ISPs you’re sending valuable content that people want. A bad score screams "spammer," and your messages will be treated accordingly.

IP Reputation Versus Domain Reputation
Your IP reputation is tied to the digital address of the server sending your emails. It’s like the physical street address of a building. If tons of junk mail comes from that one address, the whole location gets a bad name, no matter who sent the specific letter.
Your domain reputation, on the other hand, is all about your sending domain (like yourcompany.com). This is more like your business's brand name. Even if you move to a new building (a new IP address), your brand’s history follows you. ISPs look at both to make their final judgment call.
A strong sender reputation is your passport to the inbox. It's not something you can buy; it must be earned over time through consistent, positive sending practices that respect user privacy and security.
Building Trust with Mailbox Providers
Think of it like opening a new shop in a small town. You can't just expect customers to flood in; you have to earn their trust first. The same goes for email. You need to show the mailbox providers you're a good neighbor.
Positive signals that build your reputation include:
- High Open Rates: When people consistently open your emails, it shows their inbox providers that your content is welcome.
- Consistent Clicks: Clicks on your links are a clear sign of real engagement and interest.
- Replies and Forwards: These are gold. An actual conversation starting from your email is one of the strongest trust signals you can send.
On the flip side, a few negative signals can wreck your score in a hurry:
- High Spam Complaints: This is the ultimate red flag. A complaint rate as low as 0.1% can do serious damage to your deliverability.
- High Bounce Rates: Hard bounces (emails to invalid addresses) tell ISPs that your list is old and unkempt.
- Spam Traps: Hitting one of these "honeypot" email addresses, which exist only to catch spammers, can get you blacklisted almost instantly.
Of course, to get those positive engagement signals, you first need people to open your emails. That's where crafting compelling email subject lines becomes an essential skill.
Strategies for a Strong Sender Reputation
Building a solid reputation needs to be a priority from day one. If you're starting with a new domain or IP, you absolutely have to "warm it up." This process, known as IP warming, means you start by sending a small number of emails to your most engaged subscribers and then slowly ramp up the volume over weeks. This slow-and-steady approach proves to ISPs you're a legitimate sender, not a spammer trying to blast out a million emails overnight.
Using a dedicated IP address, especially from a secure email host like Typewire, puts you in the driver's seat of your own reputation. Unlike a shared IP, where a bad neighbor can ruin things for everyone, a dedicated IP means your score is based entirely on your actions. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on 7 email deliverability best practices for 2025. Getting this right is a non-negotiable part of any serious email strategy.
Why User Privacy Is Your Greatest Asset
When we talk about email deliverability, it’s easy to get lost in the technical weeds—authentication protocols, IP scores, and all the behind-the-scenes magic. But those technical fixes often miss the most fundamental piece of the puzzle: user privacy.
Think about it. Respecting your subscribers isn't just about following the law; it's the very foundation of a healthy email program that actually works.
Your email list isn't just a database you own. It's a community you’ve built on trust. Mailbox providers like Gmail and Outlook are incredibly protective of their users, and for good reason. When they see you acting as a good steward of that trust—by respecting consent and privacy—they view you as a reliable sender. That’s how you get preferential treatment straight to the inbox.
Every single action, from the moment you capture an email to how you process an unsubscribe, sends a powerful signal. A real commitment to privacy proves you’re sending emails that people actually want, which is the ultimate goal for everyone involved.
Building Trust Through Bulletproof Consent
The quickest way to tank your deliverability is to send emails to people who never asked for them. That’s why securing explicit, enthusiastic consent is non-negotiable.
This is where the double opt-in method is your best friend. Instead of just adding someone to your list after they submit a form, you send them a quick confirmation email. They have to click a link in that email to prove it’s really them and that they really want to hear from you.
It’s a simple step, but the payoff is huge:
- Filters Out Bad Data: It catches typos and fake addresses before they ever hit your list.
- Confirms Real Interest: You end up with a list of people who are genuinely engaged from day one.
- Creates a Legal Paper Trail: It gives you undeniable proof of consent, which is crucial for privacy regulations.
By prioritizing clear consent, you're not just ticking a compliance box. You're building an audience that is far less likely to report you as spam, which is a core pillar of excellent deliverability.
List Hygiene: The Secret to a Strong Sender Score
A clean email list tells mailbox providers that you're a professional, responsible sender. Regularly cleaning up your list isn’t about losing subscribers—it's about focusing on a high-quality, engaged audience that actively protects your reputation.
A high bounce rate is one of the most toxic things for your sender score, and it’s caused by sending to addresses that don't exist. You also need to regularly remove inactive subscribers, meaning people who haven't opened or clicked an email in months. An unengaged user is far more likely to eventually hit the spam button than to suddenly convert.
It's also absolutely critical to honor unsubscribe requests immediately. If someone can't find your unsubscribe link, their next move will be the "report spam" button. That’s a massive red flag for their email provider.
The Strategic Advantage of Privacy Compliance
Modern data privacy laws aren't just a bunch of annoying rules; they’re a roadmap for building lasting user trust. Aligning your email practices with regulations like GDPR is essential for maintaining that trust and keeping your emails out of the spam folder.
Following these guidelines shows you take security and user data seriously. For a closer look at how these rules affect your campaigns, check out this guide on GDPR Compliance and Email Deliverability.
This is also where your choice of tools matters. Using a privacy-first email platform like Typewire helps you uphold these standards by default, protecting both your subscribers and your hard-earned sender reputation.
The Role of Hosted Email Platforms in Deliverability
Your choice of email service provider is so much more than a tool—it's the single most important partnership you'll have in the fight for better deliverability. The platform's infrastructure is the bedrock your entire sender reputation is built on. Without a solid, secure foundation, even the most amazing content and pristine email lists will fail to reach the inbox.
Think of it like building a house. You can have the best blueprints in the world, but if you build on unstable ground, the whole structure is at risk. A top-tier hosted email platform provides that stable ground through expertly managed servers, constant security monitoring, and a deep, real-world understanding of what mailbox providers like Gmail and Outlook demand from senders.

Shared IPs vs. Dedicated IPs: A Neighborhood Analogy
When you first start sending emails, you'll almost certainly use a shared IP address. This is like living in an apartment building. You have your own unit, but you share the building's street address and reputation with everyone else. If one of your neighbors is a spammer throwing wild parties and leaving garbage everywhere, the building manager (the ISP) might start penalizing the whole building.
This "bad neighbor" problem can drag down your deliverability, even if you’re following all the rules.
A dedicated IP address, on the other hand, is like owning your own home. The address is yours and yours alone. Your reputation is built solely on what you do. While this gives you total control, it also means you're 100% responsible for keeping the property in good shape. This is the best path forward for high-volume senders who need to protect their hard-earned reputation.
Essential Security and Privacy Features
Choosing a hosted email platform is a huge strategic decision that directly impacts your ability to land in the inbox. A security-first provider isn't just a vendor; they're a partner in protecting your brand and your data. Their entire infrastructure is designed to send strong trust signals to mailbox providers.
Here are the non-negotiable features a quality platform absolutely must provide:
- Built-in Authentication Support: A great host makes setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC almost foolproof, helping you establish technical credibility from day one.
- Proactive Infrastructure Monitoring: They are constantly watching their IP pools for blacklistings and shady activity, protecting everyone from potential threats.
- Data Security and Encryption: They must offer serious security measures, like TLS encryption, to protect your emails and subscriber data in transit.
- Privacy-by-Design Philosophy: Platforms like Typewire operate on their own private infrastructure. This means no data mining or creepy tracking, which aligns perfectly with modern privacy laws and what users expect.
Investing in a secure, privacy-focused email platform is one of the most effective long-term strategies for ensuring high email deliverability. It demonstrates a commitment to best practices that mailbox providers actively reward.
How Your Platform Choice Affects Inbox Placement
Every Internet Service Provider (ISP) has its own personality and filtering algorithms. Navigating this complex world requires a platform that's been there and done that. For example, while Google has an impressive overall delivery rate of 95.54%, a lot of legitimate marketing email ends up in the promotions tab. Meanwhile, Microsoft Outlook is notorious for its aggressive corporate filters that scrutinize any sender who isn't properly verified. A savvy provider helps you meet these specific ISP demands, like staying under Google’s strict spam complaint thresholds. You can find more insights on this in a comprehensive email deliverability report.
At the end of the day, a quality hosted email provider handles the complicated technical backend so you can focus on what you do best: creating great content. They manage IP health, maintain relationships with ISPs, and provide the secure foundation you need to build and protect a stellar sender reputation.
Making the right choice is critical, which is why we’ve put together a guide on the top hosted email platforms for business security. By partnering with a provider that values security and privacy as much as you do, you're setting yourself up for success from the very beginning.
Common Questions About Email Deliverability
Even with a great strategy, you're going to have questions. Email deliverability is a tricky field where security, technology, and user privacy all collide. Let's tackle some of the most common ones with clear, straightforward answers.
How Long Does It Take to Fix Poor Email Deliverability?
This is the big one, and the honest answer is: it depends. Fixing bad deliverability isn't like flipping a switch; it's more like rebuilding a damaged reputation. The whole process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on how deep the hole is.
If you just have a simple technical glitch, like a missing SPF record, you might see improvements within a few days of fixing it. But if you’ve been hitting spam traps or racking up high complaint rates, you’re looking at a much longer road to recovery. You'll need to slowly "re-warm" your sending reputation.
That process looks something like this:
- Hit the brakes on big campaigns. First things first, stop sending massive email blasts to prevent any more damage.
- Focus on your fans. Start sending small batches of high-value emails only to the people who've recently opened or clicked your stuff. This sends positive signals to mailbox providers.
- Slowly ramp back up. As you see positive results, you can gradually increase your sending volume week by week. This proves you’re a responsible sender.
Think of it like earning back someone's trust. Mailbox providers need to see a consistent pattern of good behavior over time. There are no shortcuts here—the only way to a lasting recovery is through consistency and a commitment to sending email people actually want.
Can My Content and Links Affect Email Deliverability?
Absolutely. Your sender reputation and authentication might get you to the front door, but it’s your content that gets you invited inside. Spam filters are incredibly sophisticated these days, and they scan every part of your message for red flags commonly used in junk mail.
They’re on the lookout for things like:
- Spam Trigger Words: Using overly aggressive or salesy phrases like "free money," "act now," or "limited time offer" can trip the alarms.
- Weird Formatting: Going overboard with ALL CAPS, using way too many exclamation points, or splashing bright red text everywhere can make your email look like classic spam.
- Sketchy Links: The links you include matter a lot. Stay away from public URL shorteners (like bit.ly), as phishers love using them to hide malicious sites. Always link out to your full, reputable domain.
Most importantly, linking to a website with a bad reputation can drag your own deliverability down with it. Mailbox providers see it as you vouching for a bad neighborhood. The fix is simple: create valuable, trustworthy content for your audience, and make sure every link points to a secure, reputable site.
How Does a Hosted Email Platform Enhance Security?
A high-quality hosted email platform is probably the single best ally you can have in the fight for good deliverability. It acts as a security force multiplier, giving you a solid foundation that would be incredibly difficult and expensive to build and manage on your own.
A platform like Typewire helps boost your security in a few key ways:
- Simplified Authentication: It makes setting up essential security protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC much easier, ensuring your emails are properly verified right out of the gate.
- Managed IP Reputation: The platform's administrators obsess over managing their IP address pools to maintain a pristine reputation. This shields you from the "bad neighbor" effect you might find on cheaper services. For those who need it, they also offer dedicated IPs for full control.
- Built-in Encryption: They provide crucial features like TLS encryption by default, which protects your email content as it travels from one server to another.
- Proactive Monitoring and Compliance: Their teams are constantly watching for new threats, managing relationships with blocklist operators, and making sure the platform stays compliant with global privacy laws like GDPR.
When you choose a privacy-first hosted email platform, you're essentially outsourcing the complex security grunt work to experts. This gives you a secure, reliable foundation, letting you focus on your message with the confidence that the technical backbone is solid. It's a smart investment in the long-term health of your entire email program.
Ready to take control of your email deliverability with a platform built on security and privacy? Typewire offers private email hosting that puts you in the driver's seat, free from tracking and data mining. Start your free trial and experience the difference.





