When you decide to send an encrypted email, the goal is to protect that message all the way from your outbox to the recipient's inbox. This is what we call end-to-end encryption. It’s the digital equivalent of sealing a letter in an envelope that only the intended person can open, guaranteeing your email privacy from prying eyes—whether that’s your email provider or someone trying to intercept your data.
This focus on privacy and security is a big reason why hosted email platforms like Typewire exist; they build these privacy-first features right into the service, so you don't have to bolt them on yourself.
Why Encrypting Your Email Is Now Essential for Your Privacy
Think about your inbox for a second. It's a goldmine of information, holding everything from quiet personal chats to high-stakes business deals. Sending a regular, unencrypted email is like mailing a postcard. Anyone who gets their hands on it along its journey can read it, compromising your email security.
Most email providers today use something called Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is a good start. It protects your message while it’s zipping between servers. But here’s the catch: it doesn't stop your email provider from seeing, scanning, or even analyzing the content of your emails once they arrive. This is a significant gap in email privacy.
True privacy demands more. That's where end-to-end encryption comes in, locking the message's content on your device before it's even sent. The only person who can unlock it is the recipient holding the unique private key. This simple act provides a few layers of powerful protection for your email security:
- Confidentiality: Keeps your communications private from everyone else—ISPs, email hosts, and government agencies included.
- Integrity: Confirms that your message wasn't altered or messed with on its way to the recipient.
- Authentication: Helps prove that the sender is actually who they say they are.
The Growing Need for Email Security
With more people working from home and cyber threats getting smarter, email has become a massive target. It’s the weak link in many security plans. Understanding common threats, like learning how to prevent Man-in-the-Middle attacks, really drives home just how vulnerable an unencrypted message can be.
The market numbers tell the same story. The global email encryption market is already valued at USD 7.75 billion and is expected to rocket to USD 40.16 billion by 2033. This isn't just a niche concern anymore. It's being driven by the hard realities of data breaches and the fact that an estimated 32.6 million workers in the US alone now rely on secure communication outside of a protected office network.
Taking email security seriously isn't just a "nice-to-have" anymore. It's a core part of protecting your digital life and sensitive data. Encryption puts you back in the driver's seat, letting you decide who gets access to your information.
Comparing Your Email Encryption Options
To help you figure out what's what, here's a quick look at the primary methods for securing your emails. Each has its own strengths, weaknesses, and is suited for different situations, especially when considering hosted email platforms versus manual setup.
| Method | How It Works | Best For | Technical Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| End-to-End (PGP/S/MIME) | Encrypts the message on your device; only the recipient's private key can decrypt it. | Maximum security for sensitive business, legal, or personal communication. | Intermediate to Advanced |
| In-Transit (TLS) | Encrypts the "tunnel" between mail servers. The provider can still see the message. | Basic, automatic protection for everyday, non-sensitive emails. | Beginner (Automatic) |
| Hosted Email Platforms | The service manages keys and encryption automatically for you. | Users who want high security without the technical overhead. | Beginner |
Ultimately, choosing the right method depends on your needs. For most people, a combination of automatic TLS for day-to-day mail and a secure hosted email platform for the important stuff is the best approach.
In the end, sending encrypted emails is really about taking back control of your digital privacy. The benefits go way beyond just locking down data; it's about building trust with clients, protecting valuable ideas, and meeting data protection rules. If you want to go deeper on this, check out our guide on the top benefits of encrypted email you need to know.
Setting Up PGP and S/MIME for Full Control
If you want to send encrypted emails and be absolutely certain no third party can read them, the best way is to set up your own encryption. This approach puts you in complete control, using battle-tested standards like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) and S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) to lock down your messages from end to end.
Sure, it takes a few more steps than using a pre-packaged secure email service, but the reward is total sovereignty over your email privacy. It all starts with generating a "key pair": a public key you can share freely and a private key that you guard with your life.
Without this level of security, your emails are essentially digital postcards, open for anyone to read as they travel across the internet.
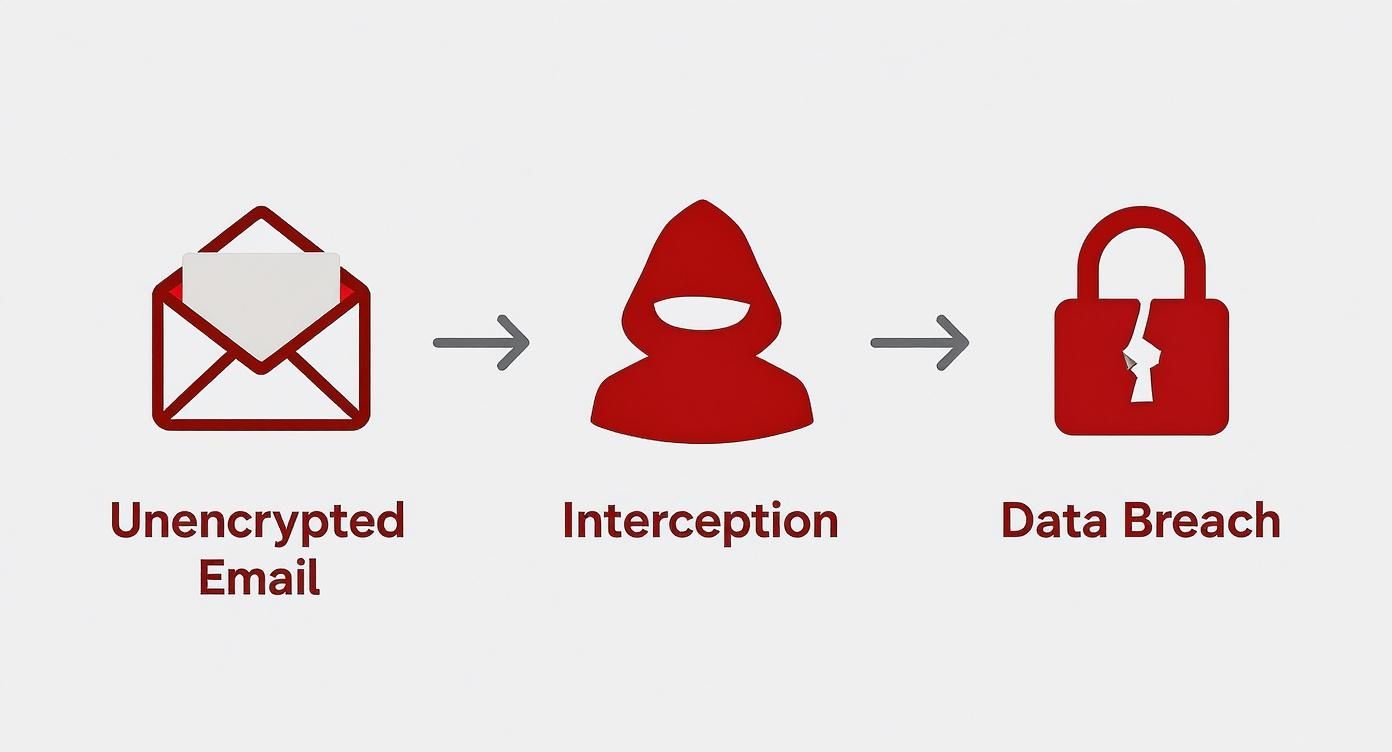
This diagram drives home why direct encryption is so crucial. It slams the door on interception by scrambling the message before it even leaves your device.
Getting Started with PGP Encryption
PGP is the grassroots standard for email encryption, loved by privacy advocates for its open, decentralized nature. You don't need anyone's permission to use it. The first thing you'll do is generate your key pair, which is easy to do with free, trusted software.
- For Windows users: Gpg4win is the gold standard. It’s an all-in-one installer that includes Kleopatra, a really intuitive key manager.
- For macOS users: GPG Suite provides the same powerful tools and integrates seamlessly into the Apple ecosystem.
With your key pair created, the next step is to hook it into your email client. A fantastic choice here is Thunderbird, the open-source client that has PGP support built right in. Once you import your keys, you can start sharing your public key with your contacts so they can send you properly encrypted messages. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on PGP encryption online and securing your email.
Understanding S/MIME for Corporate Environments
S/MIME works on a similar principle as PGP but with one major twist: it uses a centralized trust model. To get started with S/MIME, you have to get a digital certificate from a recognized Certificate Authority (CA). It's like a digital passport that officially verifies who you are.
This certificate-based system makes S/MIME a favorite in corporate settings, where IT departments can centrally manage and issue certificates to the entire team. Popular email clients like Microsoft Outlook and Apple Mail have native S/MIME support, so the setup is pretty simple once you have your certificate in hand.
Key Takeaway: The real difference between PGP and S/MIME boils down to trust. PGP is built on a "web of trust," where you personally decide which keys to trust. S/MIME relies on a formal hierarchy of CAs to validate identities for you.
Your choice often depends on your communication partners. PGP is perfect for talking with a diverse, independent group of people, while S/MIME excels within a structured business or organizational environment.
The Broader Trend Toward User-Controlled Encryption
The demand for better email privacy isn't just a niche concern anymore; it’s a full-blown market shift. As people become more aware of the risks, we're seeing huge growth in the adoption of these technologies. The global email encryption software market, currently valued at USD 4.35 billion, is projected to skyrocket to around USD 14.09 billion by 2034.
Even the giants are getting on board. Google, for instance, has introduced client-side, end-to-end encryption for Gmail, giving organizations the power to manage their own keys. This move signals a wider trend of making powerful encryption more accessible and user-friendly. You can dig into the numbers and analysis in a full report from Precedence Research on the email encryption software market.
Sending Encrypted Emails from Any Device
Your need for email privacy doesn’t end when you leave your desk. Thankfully, you can send encrypted emails from pretty much any device, whether you're using a webmail client on a laptop or a dedicated app on your smartphone. The real trick is finding the right tools that bridge the gap between powerful PGP encryption and the convenience we all need.
For most of us, that means bringing encryption directly into the web browser. Services like Gmail don't handle PGP on their own, but that’s where browser extensions come in to fill the gap—and they do it quite well.

Bringing PGP to Your Webmail
Browser extensions are the most straightforward way to add end-to-end encryption to your webmail routine. Think of them as a secure layer that sits on top of your inbox, handling all the heavy lifting of encryption and decryption without making you switch to a whole new platform.
A popular and trusted choice here is Mailvelope. It’s an open-source extension for Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. After you install it, you can import your existing PGP key pair right into the browser. The next time you go to write an email in Gmail, Mailvelope adds a new button to the composition window, opening a secure editor where you can write and encrypt your message.
This method lets you stick with an interface you already know while adding a critical layer of security. If you’re a Gmail user, learning how to send a secure email in Gmail with these tools is a fantastic first step.
Securing Your Mobile Communications
On mobile, the game changes. Instead of browser extensions, you'll be looking for dedicated email apps with PGP support baked right in. Handing over your security to a third-party app requires a bit of trust, so it's vital to pick one with a solid reputation for security and transparency.
Here are a couple of great options for mobile PGP:
- Canary Mail: Available for iOS, macOS, and Android, this app offers a clean user experience with really solid PGP encryption built-in. It hooks into your existing email accounts (like Gmail or any IMAP account) and makes managing your keys on the go surprisingly simple.
- FairEmail: This one is an open-source, privacy-first client for Android. FairEmail gives you a ton of control over your email security, including fantastic PGP support that integrates with OpenKeychain.
The big trade-off with third-party tools always comes down to convenience versus control. While these apps and extensions make encryption incredibly easy, you are trusting them to handle your private key securely. That's why you should always protect your key with a strong passphrase, even within these applications.
Ultimately, you want to build a security workflow that feels seamless across all your devices. The most critical piece of this puzzle is managing your private key. My advice is to generate your main key pair on a trusted desktop computer, then securely export it for use on your mobile devices. Just make sure you never store an unencrypted copy anywhere insecure.
And one last tip: if you plan on sending large attachments with your encrypted messages, it’s a good idea to learn how to compress files specifically for email to make sure everything gets delivered without a hitch.
Exploring Secure Hosted Email Platforms
Let's be honest: managing your own PGP keys can feel like a full-time job. If that sounds like more trouble than it's worth, you're not alone. For a lot of people, the easiest path to send encrypted emails is to use a dedicated secure email platform. These hosted email platforms are designed from the ground up with privacy as their central promise, not just another feature tacked on at the end.
Take platforms like ProtonMail or Tutanota. They handle all the heavy lifting for you. When you create an account, they generate your key pair behind the scenes, so you don't have to touch a command line or install special software. If you email someone else on the same platform, your message is automatically end-to-end encrypted. It just works.
This approach is a game-changer for usability. It makes high-level email security and privacy genuinely accessible to anyone, regardless of how tech-savvy they are.
What to Look for in a Secure Email Provider
Not all secure email providers are built the same. When you’re handing over your private conversations to a company, it’s critical to vet them carefully. A hosted email platform like Typewire, for example, is built around the non-negotiable aspects of modern email security and privacy.
Here are a few things I always look for when evaluating a service:
- Zero-Knowledge Architecture: This is a big one. It means the provider can't read your emails, even if they wanted to. Everything is encrypted on your device before it ever reaches their servers.
- Open-Source Code: Trust but verify. Reputable providers publish their code for public review. This transparency allows independent security experts to audit it for flaws, which builds a ton of confidence.
- Strong Legal Jurisdiction: Where a company is based really matters. Services headquartered in countries with robust privacy laws, like Switzerland or Germany, offer a much stronger shield against government overreach.
- Anonymous Sign-Up Options: A true privacy-first service lets you create an account without tying it to your real-world identity.
The real goal is to find a provider that believes in true data ownership. You're looking for a service where privacy isn't just a setting you can turn on, but the very foundation the entire platform is built on.
The Growing Market for Email Privacy
The demand for simple, secure email is exploding. The global email encryption market, currently valued at USD 6.4 billion, is expected to skyrocket to USD 31.1 billion by 2034. This isn't just a niche interest anymore. It's being driven by everyone from businesses needing to comply with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to everyday people who just want to protect their digital conversations. You can dig into the numbers and trends in this market research report.
Ultimately, going with a hosted email platform is an investment in your own peace of mind. It takes the friction out of sending encrypted email, letting you focus on what you're writing, not on whether someone else is reading it.
Building Good Email Security Habits
Having the right encryption tools is one thing, but how you use them day-to-day is what truly keeps your emails private. Think of it less as a technical setup and more as a mindset. Weaving a few key security habits into your routine is what transforms a decent defense into a rock-solid one, making sure you can consistently and safely send encrypted emails without any accidental leaks.
Your private key's passphrase is the last line of defense. It's the master lock. If someone ever got their hands on your encrypted key file, a weak passphrase is all that stands between them and your entire history of private conversations. It absolutely must be long, completely unique, and something only you could remember. Never, ever reuse it.

Beyond the Passphrase
Your security posture also depends on how you handle interactions with others. Before you fire off that first encrypted message to a new person, you have to be sure their public key is legitimate. A classic attack involves an imposter sending you a fraudulent key, hoping you'll use it to encrypt messages meant for your actual contact.
- Out-of-Band Verification: The gold standard is to verify the key’s unique fingerprint over a completely separate channel. A quick phone call, a video chat, or a message on a secure app like Signal works perfectly.
- Trust on First Use (TOFU): This is a more convenient, though slightly less secure, approach. You save the contact's key the first time you get it, and your email client will warn you if it ever changes down the line.
Taking a moment to verify a key is your best protection against a "man-in-the-middle" attack, where a third party tries to position themselves between you and your contact to intercept everything.
Security is a continuous practice, not a one-time setup. It’s the small, consistent actions—like double-checking a key's fingerprint or being wary of suspicious links—that create a truly secure communication channel.
Avoiding Human Error
Attackers are smart; they know the easiest way in is often by exploiting human nature. Phishing attacks have become incredibly sophisticated, with emails crafted to trick you into giving up your private key's passphrase or installing malware that simply steals the keys from your device. Always treat unexpected requests with suspicion, even if they seem to be from someone you know.
Another surprisingly common mistake is putting sensitive information right in the subject line. Here’s a critical reminder: subject lines are not encrypted, even when the body of the email is. This is a crucial aspect of email privacy to remember.
A subject like "Confidential Q4 Financials Attached" gives the game away before the message is even opened. Opt for something generic instead, like "Following up" or "Document for your review." Let the encrypted content speak for itself. Making these practices second nature is what ensures that powerful tools like PGP or a secure hosted email platform like Typewire deliver the robust protection you need.
Got Questions About Email Encryption? We've Got Answers
Diving into email encryption can feel a bit like learning a new language. You'll probably have a few questions as you get started. Let's clear up some of the most common ones so you can feel confident about protecting your conversations and ensuring your email privacy.
What's the Real Difference Between TLS and End-to-End Encryption?
This is a fantastic question, and the distinction is crucial for email security.
Think of TLS (Transport Layer Security) as the secure tunnel your email travels through from your outbox to your recipient's inbox. While the email is in transit, it's protected from anyone trying to eavesdrop along the way. But here's the catch: your email provider (and theirs) can still see the contents on their servers.
End-to-end encryption (like PGP or that used by hosted email platforms) is a whole different ballgame. It's like sealing your message in a tamper-proof box before it even leaves your computer, and only your recipient has the unique key to open it. Even your email host, like Typewire, has zero access to what's inside. It's the ultimate standard for private communication.
Should I Really Encrypt Every Single Email?
Probably not, and that's okay. You don't need to encrypt the email to your cousin about weekend plans. But for anything sensitive, encryption should be your go-to to maintain email privacy.
We're talking about things like:
- Financial statements or bank details
- Medical records or health information
- Confidential business strategies or trade secrets
- Legal documents and client communications
A good personal rule? If you wouldn't be comfortable with the contents being pinned to a public noticeboard, encrypt it.
Making encryption your default for anything important is the simplest way to maintain strong email privacy without overthinking it. It’s about creating a secure baseline for your communications.
Can I Send an Encrypted Email to Someone Who Doesn't Use It?
For true end-to-end encryption with PGP or S/MIME, both you and the recipient need to be set up. You need their public key to encrypt the message, and they need their private key to decrypt it. This "key exchange" is often the biggest hurdle for people.
However, many secure hosted email platforms have found a clever way around this. They let you send an encrypted message to a regular email address. Your recipient gets a notification with a secure link, and they can click it, verify their identity (often with a password you set), and view the message in a secure web portal. It's a great bridge for communicating securely with anyone.
So, Which Encryption Method Is Right for Me?
It really boils down to your technical comfort level and what you need to protect.
-
PGP/S/MIME: This is the DIY route. It gives you the most control but requires you to manage your own keys and configure your email client. It's a great fit for tech-savvy users, journalists, activists, or anyone in a field with strict security requirements.
-
Secure Hosted Email Platforms: This is the "it just works" solution. Services from providers like ProtonMail or Typewire build encryption right into the platform. You get the security of end-to-end encryption without the manual setup, making it perfect for most individuals and businesses who prioritize email privacy and ease of use.
Ready for an email experience where privacy and security are built-in, not bolted on? Typewire offers secure, private email hosting that puts you in control. Explore our features and start your free trial today.