Think of your email like a piece of mail. Using a free service like Gmail is a bit like sending a postcard from the public post office. It gets the job done, but it’s not exactly private or secure.
Email hosting, on the other hand, is like having a secure, private mailbox at your own business address. It gives you a custom account like you@yourbrand.com that’s tied directly to your domain, putting email privacy and email security first.
Your Professional Address on the Internet Explained
So, what exactly is email hosting? At its heart, it's a dedicated service that gives you the server space and all the technical bits and pieces needed to send, receive, and store emails under your own domain name. Instead of being one of millions using a generic address like yourname@gmail.com, you're essentially renting a secure, private corner of the internet just for your messages.
It’s the difference between a generic P.O. box and a prime office address. A free email account tells the world you’re just another user on a massive public platform. A hosted email address, however, instantly establishes a professional identity and builds trust. It shows clients and partners you’re a serious business with your own digital real estate.
The Foundation of Digital Trust and Security
This difference is about more than just looks. Professional email hosting is built from the ground up with email security and privacy in mind. Free services often pay the bills by analyzing your data to show you ads, which means you are the product. A paid hosting service, especially a dedicated hosted email platform, puts you back in the driver's seat.
Here’s why having that control is so crucial today:
- Enhanced Security: Hosted email almost always comes with advanced security features, like powerful spam filters, malware protection, and encryption to protect your sensitive information from online threats.
- Guaranteed Privacy: Unlike many free platforms, good email hosts have strict privacy policies. They won't scan your emails to sell you things, so your conversations stay confidential.
- Brand Ownership: A custom domain reinforces your brand with every single email you send. For any business, that consistency is key to building a recognizable and trustworthy presence. You can learn more about how a professional email address builds credibility in our guide.
The core value of email hosting is simple: it transforms your email from a borrowed utility into a privately-owned asset. You gain full control over your digital identity, security protocols, and data, ensuring your most critical communications are protected.
Email isn't going anywhere. It’s still one of the most fundamental tools we use to communicate. Globally, an estimated 4.5 billion people are projected to use email in 2025, and that number is expected to climb past 4.8 billion by 2027. This just underscores how vital it is to have a secure and professional channel for your conversations. This service isn't just a technical upgrade; it's a strategic move to secure your digital identity.
How Email Travels Through Its Digital Postal System
To really appreciate what a dedicated email host does, it helps to pull back the curtain and see how a message gets from you to its destination. The whole thing runs like a high-tech postal service, where your email host is the postmaster, making sure every message is handled securely and delivered without a hitch.
Think of the email app on your phone or computer—like Outlook or Apple Mail—as your personal letterbox. When you hit "send," you're essentially dropping a sealed envelope inside.
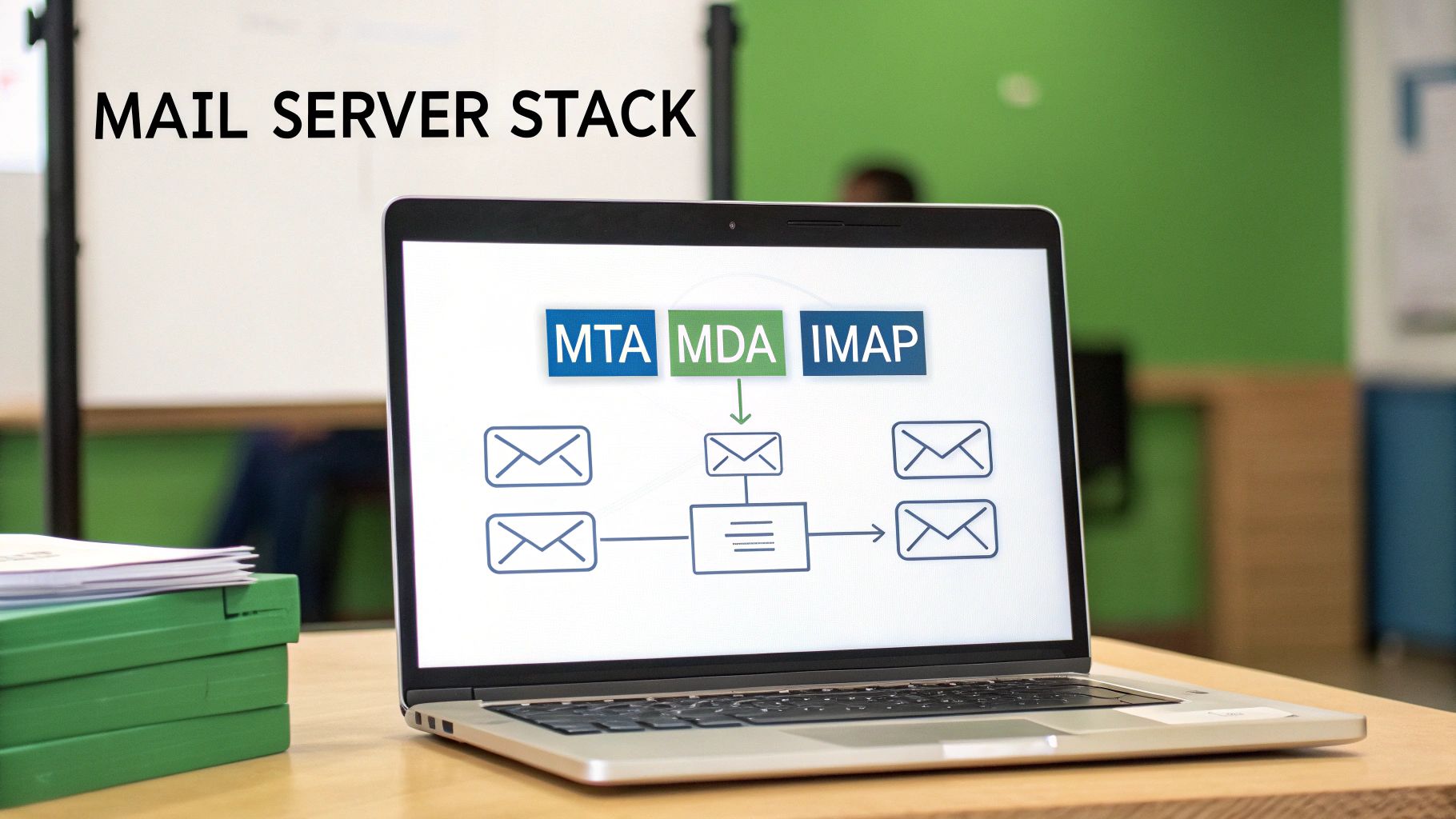
That's when a protocol called SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) springs into action. SMTP is the mail truck of the internet. Its one and only job is to pick up your message from your outbox and start driving it across the digital superhighway. This is the first place where a quality email host makes a huge difference, ensuring that this "mail truck" is armored with encryption so no one can snoop on your message along the way.
Finding the Right Digital Address
Once the SMTP mail truck is on the road, it needs to find the recipient's "house." It does this by checking the domain's MX (Mail Exchanger) records. Think of an MX record as the digital version of a zip code. It points the sending server to the exact mail server—the recipient's email host—that's set up to receive mail for that domain (like @yourbusiness.com).
This lookup happens in a blink of an eye, but it's crucial. It guarantees your important proposal doesn't get lost in cyberspace and instead goes directly to the secure "post office" that handles the recipient's inbox.
Your email host takes care of all these behind-the-scenes routing instructions. They manage the MX records and maintain a fast, secure, and reliable delivery network. This is what stops your messages from disappearing and keeps your communications private.
As you can see below, this professional and secure setup is a direct line to building trust in your brand.
The leap from a generic personal account to a trusted brand identity really depends on the reliability and security that a hosted email service brings to the table.
The Final Delivery to a Secure Mailbox
Once your email arrives at the recipient's mail server, it's time for the final delivery. This last step is handled by one of two protocols: IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) or POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3). These are the mail carriers who slot the letter into the recipient's private mailbox.
They work a bit differently:
- IMAP is all about syncing. It keeps the original email on the server, so you see the same inbox whether you're on your laptop, tablet, or phone. It’s like a cloud-based filing cabinet.
- POP3 downloads the email to just one device, usually deleting it from the server afterward. This is like taking your mail inside the house—it’s now only in that one location.
Your workflow often determines which one is better for you. If you're curious about the nitty-gritty, you can check out our guide that breaks down SMTP vs. POP3 and which email protocol is right for you.
At the end of the day, your email host manages this entire ecosystem. They provide the secure servers, keep the delivery protocols humming, and make sure your digital mail is stored safely until you're ready to read it. Without a solid host, your digital communication would be unreliable, vulnerable, and far from professional.
Comparing The Different Email Hosting Options
When it comes to email hosting, one size definitely does not fit all. Getting your head around the different types is the first step to finding the right balance of cost, control, and security for what you actually need. The choice you make here has a real impact on your email privacy, how much technical work is on your plate, and your overall email security.
So, let's break down the three main flavors of email hosting, starting with the most common and budget-friendly option. A good way to think about it is like choosing a place to live: are you renting an apartment, buying a house, or moving into a full-service condo?

Shared Hosting: An Affordable Starting Point
Think of shared hosting as renting an apartment in a big building. You get your own private space (your mailbox), but you're sharing the building's core resources—the plumbing, electricity, and security staff—with all the other tenants. On a technical level, this means your email accounts sit on a server alongside many other customers.
This model is super cost-effective, which is why it’s so popular for personal projects, freelancers, and small businesses just getting off the ground. But, just like apartment living, this shared setup has a few potential downsides to email privacy and security.
- The "Noisy Neighbor" Problem: If another user on your shared server starts sending spam and gets blacklisted, it can sometimes hurt your email deliverability, even if you’ve done everything right.
- Limited Resources: Since you're all sharing the same server power, you might notice things slow down if other accounts are having a particularly busy day.
- One-Size-Fits-All Security: You get the standard security the host provides, but there’s little to no wiggle room for custom setups. It's usually solid, but it’s not designed for specific, high-security demands.
Dedicated Hosting: The Private House
Next up is dedicated hosting, which is like owning your own house. You get an entire server all to yourself. This hands you the keys to the kingdom, giving you complete control over every single aspect of your email environment, from the operating system to the exact security tools you want to install.
This is the go-to option for large organizations with their own IT teams and very strict compliance or security mandates. You get maximum power and flexibility, but it all comes with serious responsibility. You're the one on the hook for all the maintenance, security patches, and troubleshooting.
With a dedicated server, you gain incredible control and performance. But you also take on the full weight of managing the entire system, which demands deep technical know-how and a hefty budget.
The global email hosting market was valued at around $8.86 billion USD in 2024 and is expected to climb to $16.56 billion USD by 2035. While dedicated setups have been a mainstay, their complexity and cost are pushing more people to look for a better-balanced alternative.
Hosted Email Platforms: The Full-Service Solution
Finally, we have hosted email platforms. This is your premium, full-service condominium. You get a secure, private space that’s all yours, but a professional management company takes care of all the maintenance, security, and amenities behind the scenes.
Platforms like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, or privacy-first services like Typewire are built from the ground up to deliver a powerful and secure email experience without the technical headaches. They manage the servers, push software updates, and constantly watch for threats, which lets you get back to focusing on your work. For a broader look at hosting, a comparison of various web hosting services can be quite useful, as many of the core ideas apply to email, too.
For most businesses and individuals, this model is the best of both worlds. It delivers the robust email security and email privacy of a dedicated environment without the technical complexity. Specialized hosted email platforms are designed specifically for secure communication, making them an ideal choice for anyone who prioritizes protecting their data. To see more options in this space, take a look at our guide to 12 email hosting solutions you should know.
What Really Matters: Your Email Security and Privacy Checklist
Knowing the different types of email hosting is a great start, but the real test comes down to the features that actually protect your information. When you sign up for a hosted email platform, you're not just getting an inbox—you're hiring a security team for your most private conversations. These features are the non-negotiables that stand between you and a world of digital threats, from nosy data brokers to sophisticated cyberattacks.
Let's cut through the jargon and focus on the security and privacy tools that any top-tier provider must have. Think of these as the layers of a digital fortress, built to ensure only you and the people you trust can access your messages.

End-to-End Encryption: The Unbreakable Digital Seal
The absolute cornerstone of email privacy is end-to-end encryption (E2EE). Imagine you wrote a letter, sealed it in an envelope, and then locked that envelope inside a special box. Only the person you're sending it to has the key to open that box. That’s exactly how E2EE works for your emails.
Your message gets scrambled on your device before it ever hits the internet, and it can only be unscrambled by the recipient's device. Nobody in the middle—not your internet provider, not government agencies, not even the email host itself—can read what you wrote. It’s the ultimate guarantee of a confidential conversation.
Think of it this way: standard encryption is like sending a postcard. The mail carrier can read it. End-to-end encryption turns that postcard into a locked briefcase, making your messages completely unreadable to anyone but the final recipient. It's the gold standard for private communication.
This isn't just a "nice-to-have." For anyone dealing with sensitive information—business contracts, financial records, or personal health details—E2EE is an absolute must.
Two-Factor Authentication: Your Personal Mailbox Key
If encryption is the sealed envelope, then two-factor authentication (2FA) is the unique key needed to unlock your mailbox in the first place. It adds a second, powerful layer of security that stops hackers in their tracks, even if they somehow manage to steal your password.
It's a simple, two-step process:
- You enter your password: This is the first factor, something you know.
- You provide a second code: This is something you have, like a temporary code sent to your phone or generated by an app like Google Authenticator or Authy.
This one simple step is incredibly effective. It's proven to block a staggering 99.9% of all compromised account attacks. A trustworthy email host won't just offer 2FA; they'll actively encourage you to use it.
Advanced Spam and Phishing Filters: Your Digital Bodyguard
Your email provider should also act as a vigilant guard at the gate, screening every incoming message for threats before they can do any harm. This is about more than just a basic junk folder. Modern email security depends on smart, proactive systems that identify and block malicious attacks.
- Spam Filters: These use sophisticated logic to recognize and quarantine unwanted junk mail, keeping your inbox clean and letting you focus on what matters.
- Phishing Protection: This is the real game-changer. Phishing emails are designed to trick you into giving away passwords or financial information. Advanced filters spot the red flags—like suspicious links or forged sender addresses—and neutralize the threat automatically.
Think of these filters as a proactive defense. They don't just clean up the mess; they prevent security breaches from ever happening, protecting you from fraud and identity theft.
Data Sovereignty: Knowing Where Your Data Lives
Finally, there’s a critical piece of the email privacy puzzle that often gets missed: data sovereignty. In simple terms, this means you know—and have some control over—the physical country where your email data is stored. Why does this matter? Because the location of the server determines which country's laws apply to your data.
For instance, data stored on servers in the United States could be subject to laws like the CLOUD Act, which can give government agencies access. In contrast, providers who store data in countries with strict privacy laws, like Switzerland or Germany, offer a powerful layer of legal protection.
A transparent email host will be upfront about their server locations. Choosing a provider in a jurisdiction with strong privacy laws means your data isn't just protected by technology—it's also protected by law. That’s true peace of mind.
Your Security and Privacy Feature Checklist
Use this checklist to evaluate hosted email platforms and ensure they meet the highest standards for data protection.
| Feature | Why It's Critical for Privacy | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| End-to-End Encryption | Makes your emails unreadable to everyone except you and the recipient. | Clear implementation of PGP or similar open-source standards. It should be easy to use, not just a technical option. |
| Two-Factor Authentication | Prevents unauthorized access even if your password is stolen. | Support for authenticator apps (TOTP), security keys (U2F/WebAuthn), and SMS codes. |
| Zero-Knowledge Architecture | Ensures the provider cannot access your data because they don't hold the encryption keys. | Explicit statements in their privacy policy confirming they cannot decrypt your stored emails or attachments. |
| Spam & Phishing Filters | Proactively blocks malicious emails, scams, and malware from reaching your inbox. | Advanced, learning-based filters that can be customized. Look for protection against spoofing and impersonation. |
| Data Sovereignty | Puts your data under the protection of strong, privacy-friendly laws. | Transparent information about server locations (e.g., Switzerland, Germany, Canada). Avoid providers in Five Eyes countries. |
| Anonymous Signup | Allows you to create an account without providing personally identifiable information. | Options to sign up without a phone number and pay with privacy-preserving methods like cryptocurrency. |
Choosing a service that checks all these boxes is the best way to ensure your digital communications remain truly yours. It moves your email from being a potential liability to a secure asset.
How to Choose the Right Email Hosting Provider
Picking an email hosting provider is a big deal. It’s a decision that goes straight to the heart of your digital privacy and security. The key is to look past the flashy marketing and figure out what really matters: their actual commitment to keeping your data safe. This means taking a hard look at their security setup, their privacy policies, and how transparent they are about their business.
Think of it like hiring a security guard for your most sensitive conversations. You wouldn't just hire the first person who showed up; you'd ask some tough questions first. The same goes for your email host. A provider you can trust will be open to that scrutiny and won't hide how they handle your information.
Evaluating Security and Privacy Policies
Your first stop should be the provider's privacy policy. This isn't just a wall of legal text—it's a mission statement. It tells you exactly how they make money. Are you paying them for a service, or are they making money by analyzing and selling your data?
Look for plain, direct language. A provider who genuinely cares about email privacy will come right out and say they don't scan your emails for ads, track what you do, or sell your data to anyone. If you have to dig through paragraphs of confusing jargon to find that promise, or if it's missing entirely, that's a huge red flag.
A great example of this is a privacy-first hosted email platform like Typewire, which is built on a zero-knowledge principle. Their entire system is designed so that no one—not even their own employees—can access or read your messages. That’s how you know your conversations stay private.
Your main goal here is simple: figure out if you're the customer or the product. A secure email host sells a service to protect your data. A free platform often sells your data as its service.
This is a critical distinction. When your data is the product, your privacy will always take a backseat to the provider's bottom line. By choosing a paid, privacy-focused service, you ensure their goals are aligned with yours: keeping your information secure.
Key Questions to Ask Potential Providers
After you've checked out their privacy stance, it's time to get into the nuts and bolts. The answers to these questions will reveal how serious a provider really is about email security. Don't be shy about contacting their support team to get straight answers.
Here are the essential questions everyone should be asking:
-
Where are your servers located? As we've covered, data sovereignty is a big deal. The physical location of the servers dictates which country's laws apply to your data. You want a provider with servers in countries known for strong privacy laws, like Switzerland, Germany, or Canada.
-
What is your data retention policy? You need to know how long they hang onto your data after you delete it and what happens if you decide to close your account. A provider who respects your privacy should have a policy of immediate and permanent deletion.
-
What encryption standards do you use? Find out if they offer end-to-end encryption (E2EE). Ask them what protocols they use to protect your data when it's moving (TLS) and when it's stored on their servers (like AES-256). The stronger and more transparent their encryption, the better.
-
Do you support two-factor authentication (2FA)? This is a basic, non-negotiable security layer. Make sure they support modern 2FA methods like authenticator apps or physical security keys, not just the less-secure SMS option.
Making a Confident and Informed Decision
Once you have this information, you can compare different hosted email platforms with confidence and pick a partner that truly has your back. The demand for reliable, secure email hosting is skyrocketing, which is part of a much larger shift in how we handle our digital lives. In fact, the global email hosting services market is set for major growth, pushed by the needs of small and medium businesses all over the world. You can learn more about the email hosting market's growth and what's driving it.
Ultimately, making the right choice isn't about finding the cheapest service. It's an investment in a partner that will act as a true guardian for your digital identity. When you prioritize providers with transparent policies, solid security, and a real dedication to user privacy, you're taking a huge step toward locking down your communications for good.
Taking Control of Your Digital Identity and Security
We started this guide with a simple question: "what is email hosting?" By now, it's clear that the answer goes far beyond a technical definition. The real takeaway is that your choice in email hosting is a huge investment in your professional brand, your digital privacy, and your online security.
When you ditch the free services that mine your data and treat you as the product, you're making a conscious decision to take back control. You're choosing how your information is handled. As we've seen, the right provider becomes a digital guardian, wrapping your conversations in layers of robust security.
Building Your Digital Brand with Confidence
Opting for a secure, hosted email platform is your first big step in protecting your professional communications. It sends a clear signal to clients and partners that you're serious, trustworthy, and that you value privacy in every email you send.
This control over your primary communication channel is the bedrock of your entire digital presence. Of course, securing your professional email is just one piece of the puzzle. Actively managing your online footprint is just as vital. For a closer look at this topic, this a guide to managing your online reputation offers some fantastic insights.
Ultimately, selecting the right email hosting service is about empowerment. It’s a conscious decision to own your digital identity rather than renting it from a corporation that profits from your data.
This single choice lets you communicate with the confidence that comes from knowing your data is locked down with strong encryption and backed by transparent privacy policies. You stop being just another user in a massive system and become a valued client whose privacy is the priority.
You now have the knowledge to pick a service that not only protects your identity but empowers you to communicate with the security you deserve. With a privacy-first provider, you’re investing in a platform built from the ground up to keep your digital conversations secure, private, and truly your own.
Frequently Asked Questions About Email Hosting
Even after you've got a good handle on the basics, a few practical questions always seem to come up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to clear up any lingering confusion about email hosting, security, and privacy.
Can I Use Email Hosting Without a Website?
Absolutely. You don't need a website to set up a professional email address. All you really need is a registered domain name (like yourbrand.com).
Once you have that, you can connect it directly to a dedicated hosted email platform. This is a fantastic route for freelancers, consultants, or new businesses that want to look professional and keep their communications secure right from the start, even before a full website is in the picture.
What Is the Difference Between Email Hosting and Web Hosting?
Think of it like renting two different spaces: one is your storefront, and the other is your private mailroom.
Web hosting is the storefront—it provides the online space and technology to store your website's files and make them visible to the world. Email hosting, on the other hand, is your secure mailroom, built specifically to handle sending, receiving, and storing all your messages.
Many web hosts bundle the two together, which can be convenient. However, a dedicated hosted email platform is almost always better for email security and email privacy because that's their entire focus.
Is Paid Email Hosting Really More Secure Than Free Services?
Yes, and the difference is night and day. Free email services aren't truly free; you often pay with your privacy. Many of these providers scan your email content to build an advertising profile on you.
Paid hosting services have a completely different business model: you are the customer, not the product. Their job is to protect your information, not sell it. This means you get much stronger security features, like end-to-end encryption, advanced spam filtering, and strict privacy policies that prohibit data mining.
Think about it this way: a data breach on a huge free platform can affect billions of accounts. A dedicated host offers a smaller, more secure, and less attractive target for attackers, drastically lowering your risk.
How Much Technical Skill Do I Need to Set Up Hosted Email?
For most modern hosted email platforms, you need almost no technical skill. Good providers know their customers aren't all IT experts, so they make the setup process incredibly simple.
Usually, the most "technical" part is just changing a couple of settings with your domain registrar to point your email to the new servers. Even then, most services provide clear, step-by-step guides and have a support team ready to help if you get stuck. The whole point is to give you powerful security without the headache of managing the tech yourself.
Ready to take control of your digital communications? Typewire offers a secure, private email hosting platform designed to protect your data. With no ads, no tracking, and a commitment to your privacy, you can communicate with confidence. Start your free trial and experience the difference at https://typewire.com.