Imagine your company's emails are like sensitive files locked away in a physical safe. Data residency requirements are simply the laws that tell you which country that safe has to be in. It’s a legal mandate ensuring your email data—often packed with private information and trade secrets—stays within a specific geographic border, safe from foreign laws and access.
Understanding Data Residency in Email Hosting
At its heart, data residency is all about geography. These regulations demand that certain kinds of data, especially the personal and sensitive details common in emails, must be physically stored and processed inside a particular country or region. This isn't just some minor technicality; it's a fundamental legal protection for email privacy.
When you sign up for a hosted email service, you're not just picking a platform—you're also choosing a legal jurisdiction. The physical location of your provider's servers dictates which country's laws apply to your email data. This choice has huge consequences for both email privacy and security, as nations have vastly different rules on government surveillance, data access, and individual privacy.
Key Concepts You Need to Know
To get a firm handle on this, you need to understand three closely related terms. Mixing them up is a common and often expensive mistake when choosing a hosted email platform.
-
Data Residency: This is the most straightforward concept. It simply dictates the geographical location where your data must be stored. Think of it as the "where." For a hosted email platform, this means the physical location of the servers storing your inboxes.
-
Data Localization: This is a much stricter version of residency. It doesn't just say email data has to be stored locally; it often mandates that it can't be moved or even copied outside that country's borders. It effectively creates a digital wall around specific email datasets.
-
Data Sovereignty: This is the big-picture idea. It asserts that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it is physically located. This means local courts, law enforcement, and government agencies can legally compel access to your email data, regardless of where your company is headquartered. You can explore this topic further in our complete guide on what data sovereignty means and its implications for data control.
Getting these definitions straight is the first critical step in building a compliant email hosting strategy.
Why Data Residency Is Non-Negotiable for Email
Email isn't just communication; it's a goldmine of sensitive information. It holds everything from personal chats and financial records to intellectual property and confidential business plans. Simply leaving the storage location of your hosted email platform to chance is a massive and unnecessary business risk.
Non-compliance with data residency requirements isn’t just a legal misstep; it's a direct threat to your email security and business continuity. The penalties can include crippling fines, forced operational shutdowns, and a severe loss of customer trust that can be nearly impossible to rebuild.
Ignoring these rules means you could be exposing your most important communications to governments with weak privacy laws or sweeping surveillance powers. That puts your email data—and your customers' email data—in a vulnerable position. For any organization using a hosted email platform for users in different countries, following data residency requirements isn't a choice; it's a cornerstone of modern email security and corporate responsibility.
Navigating the Global Maze of Data Privacy Laws
Think of data privacy not as a single rulebook, but as a complicated patchwork of local laws. Each country has its own ideas about what it means to protect personal information, especially when it comes to email communications. Trying to use a one-size-fits-all approach for your hosted email platform just won't cut it—it's a surefire way to run into compliance headaches.
The heart of the issue is that what’s considered "secure enough" for email in one country might be completely inadequate in another. This is exactly why data residency requirements—the rules dictating where email data must physically be stored—have become so important for any business operating across borders.
This isn't a fringe issue anymore. The push for stronger email privacy has exploded. Back in 2000, only about 10% of countries had these kinds of laws. By 2025, that number is expected to jump to over 75%. Major players like the EU, Canada, Brazil, and China are leading the charge, setting firm rules on where personal data can live and how it can travel. For a global overview, the UNCTAD offers a report on data protection legislation worldwide.
Key Data Residency Regulations at a Glance
To make sense of this complex landscape, it helps to see the major regulations side-by-side. The table below breaks down some of the most influential data privacy laws and highlights what they mean for your hosted email platform choices.
| Region/Law | Key Data Storage Requirement | Impact on Email Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| EU (GDPR) | Data can only be transferred outside the EU to countries with "adequate" data protection. | Storing EU resident emails on servers in a non-adequate country is a major compliance risk without complex legal safeguards. |
| Canada (PIPEDA) | Data can leave Canada, but the original organization remains responsible for ensuring it receives comparable protection abroad. | You're on the hook for your email provider's security. Choosing a Canadian host simplifies demonstrating compliance. |
| US (CCPA/CPRA) | No strict data residency mandate, but requires transparency and gives consumers rights over their data. | Your hosted email platform must have features that support consumer data rights, like deletion and access requests. |
| APAC (e.g., China's PIPL) | Strict requirements for certain types of data to be stored locally within the country's borders. | If you do business in China, you'll likely need a hosted email solution with data centers located there. |
As you can see, where you host your email isn't just a technical detail—it's a critical compliance decision driven by geography.
The European Union's GDPR: The Global Gold Standard
When people talk about data privacy, the conversation almost always starts with the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It's widely considered the toughest and most comprehensive privacy law on the planet, and it sets the bar for anyone handling the personal data of EU residents—no matter where your business is based.
A central rule in the GDPR is its tight grip on cross-border data transfers. You can't just move EU data to a server anywhere in the world. The destination country must have data protection laws that the European Commission officially deems "adequate." This has huge implications for email hosting. If your provider’s servers are in a country without that stamp of approval, you could be in violation from day one. To get into the specifics, check out our GDPR compliance checklist for ensuring your data privacy success.
Key Takeaway: The GDPR forces you to be incredibly deliberate about where your email is hosted. Storing EU citizen data on servers in a jurisdiction without an adequacy decision means jumping through complex legal hoops. A much safer and simpler path is to choose a hosted email platform based in Europe or an adequate country like Canada.
Understanding and implementing effective GDPR compliance strategies is fundamental, as it often covers the requirements of many other global laws.
Major Regulations Beyond the European Union
While the GDPR gets most of the attention, it’s far from the only game in town. Several other key regulations create their own set of rules for email security and privacy.
-
Canada's PIPEDA: Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is the main federal privacy law for private-sector businesses. It doesn’t strictly forbid data from leaving Canada, but it places the responsibility squarely on the organization to ensure that email data gets a comparable level of protection wherever it goes.
-
US State Laws (CCPA/CPRA): The United States doesn't have a single, overarching federal privacy law, which creates a messy patchwork of state rules. The most well-known is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), now strengthened by the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA). These laws give consumers powerful rights over their data and require businesses to be transparent, which directly impacts the features you need from your hosted email platform.
-
APAC Region Policies: The Asia-Pacific region is a mix of different approaches. China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) is one of the world's most restrictive, often requiring personal and other "important" data to be stored on local servers. Other countries, like India and Australia, are also moving toward rules that mandate local data storage for certain types of information.
This variety is precisely why your hosted email platform’s data center location is a strategic business decision. Getting it wrong can lead to steep fines and a damaged reputation, making a careful, informed choice an absolute must.
How Residency Impacts Your Email Security and Privacy
When you choose a hosted email platform, you’re making one of the most critical security decisions for your business. It’s about more than just features and uptime; the physical location of your provider's servers dictates which government has legal authority over your email data. This direct line between geography and jurisdiction is the bedrock of modern email security, and it’s where data residency requirements become your first line of legal defense.
Think about it: if your email data is stored in a specific country, it falls under that nation's laws on surveillance, law enforcement access requests, and privacy rights. If that country has weak privacy protections or gives its government broad access powers, your sensitive email communications are at risk—no matter how strong your passwords are.
This is where global privacy laws like GDPR come into play, creating a framework that strengthens jurisdictional protections for individuals and organizations alike.
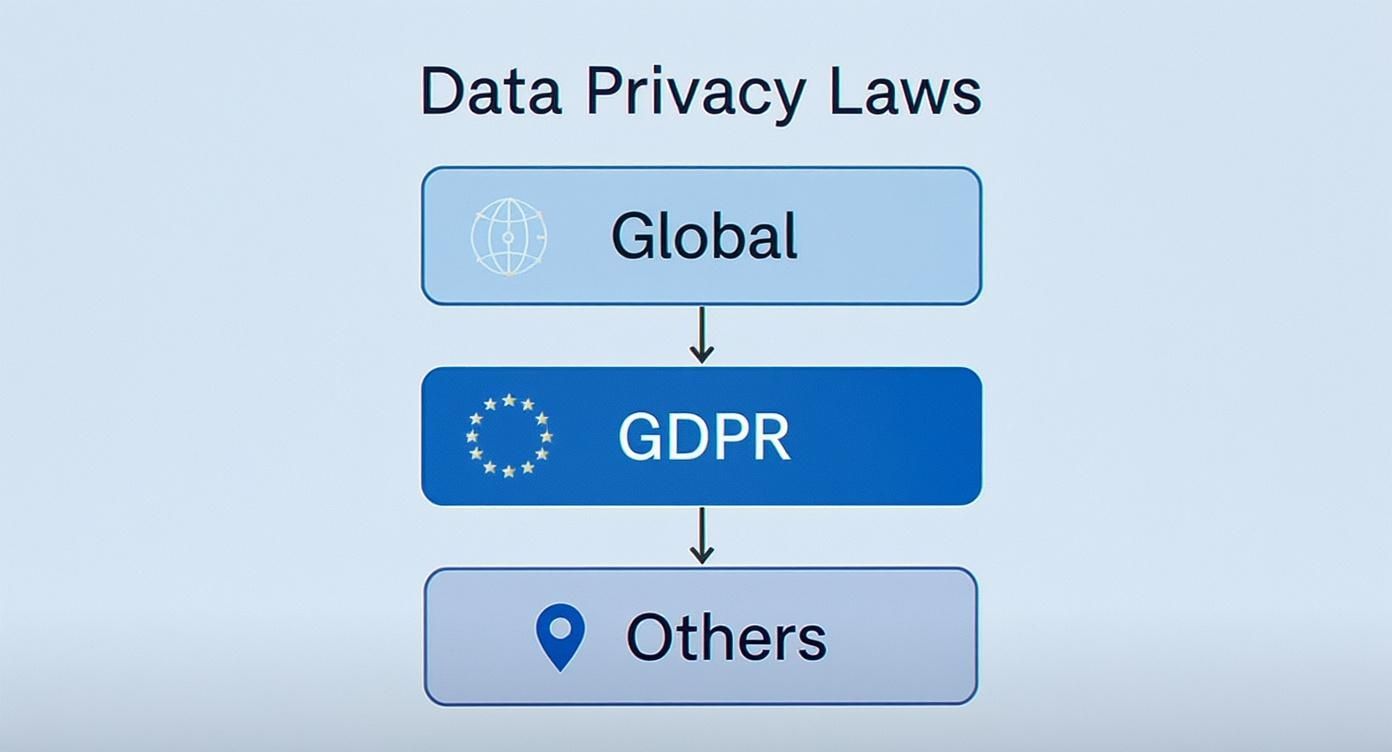
As the diagram shows, powerful regulations like GDPR set a high bar that many national laws aim to meet, shaping a complex but essential legal landscape you need to navigate for your email hosting.
The Intersection of Legal and Technical Safeguards
It’s easy to think that strong encryption is the ultimate answer to email security. While technical tools like end-to-end encryption are vital for scrambling your message content, they don't solve the legal risks tied to where that encrypted email data lives.
Here’s an analogy: encryption locks your email data in a safe, but data residency determines which country's government holds the legal master key.
True email security only happens when your legal and technical protections are working together. You need both to build a defense that actually holds up.
- Legal Protections (Data Residency): This ensures your email data is stored in a country with strong privacy laws, limiting who can legally access it and shielding it from foreign surveillance.
- Technical Protections (Encryption): This scrambles your email data, making it unreadable to anyone who might get unauthorized access to the server itself.
Without the right residency rules, even the best encryption can be undone by a legal order from a government with intrusive laws.
How Government Surveillance Changes the Game
The jurisdiction of your hosted email platform matters immensely. Some countries have laws that force companies to hand over customer data, sometimes without a warrant or even telling you it happened. For any business dealing with client emails, trade secrets, or intellectual property, this is a massive, often unacceptable, risk to email privacy.
By choosing an email provider that operates exclusively within a privacy-forward jurisdiction, you place your data under a legal umbrella that prioritizes individual rights and due process. This is not a minor detail—it's a strategic decision to shield your email communications from overreaching surveillance programs.
That's why you have to scrutinize the legal landscape of your provider's home country just as closely as you review their security features. A provider’s commitment to email privacy is only as strong as the laws of the land they operate in.
Building a Multi-Layered Defense for Email
At the end of the day, a solid email security strategy has to be multi-layered. It all starts with understanding data residency requirements and picking a hosted email platform whose data centers are physically located in a country with strong legal protections.
On top of that foundation, you add the technical safeguards. This includes making sure your provider offers robust encryption for email data both in transit and at rest. You also need to look for strict access controls, regular security audits, and transparent privacy policies. Each layer reinforces the others, creating a powerful barrier that protects your emails from both hackers and legal overreach.
So, when you're choosing a provider, be sure to ask the tough questions about both: where are the email servers, and how is the data truly secured?
A Practical Checklist for Email Hosting Compliance
https://www.youtube.com/embed/VatpDAklHKA
Knowing the rules of data residency is one thing, but actually putting them into practice is a completely different ballgame. To close that gap, you need a clear, actionable plan.
This checklist breaks down the whole process into five manageable stages. Think of it as a roadmap to help you build a solid strategy for your hosted email platform, one that’s not just technically sound but legally bulletproof.
Stage 1: Map Your Email Data Flow
Before you can comply with any regulations, you have to know what data you have and where it’s going. This is the absolute foundation of meeting data residency requirements. It’s like drawing up a detailed blueprint of your company’s entire email ecosystem.
Start by identifying every type of information that flows through your email system. This includes everything from customer PII and financial records to internal employee data and your own trade secrets. Once you know what you have, you need to trace its journey from the moment an email is created to when it’s finally archived or deleted.
This mapping exercise should give you clear answers to a few critical questions:
- What specific data categories are in our emails?
- Where are our users actually located, and which email privacy laws apply to them?
- Where are our current email servers physically sitting?
- Does our email data cross borders through third-party apps, marketing tools, or even backup services?
Getting these answers gives you a bird's-eye view of your data footprint and instantly flags any compliance red zones you need to tackle first.
Stage 2: Identify Applicable Regulations
With your data map complete, the next step is to figure out which specific laws and regulations apply to your business. This isn't just about where your headquarters is located; it's about where the individuals you are emailing live and work.
If you have customers in the European Union, GDPR is non-negotiable for their email data. If you do business in Canada, PIPEDA comes into play. You have to carefully review your user base and operations to build a complete list of every legal framework you're accountable to.
Don't fall into the common trap of thinking only your home country's laws matter. In today’s world, a single email can trigger compliance duties in multiple countries at once. A thorough analysis is the only way to avoid nasty surprises with your hosted email platform.
Once you have your list, you can dig into the specific rules each regulation has about email data storage and cross-border transfers.
Stage 3: Scrutinize Provider Contracts and DPAs
Your email hosting provider is your most critical partner in this process. Their contracts—especially the Data Processing Agreement (DPA)—are legally binding documents that spell out exactly how they’ll protect your email data. You need to review these with a fine-toothed comb.
Look for crystal-clear guarantees about the physical location of the data centers storing your primary email data, backups, and metadata. Any vague language here is a massive red flag. The DPA should explicitly state that your email data will stay within a specific, agreed-upon region and detail the security measures and protocols for handling government data access requests.
Stage 4: Implement Technical and Organizational Controls
Compliance isn't just about paperwork. It's about putting real technical and organizational controls in place to enforce your policies. You’ll need to work with your provider to configure your email hosting environment to match the data residency requirements you've identified.
Here are the key controls to focus on:
- Region-Specific Hosting: Make a deliberate choice to host your email in a data center located in a jurisdiction that satisfies your legal obligations.
- Access Controls: Put strict, role-based access controls in place. This ensures only authorized staff can see or manage sensitive email data.
- Encryption: Use strong encryption for email data both at rest (sitting on the server) and in transit (moving across the internet) to keep it confidential.
- Data Retention Policies: Set up clear rules for how long emails are kept before being securely wiped. For a deeper dive, you can learn more about creating a complete email record retention policy in our detailed guide.
Stage 5: Schedule Regular Audits and Reviews
Finally, remember that data residency compliance is never a "set it and forget it" project. It’s an ongoing commitment. Regulations evolve, your business expands, and new threats to email security constantly pop up.
Set a schedule for regular audits to make sure your controls are still working and your provider is holding up their end of the bargain. Beyond the initial setup, it's also vital to consider the full lifecycle of your data-bearing hardware. A solid data protection strategy includes proper IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) explained to ensure data is completely destroyed when equipment is retired. These reviews will help you stay agile and maintain a strong compliance posture for years to come.
Choosing an Email Host That Prioritizes Compliance

When it comes to compliance, picking the right hosted email platform isn’t just another vendor decision—it’s the single most important one you’ll make. It’s not about flashy features or a low price point. It's about finding a provider whose entire infrastructure is built to be the bedrock of your data protection strategy. This choice directly determines whether you can meet data residency requirements and truly protect sensitive email communications.
The global legal landscape is a tangled web, and it's only getting more complex. As we head into 2025, a staggering 144 countries have their own data and privacy laws on the books, affecting roughly 79% of the world's population. This explosion in regulation has pushed compliance to the top of the priority list, forcing businesses to be incredibly careful about where their email data lives. You can get a deeper dive into how data residency compliance is evolving on whisperit.ai.
What to Look for in a Compliant Provider
When you’re vetting email hosts, you need to cut through the marketing fluff and get into the operational weeds. A provider’s physical data center location, its ownership structure, and the laws it operates under are far more critical than any superficial feature for email security.
Your main goal is to find a partner that gives you ironclad control over where your email data is stored. Vague promises about a "global cloud" should be a major red flag. Often, that’s just a nice way of saying your data could be bouncing between countries without you ever knowing, putting you in direct violation of laws like GDPR.
Here’s what you absolutely must scrutinize:
- Region-Specific Hosting: Can you pin your email data to a specific country? This is non-negotiable. If they can’t guarantee your data will stay put, walk away.
- Data Center Ownership: Does the provider own and operate its own hardware and facilities, or are they just reselling services from one of the big cloud players? Direct ownership means more control and clearer accountability for your email hosting.
- Transparent Privacy Policies: They need to be crystal clear about how they handle your data, what they do when the government comes knocking, and how they protect user email privacy.
- Clear Data Processing Agreements (DPAs): A DPA is a binding legal contract. It must explicitly name the physical location of your email data—including every backup and all metadata—and guarantee it won’t be moved without your permission.
These are the things that separate the providers who just talk about compliance from those who actually build their service around email privacy and security.
The Power of Privately Owned Infrastructure
There’s a massive advantage in choosing a provider with its own privately owned and operated data centers. When a company like Typewire manages its own infrastructure from top to bottom, it sidesteps all the headaches and potential compliance gaps that come with relying on third-party cloud giants for email hosting.
This approach gives you a direct line of sight into email security and data handling. You know exactly who has your data, where it is, and how it’s being protected. There are no murky layers of subcontracting that could accidentally expose your information to a different country’s laws.
Key Takeaway: A provider that owns its infrastructure offers unparalleled control and transparency for your hosted email platform. This model ensures the company you have a direct relationship with is the one enforcing security and compliance—not some faceless third party.
Typewire: A Real-World Example in Compliance
To see how this works in practice, just look at Typewire's approach. We operate exclusively from our privately owned data centers in Vancouver, Canada. This isn’t a random choice; it’s the entire foundation of our commitment to email security and privacy.
Canada's privacy laws are recognized by the European Commission as providing an "adequate" level of data protection. This makes it a safe harbor for any business that handles email data from EU customers. For our clients, that means choosing a Canadian-based host like Typewire automatically simplifies GDPR compliance.
For businesses trying to navigate the maze of data residency requirements for their email, this model provides genuine peace of mind. Your data sits in one secure location, governed by strong, predictable privacy laws. It eliminates the ambiguity and gives your organization a solid, defensible foundation for its global compliance strategy.
Common Questions About Data Residency
When you start digging into email security and global privacy laws, a lot of questions pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common points of confusion that businesses face when choosing a hosted email platform.
What’s the Difference Between Data Residency and Data Sovereignty?
It's easy to mix these two up, but the distinction is critical for email hosting.
Data residency is straightforward: it’s the physical, geographic location where your email data is stored. Think of it as the street address for your server. If a law says your email data must reside in Canada, it means the hard drives holding that data must be physically inside Canadian borders.
Data sovereignty goes a big step further. It means that your email data is not only stored in a specific country but is also subject to the laws and legal authority of that nation. This is where it gets serious. If your email data is "sovereign" in a particular country, that country's government could potentially demand legal access to it. This is precisely why choosing an email provider in a jurisdiction with strong privacy protections is so important.
Does Using a Big Cloud Email Provider Automatically Make Me Compliant?
No, and this is a dangerous assumption to make for email hosting. Many of the huge cloud providers run massive, interconnected global networks. To keep things fast and reliable, they often shift data between data centers around the world, sometimes without telling you exactly where your information is at any given moment.
That constant movement can easily put you in accidental violation of strict data residency rules.
To stay compliant, you can't just sign up and hope for the best. You have to explicitly configure your service to lock your email data—including every email, attachment, bit of metadata, and backup file—into a specific, approved region. Then, you need to get that commitment in writing in your contract and your Data Processing Agreement (DPA). Just because you're using a famous brand doesn't mean you've outsourced your email security responsibility.
Key Insight: True compliance demands hands-on configuration and solid contractual guarantees. Never assume a major provider is handling your data residency obligations by default. The buck stops with your organization.
How Does Encryption Affect Data Residency Requirements?
Encryption is absolutely essential for email security, but it's not a magic wand that makes residency rules disappear. While encrypting your email data turns it into unreadable code for anyone without the key, most regulations still focus on the physical location of that scrambled data. The law cares about jurisdiction first.
Think of it like this: putting your important emails in a locked safe (encryption) is a smart move, but the law still tells you which country that safe has to be in.
Some regulations might be a bit more lenient about transferring encrypted data across borders, but the core requirement to store data within a specific geographical area nearly always applies. Encryption and residency are partners; one protects your email's confidentiality, while the other addresses your legal and jurisdictional obligations.
Can I Use a US-Based Email Provider If I Have European Customers?
This is a legal minefield for email privacy. Handling EU customer email data with a US-based provider is incredibly complex and comes with significant risk. The EU’s GDPR is firm: personal data can only be moved to countries that offer an "adequate" level of data protection. While agreements like the EU-US Data Privacy Framework aim to bridge this gap, they are constantly challenged in court and can be invalidated overnight, leaving businesses in a tough spot.
The simplest, safest way to avoid these legal headaches is to choose a hosted email platform that can guarantee all EU customer data is stored exclusively in data centers located inside the EU or in a country that the European Commission has deemed "adequate." Canada, for example, is one of those recognized jurisdictions, making it a reliable and compliant choice for hosting EU email data. This approach builds your compliance on a stable legal foundation, not a shifting one.
Ready to take control of your email privacy and meet data residency requirements with confidence? Typewire offers secure, private email hosting from our privately owned data centers in Vancouver, Canada—a jurisdiction recognized for its strong privacy laws. Start your free trial today and experience the peace of mind that comes with true data control. Learn more at Typewire.