When you opt for a private email hosting service, you’re choosing a secure, ad-free home for your communications. Think of it as a dedicated server where your email lives, completely separate from the free providers that scan your data for advertising. It's about taking back control of your digital privacy and security.
Why Your Business Needs Private Email Hosting
If your business is still running on a free email service, you're essentially posting your sensitive communications on a public bulletin board. It might be convenient, but those platforms treat your private messages as a product to build advertising profiles. For any serious business, the risks to your email privacy and email security are just too high to ignore.
Switching to a private email hosting service is like moving those conversations from the public board into a locked, company-owned safe. You own the space, you make the rules, and you're the only one with the key. This isn't just a technical upgrade; it's about taking full ownership of your digital assets and professional identity.
Secure Your Communications and Data
The biggest driver for making the switch is email security. Free services are gigantic, tempting targets for hackers simply because of their massive user numbers. Private email platforms, on the other hand, run on dedicated servers with much stronger security protocols in place.
This setup makes you a much harder target for anyone trying to get their hands on confidential client info, financial records, or internal company plans. By separating your email from the public pool, you drastically shrink your vulnerability to attack.
A dedicated email hosting service gives you server space to store your emails and grants you access to a domain name of your choice. It provides personalization and a professional look that free services lack.
Build a Professional Brand Identity
Security aside, private hosting is a game-changer for your brand's credibility. An address like sales@yourcompany.com immediately looks professional and trustworthy. A generic one like yourcompany123@gmail.com? Not so much. It can look amateurish and chip away at customer confidence.
A custom domain is a fundamental part of building a solid brand. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how using an email with a custom domain can boost your business credibility.
This control also gives you some serious operational advantages that help you grow:
- Guaranteed Privacy: Your provider’s business model is selling you a service, not selling your data. Your conversations stay confidential.
- Complete Control: You can create custom addresses for different teams (
support@,billing@, etc.) and easily manage accounts as your team grows. - Enhanced Reliability: You get to skip the crowded servers of free providers, which means better uptime and faster, more reliable delivery for your important messages.
How Hosted Email Platforms Actually Work
When you hit 'send' on an email, it kicks off a surprisingly complex digital journey. If you're using a free service like Gmail, think of it like dropping a postcard into a massive public postal system. Your message gets sorted and transported alongside millions of others, and it's often scanned for keywords to help advertisers target you.
Private email hosting works on a completely different principle. It’s more like hiring a private courier to deliver a sealed, confidential document. Your message travels a direct, secure route, handled by infrastructure that's dedicated solely to you or a small, controlled group.
That distinction is everything when it comes to email privacy and email security. Instead of being just another package on a public conveyor belt, your communications are treated as a priority, ensuring they stay confidential and arrive without being snooped on.
The Infrastructure Powering Your Privacy
So, what’s the secret sauce? It all comes down to the server setup. Free services cram everyone’s data onto enormous, shared servers to keep costs down. Hosted email platforms, on the other hand, give you a more isolated and secure environment to operate in.
There are three main flavors of infrastructure you'll encounter:
- Dedicated Servers: This is the gold standard for privacy. You get an entire physical server all to yourself. It’s like owning the entire courier truck instead of just renting a small lockbox inside. This gives you unparalleled control, performance, and security.
- Virtual Private Servers (VPS): A VPS is a clever compromise. A single, powerful physical server is partitioned into multiple, completely isolated virtual machines. Each one acts like its own dedicated server, giving you dedicated resources and solid security without the price tag of a full physical machine.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Private cloud hosting uses a distributed network of servers to run your email, which is great for reliability and scaling up as you grow. The key here is that a private provider ensures your data is kept separate and secure within their cloud—a world away from the massive public clouds used by free services.
This visual breaks down the direct, secure path an email takes with a private hosting service, from the moment you send it to when it’s received.

As the infographic shows, using a private server cuts out the middle-man stops where data scanning and analysis typically happen on free platforms.
Why Server Choice Matters for Security
The type of hosting you choose has a direct impact on your security and how much control you have. The VPS model, for example, is hitting a sweet spot for many people, offering a great balance of performance and affordability. In fact, VPS hosting is projected to grab 20-25% of the total hosting market by 2026, which shows a clear shift toward more private and controlled online spaces. You can dig into the numbers in this detailed industry analysis.
The real advantage of any private hosting model—whether it’s dedicated, VPS, or cloud—is isolation. By walling off your email from the sprawling systems of free providers, you dramatically shrink your attack surface and stop your data from being mined for profit.
Ultimately, these platforms work by giving you your own secure, exclusive space on the internet. Your provider takes care of the technical heavy lifting—managing the servers, patching security vulnerabilities, and keeping the network running smoothly—so you can just focus on communicating. They handle the sending protocols (SMTP) and the retrieval protocols (IMAP or POP3) that let your email client securely fetch your messages. If you're curious about how that last part works, we have an article that explains the differences between IMAP and POP3. It's a managed environment designed to make your email not just private, but also reliable.
The Real-World Benefits of Private Email Hosting
Once you get past the technical side of things, switching to private email hosting services offers some very real, tangible perks that touch everything from your company's reputation to its day-to-day operations. The whole idea is built on three core pillars: rock-solid email security, guaranteed email privacy, and absolute control over your communications.
Think of it less as a simple upgrade and more like putting a high-tech security system on your digital headquarters. Every single email you send or receive is a small piece of your business, and it's an asset worth protecting. A professional email host turns your inbox from a potential weak spot into a secure, efficient tool that actually helps you grow.
Pillar 1: Fortifying Your Digital Defenses With Enhanced Security
In a world where cyber threats are a daily reality, using a free email service for your business is kind of like leaving your office door unlocked overnight. Private email hosting services give you a whole suite of advanced security features that act like a dedicated digital security guard, actively shielding you from hackers and scammers.
This kind of proactive defense is light-years ahead of what you get with free platforms. It works 24/7 to make sure your sensitive conversations with clients, partners, and your own team stay confidential and out of the wrong hands.
These aren't just abstract ideas; they have a real impact every day:
- Advanced Spam and Malware Filtering: The best private hosts use incredibly sophisticated filters that catch malicious emails before they ever land in your inbox. This dramatically cuts your risk from phishing scams and malware. A single successful phishing attack can cost a small business thousands, making this first line of defense absolutely essential.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Many private providers offer E2EE, which essentially scrambles your message the second you hit "send" and keeps it that way until your recipient opens it. Nobody in between—not even your email provider—can decipher its contents.
- Targeted Attack Resistance: When you use a free service, you're part of a massive, attractive target for hackers. By moving your email to a separate, dedicated server, you become a much smaller, more difficult target. It’s like moving from a giant, crowded apartment building to a private, gated home.
Pillar 2: Reclaiming Your Data With Guaranteed Privacy
Let's be honest about how most free email providers make their money: they scan your emails. They look for keywords to build detailed advertising profiles, turning your private business conversations into a product they can sell. With a private hosted email platform, that entire conflict of interest vanishes. You're the customer, not the product.
The core promise of private email is simple: your data belongs to you. The provider's job is to protect it, not profit from it. This alignment ensures your confidential business strategies, client details, and internal discussions remain truly private.
This commitment to email privacy is huge for building trust with clients and staying on the right side of data protection laws. If you do business with anyone in Europe, this isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a legal requirement to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Getting it wrong can lead to massive fines, making privacy a critical part of managing your business risk.
Pillar 3: Taking Command With Complete Control
Beyond just security and privacy, private hosting gives you something incredibly valuable: total control. This is your most important communication channel, and you get to be in the driver's seat. It starts with your professional image.
Using a custom domain like you@yourcompany.com instead of a generic Gmail address instantly builds credibility and reinforces your brand every time you communicate. It’s a small detail that makes a huge difference in how clients see you. But a professional address is just the start.
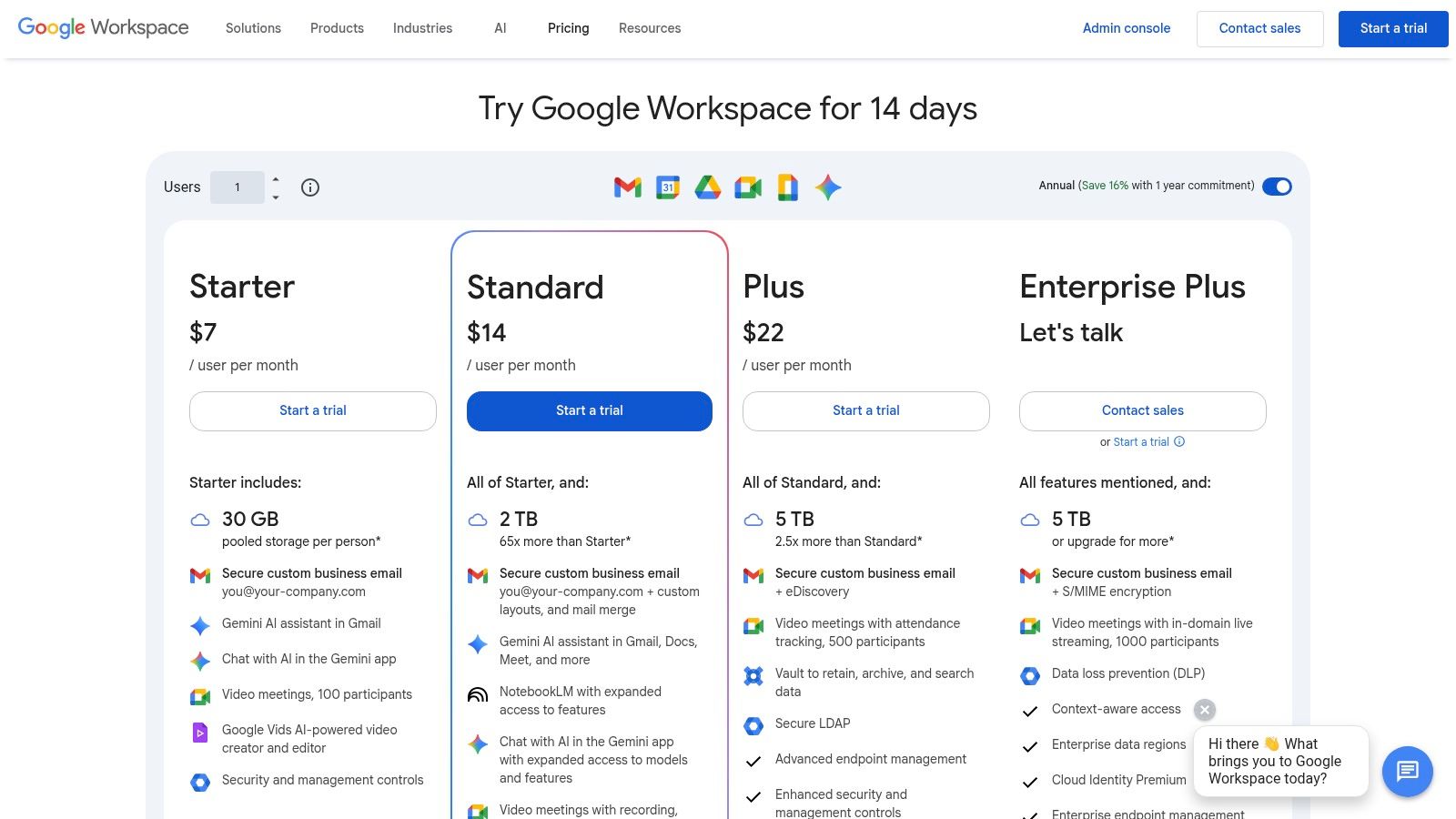
Free Public Email vs Private Hosted Email
To really see the difference, it helps to put them side-by-side. The gap between a free service and a professional one becomes pretty clear when you look at what you get—and what you give up in terms of privacy and security.
| Feature | Free Public Email (e.g., Gmail, Yahoo) | Private Hosted Email |
|---|---|---|
| Email Address | Generic (yourname@gmail.com) | Custom Domain (you@yourbrand.com) |
| Data Privacy | Data is scanned for advertising | Data remains private and is not monetized |
| Storage | Limited, shared resources | Generous, dedicated storage that scales |
| Admin Control | Limited to a single account | Full admin panel to manage users and aliases |
| Integrations | Locked into a specific ecosystem | Flexible integration with business tools |
This table really just scratches the surface. That level of control means your email system can actually grow and change with your business. You can create unlimited aliases (like support@ or info@) to keep things organized and get generous storage limits that won't hold you back.
A reliable email infrastructure is also a foundational piece for other communication strategies, like generating leads for email marketing. In the end, taking control of your email is a direct investment in your company’s long-term health and independence.
Must-Have Features in a Secure Email Provider

Jumping into private email hosting is a huge win for your business security, but it's crucial to understand that not all providers are built the same. To find a service you can genuinely trust, you need to look past the shiny marketing promises and really dig into what they offer. It’s all about vetting their security, confirming they have the tools your team needs to get work done, and scrutinizing their commitment to your email privacy.
Think of it like hiring a security firm for your digital headquarters. You wouldn't just pick the first name on the list. You'd meticulously review their credentials, their methods, and their reputation. A top-tier provider doesn't just hand you an inbox; they deliver a complete protective shield for your most sensitive information.
Security Foundations That Protect Every Message
First things first: the core security protocols. These are the absolute non-negotiables that form the bedrock of any respectable private email hosting service. They're your frontline defense against the constant barrage of digital threats, from clever phishing scams to relentless brute-force attacks.
Any provider that cuts corners here is leaving your business wide open. These features aren't just buzzwords; they work in tandem to create a multi-layered defense, making it exponentially harder for anyone to break into your accounts or read your mail.
Here are the essential security building blocks you should be looking for:
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): This is the gold standard for email security, and for good reason. E2EE scrambles your message the second you hit "send" and keeps it that way until your recipient opens it. Nobody in the middle—not even your email provider—can decipher the contents. To get a clearer picture, check out our simple guide on what end-to-end encryption is.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): A password just isn't enough anymore. 2FA adds a second layer of verification, like a code sent to your phone, creating a critical barrier that stops attackers even if they manage to steal your password.
- Intelligent Anti-Phishing and Spam Filters: Modern filters have evolved far beyond basic keyword blocking. The best ones use sophisticated algorithms to spot and neutralize advanced phishing attacks, malicious links, and dangerous attachments before they ever land in your inbox.
Productivity Essentials for Business Operations
While security is the main event, your email service still has to function as a practical tool for your business. A platform that's clunky, confusing, or missing key features will just slow your team down and cause headaches. The best hosted email platforms are the ones that flawlessly merge ironclad security with a smooth, user-friendly experience.
These features make sure your email plays nicely with all your other business tools, allowing you to manage contacts, schedule meetings, and stay connected from anywhere, all without compromising on safety.
The goal is to find a provider that enhances both your security posture and your operational efficiency. A secure email system that's too cumbersome to use is one that your team will eventually try to bypass, defeating the entire purpose.
Make sure your potential provider offers these key productivity tools:
- Reliable Calendar and Contact Syncing: Support for open standards like CalDAV (for calendars) and CardDAV (for contacts) is a must. This ensures your schedule and address book sync perfectly across every device you own, from your desktop to your smartphone.
- Flexible and Ample Storage: Your data needs will only grow. A great provider offers plenty of storage from the get-go and has simple, affordable ways to add more space as you expand. No more "inbox full" warnings.
- An Intuitive Admin Panel: If you're managing a team, you need an easy-to-use control panel. It should let you add or remove users, create email aliases (like
info@yourcompany.com), and adjust permissions without needing a degree in IT.
Privacy Guarantees That Build Trust
Finally, you have to examine the provider's fundamental dedication to your email privacy. This isn't just about features; it's about their business model, their legal structure, and their core philosophy. A truly private email service operates on one simple principle: you are the customer, not the product they sell.
This is where you can separate the genuine privacy champions from everyone else. It means taking the time to read the fine print and understanding the real-world implications of where your data is stored and who can legally demand access to it.
Here’s what you need to dig into:
- A Clear Privacy Policy: The provider must state, in no uncertain terms, that they don't scan your emails, track what you do, or sell your information. Their revenue should come from your subscription fee, period.
- Zero-Knowledge Encryption: This takes privacy a step further. It means the provider has "zero knowledge" of your encryption key and, by extension, your password. They are physically incapable of decrypting your data, even if forced by law.
- Legal Jurisdiction: Where a company is based makes a huge difference. A provider headquartered in a country with strong privacy laws, like Switzerland, offers far greater legal protection than one based in a "Five Eyes" intelligence-sharing nation (US, UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand).
How to Choose the Right Email Hosting Service

You get the "why," but now it's time for the "how." Turning your knowledge of private email hosting services into a smart decision takes a clear game plan. The goal isn't to find some mythical "best" service, but to find the one that fits your business like a glove. The process feels a lot like choosing a web hosting provider, where the essentials—reliability, security, and solid support—are non-negotiable.
First thing's first: set a realistic budget. Sure, free email is out there, but a private email host is an investment in your security and professional brand. Look past the price tag and focus on the value you're getting, like storage space per user, built-in security features, and access to real human support when you need it.
Define Your Core Requirements
With a budget in mind, you can start to filter your options by asking some key questions about what you actually need. Think of this as building your wishlist to find a service that matches your vision for email security and email privacy.
Start with how hands-on you want to be. Are you looking for a "set it and forget it" managed solution where the provider takes care of all the technical heavy lifting? Or do you need the keys to the kingdom with deep control over server settings? For most businesses without a dedicated IT staff, a managed service is the way to go.
Next, make a list of your absolute must-have security features. Does every message need end-to-end encryption? Are you in an industry where you have to comply with data privacy laws like GDPR or HIPAA? Answering these questions will quickly narrow down your list to only the serious contenders.
The demand for professional-grade email is exploding. The global email hosting services market is expected to jump from $27.04 billion in 2024 to an incredible $108.73 billion by 2032. This growth is all about the increasing need for secure, reliable communication tools.
Planning a Smooth Migration
Finally, think about the switch itself, especially if you’re moving away from a free service like Gmail. The idea of migrating years of emails and contacts can feel overwhelming, but a good hosted email platform should make the process almost painless.
Here’s what to look for to ensure a headache-free transition:
- Dedicated Migration Tools: The best providers offer automated tools that can pull in your entire inbox, contacts, and calendars from other platforms in just a few clicks.
- Clear Documentation: Look for easy-to-follow guides and video tutorials that walk you through setting up your accounts and connecting your devices.
- Responsive Customer Support: Nothing beats the peace of mind that comes from knowing help is just a call or a chat away if you run into any trouble.
By thinking through your budget, your technical needs, and the migration plan ahead of time, you can confidently pick the right private email hosting service from the start.
Common Questions About Private Email Hosting
Thinking about moving to a private email host? It's a smart step, but it's natural to have a few questions. Most people wonder about the cost, the setup process, and whether it’s really that different from just using a custom domain with a free service.
Let's break down these common concerns so you can feel confident you're making the right move for your business.
Is Paying for Email Really Worth It?
Here’s the thing: when you pay for an email service, you become the customer, not the product. That monthly fee isn't just for an inbox—it's an investment in serious email security, guaranteed email privacy, and real customer support when you need it. Free services have to make money somehow, and they often do it by scanning your data for advertising. That's a hidden cost that puts your privacy on the line.
Think of it this way: the true value isn't just about a few dollars a month. It's about preventing a single data breach that could cost your business thousands in lost revenue and, more importantly, your customers' trust.
Isn't a Custom Domain on Gmail the Same Thing?
Using your own domain with a service like Gmail is a great start for branding, but it doesn't touch the core privacy problem. Your emails are still sitting on their servers, which means they're subject to their data-mining practices and terms of service. You get the professional look, but you miss out on the crucial security and privacy that a true hosted email platform provides.
With a private host, your data is kept in a secure, separate environment. This isolation is key to protecting your conversations from both prying eyes and the massive-scale cyberattacks that often target big, free providers.
How Difficult Is It to Set Up and Move My Old Emails?
The idea of migrating years of emails sounds like a massive headache, right? Thankfully, modern private email hosting services have made this surprisingly painless. Most quality providers give you simple control panels and automatic migration tools that pull in your old emails, contacts, and calendars with just a few clicks.
You definitely don't need to be an IT wizard. These are managed services, which means they handle all the server upkeep, security patches, and other technical stuff behind the scenes. The whole process is designed to be straightforward, getting you up and running on a more secure platform without the stress.
Ready to take full control of your inbox with a service that respects your privacy? Typewire offers secure, ad-free private email hosting with zero tracking and zero data mining. Start your 7-day free trial today!