Think of spam filtering as your inbox’s personal security guard. Its one and only job is to stand at the digital door, check the ID of every incoming email, and decide if it's a friend or a foe. It's the bouncer that keeps the junk out so you don't have to deal with it.
Instead of you manually sifting through endless promotional emails, scams, and other nonsense, this automated system spots them and shoves them aside, keeping your main inbox clean and focused.
What Is Spam Filtering In Simple Terms?
At its heart, spam filtering is a program designed to keep your email experience safe and uncluttered. It’s your first line of defense against all the unsolicited, irrelevant, or flat-out dangerous messages trying to get your attention. This isn't just about saving you a few minutes of cleanup; it's a critical security layer that protects you from phishing scams, viruses, and malware.
And let's be honest, the amount of junk email flying around is staggering. By 2025, it's estimated that 46% of the 347 billion emails sent every day will be spam. That’s a mind-boggling 160 billion junk messages daily. Thankfully, modern filters are incredibly good at their job, often catching over 99.9% of spam, which shows just how essential they are. You can get more insights on the latest email security trends to see how these systems are evolving to fight new threats.

Core Functions Of A Spam Filter
To really get what spam filtering is, it helps to look at its main tasks. Think of these as the different jobs your digital security guard performs to keep you safe.
Here's a quick overview of the primary tasks performed by spam filtering systems to protect your inbox.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Identification | Scans emails for red flags like sketchy links, common spam phrases, or weird formatting. | An email with the subject "!!! URGENT WINNER !!!" gets instantly flagged. |
| Segregation | Moves anything that looks like spam out of your main inbox and into a "junk" or "spam" folder. | A fake package delivery notice is automatically sent to your junk folder. |
| Protection | Actively blocks messages carrying known malware, viruses, or phishing links before they can do any damage. | An email with a virus hidden in an attachment never even reaches you. |
These functions work in concert to create a powerful shield for your communications. Now that we have the basics down, let's pull back the curtain and see how this all works behind the scenes.
How Spam Filtering Technology Actually Works
Ever wonder what happens behind the scenes when an email hits your server? It’s not just a simple delivery. Think of a spam filter as a digital bouncer, giving every incoming message a thorough once-over before it's allowed into your inbox. This isn't a single, random check; it’s a sophisticated, multi-step process designed to weed out junk mail.
Let's break down how that bouncer makes its decision.
Checking the Email's ID
First up is the header analysis. Every email has a header, which is basically its digital passport. It contains all the technical details about where the email came from and the route it took to get to you. The filter meticulously inspects this information, looking for anything fishy, like a forged sender address or an unusual travel path. This is a critical first line of defense against basic spoofing attacks.
Reading the Message
Next, the filter gets down to content analysis. It reads the subject line, the body of the email, and even checks out any attachments. It’s on the lookout for classic spam red flags: telltale phrases like "you've won a prize," suspicious links trying to phish for your information, or code signatures linked to known malware. The filter is essentially a detective at this stage, searching for clues within the message itself.
The Final Verdict From The Filter
The last major step is the sender reputation check. The filter doesn't just look at the email itself; it looks at who sent it. It checks the sender's IP address and domain against vast, global blacklists of known spammers. If the sender has a bad reputation, the filter immediately becomes suspicious. This reputation check is a cornerstone of modern email security and ties directly into what email authentication is and why it matters.
After weighing all the evidence from the header, content, and sender reputation, the filter assigns a "spam score." This score is the final judgment that decides the email's fate—it either gets delivered to your inbox, sent to a spam folder, or rejected entirely.
This diagram gives you a clear visual of this layered process.
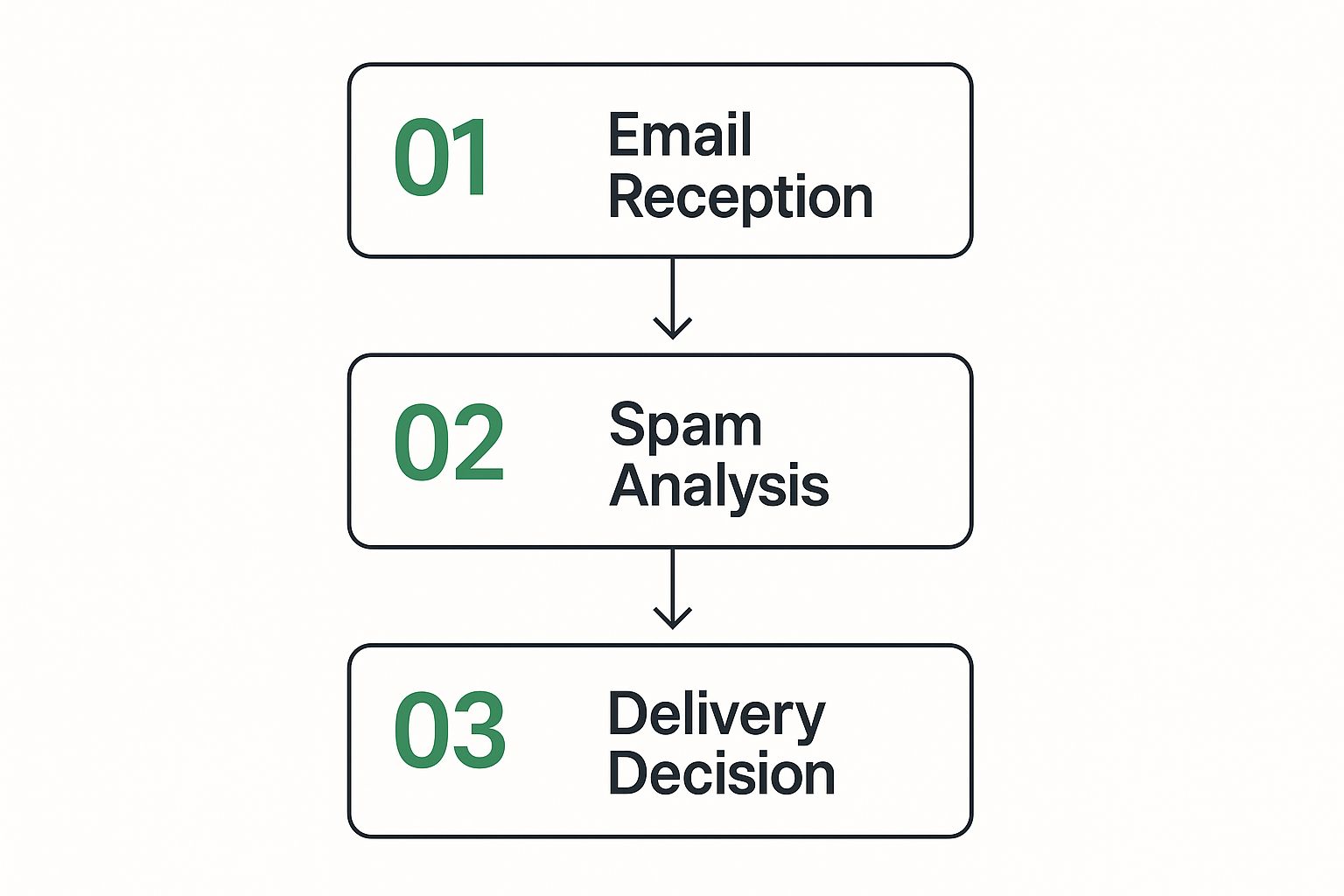
As you can see, filtering isn't just one action. It's a sequence of checks, with each step building on the last to create a powerful defense against the constant flood of unwanted email.
The Different Methods Used To Filter Spam

Spam filters aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. Think of them as a team of security specialists, each with a different skill set, all working together to guard your inbox. This multi-layered defense is crucial for catching the sheer variety of junk mail that comes our way every day.
The most straightforward methods rely on simple lists, almost like a bouncer at a club checking an ID.
- Blacklist Filtering: This is the most basic approach. It blocks any email from a sender or domain known for sending spam. It's great for stopping repeat offenders but needs to be constantly updated to be effective.
- Whitelist Filtering: This is the opposite. It's a "VIPs only" list, allowing emails only from pre-approved senders. While incredibly secure, it can be too restrictive and might block legitimate emails from new people trying to contact you.
More Dynamic Filtering Techniques
Beyond just checking the "who," smarter filters dig into the "what." These methods move past the sender's address and start analyzing the email's content for suspicious clues. It’s the difference between checking a driver's license and actually interviewing the person.
One common method is keyword and content filtering. This system scans the text of an email for red-flag words and phrases often associated with spam—things like "free money," "urgent action required," or "you've won!" If an email hits too many of these keywords, it gets flagged.
Heuristic filtering is more like a detective. It doesn't just look for specific words; it looks for spam-like behavior. It scores an email based on various characteristics, such as an all-caps subject line, an excessive number of exclamation points, or weird formatting. Each red flag adds points, and if the total score passes a certain threshold, the email is sent straight to your junk folder.
The real game-changer is Bayesian filtering. This is a smart system that actually learns from you. It analyzes the emails you manually mark as spam and compares their characteristics to the emails you keep. Over time, it builds a unique profile of what you consider junk, getting smarter and more accurate with every email you classify.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down how these common techniques stack up against each other.
Comparison Of Spam Filtering Techniques
| Filtering Method | How It Works | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Blacklist/Whitelist | Blocks or allows emails based on a pre-defined list of senders. | Quickly stopping known spammers or creating a highly restrictive inbox. |
| Keyword Filtering | Scans email content for specific suspicious words and phrases. | Catching obvious, low-effort spam campaigns. |
| Heuristic Filtering | Scores emails based on a wide range of spam-like characteristics. | Identifying suspicious patterns beyond just keywords, like formatting. |
| Bayesian Filtering | Learns from user behavior to statistically determine if an email is spam. | Creating a personalized and adaptive filter that gets smarter over time. |
Each of these methods plays a critical part in a robust email security strategy.
While we're focused on email here, the core idea of filtering unwanted communications is everywhere. You can see a similar principle in action with Apple's approach to call screening, which aims to block nuisance calls. Whether it's your inbox or your phone, these intelligent systems are essential for keeping digital noise at bay.
Here is the rewritten section, designed to sound completely human-written and natural.
Why Spam Filtering Is More Than Just A Clean Inbox
If you think of spam filtering as just a tool for a tidy inbox, you're missing the bigger picture. It's like seeing a bodyguard as just someone who opens doors. Yes, a clean inbox is nice, but the real value of spam filtering is the critical protection it offers. It's your digital frontline defense, actively shielding you and your business from a relentless stream of cyber threats.
Every single junk email it catches could be a phishing attempt trying to steal your passwords, a message carrying malware, or a sophisticated invoice scam. These aren't just minor annoyances; they're genuine security risks that can cause serious damage.
Protecting Your Most Valuable Assets
Beyond the obvious security benefits, spam filtering directly impacts your team's productivity. Manually sifting through and deleting junk mail is more than just tedious—it's a time-sucking black hole that pulls focus away from the work that actually matters. When you multiply that lost time across an entire team, the hours add up fast, draining both efficiency and morale.
Spam doesn't just waste time; it has a massive financial impact. One study estimated that lost productivity from spam costs businesses $20.5 billion globally each year.
That number alone makes a powerful case for investing in a solid filtering system. It’s not just a feature; it's an investment in your team’s focus and your company's bottom line.
Improving Security and Performance
On a more technical level, a good spam filter also keeps your network healthy. By stopping junk traffic before it even reaches your server, it prevents your systems from getting bogged down. The result? Faster, more reliable email performance for everyone.
Think about the sheer volume we're talking about here. On any given day, about 45% of all emails sent are spam. While a lot of that is just unwanted advertising, a dangerous 2.5% consists of scams and fraud, with identity theft leading the charge. You can dig deeper into the numbers in this breakdown of recent spam statistics.
Ultimately, understanding what spam filtering is means seeing it for what it truly is: an essential business strategy. It's not just for convenience, it’s for:
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: It acts as your first line of defense against phishing, malware, and ransomware attacks.
- Boosted Productivity: It frees up your team to concentrate on meaningful work instead of playing inbox janitor.
- Optimized Resources: It ensures your network performance isn't crippled by a flood of useless digital junk.
Why Advanced Filtering Is Non-Negotiable For Today's Businesses

The email threats hitting our inboxes today are a far cry from the annoying ads of the past. We're now up against highly targeted, cunning attacks like spear-phishing and Business Email Compromise (BEC). These aren't random spam blasts; they're designed to trick specific employees into making very costly mistakes.
Unfortunately, the standard filters that come with most email services just can't keep up. They often miss these subtle, sophisticated threats, leaving your entire organization wide open to attack.
This is precisely why a dedicated, multi-layered filtering solution has become a business necessity, not a luxury. An enterprise-grade system acts as a much smarter gatekeeper, using a mix of technologies to check everything from sender reputation to message content and even behavioral patterns. Investing in one of the top 8 best email spam filters to protect your inbox in 2025 isn't just an IT decision—it's a core strategy for protecting your most valuable information.
Meeting Compliance And Protecting Your Brand
If your business operates in a regulated industry, robust email security isn't just a good idea; it's the law. Industries governed by rules like GDPR or HIPAA demand strict data protection, and advanced filtering is a huge part of meeting those standards. A single data breach can lead to crippling fines and completely shatter your brand's reputation.
Think of an advanced filter as a proactive shield. It’s a foundational piece of modern corporate security that neutralizes threats before they can disrupt your operations or damage the trust you’ve built with your clients.
In this environment, powerful filtering is about much more than just convenience. It’s a critical layer in your company's overall security posture. Digging into broader data security best practices can provide even more context on how to safeguard your digital assets.
The growing need for these tools is obvious when you look at the market. The global anti-spam software market is on track to grow from $1 billion in 2021 to $1.66 billion by 2025. This surge is directly fueled by the rise in sophisticated email attacks, highlighting just how urgent it is for businesses to get ahead of cybercrime.
Common Questions About Spam Filtering
As you start to wrap your head around spam filtering, a few practical questions always seem to pop up. Getting straight answers to these is the best way to see how these systems really work day-to-day.
Let's dig into some of the most common things people ask.
Spam vs. Phishing: What's the Difference?
It’s easy to lump all junk mail together, but there's a critical difference between what’s just annoying and what’s actually dangerous.
Think of standard spam as the digital version of junk mail you get in your physical mailbox. It's unsolicited, clutters up your inbox, and is generally harmless—if a bit frustrating.
Phishing, on the other hand, is a whole different beast. It’s a con. These emails are designed to look legitimate, often mimicking your bank or a service you use, to trick you into giving up sensitive info like passwords or credit card numbers. A good spam filter helps catch both, but phishing is a direct attack on your security.
Why Do Some Spam Emails Still Get Through?
Even with the best technology in the world, no spam filter is perfect. It's a constant cat-and-mouse game; as soon as filters get smarter, cybercriminals cook up new ways to sneak past them.
It's a common myth that a great filter will catch 100% of junk mail. The reality is that top-tier systems block over 99.9% of it, but a tiny sliver might still find its way to you. That's why your own awareness is so important—knowing how to block spam emails and reclaim your inbox provides that crucial last line of defense.
How Do I Choose the Right Spam Filtering Service?
Finding the right service really comes down to what you need, but there are a few non-negotiables to look for. First, it should work seamlessly with your existing email setup. The last thing you want is a complicated tool that disrupts your workflow.
Beyond that, you need a service that offers protection on multiple fronts. A single layer of defense just doesn't cut it anymore.
Look for a solution that combines these key features:
- Anti-phishing technology to spot and neutralize those deceptive emails.
- Anti-malware and virus scanning to check attachments and links for anything nasty.
- Customizable rules so you can tweak the filter to match your specific needs, like whitelisting trusted senders.
Getting a service with this combination gives you a solid, well-rounded defense that puts you back in control of your inbox.
Ready to secure your communications? Typewire offers advanced anti-spam and virus protection built into our private email hosting. See the difference for yourself and start your free trial at https://typewire.com.