In today's competitive landscape, your email address is more than just a contact point; it's a critical branding tool. An address like contact@yourbrand.com builds instant credibility and trust, while a generic Gmail or Yahoo address can look unprofessional. But what if you're just starting out or on a tight budget? The good news is you don't have to choose between professionalism and cost. The world of free business email hosting offers surprisingly powerful solutions, from full-featured inboxes to clever email forwarding services that give you a custom domain address without the monthly fee.
This guide breaks down the best options available today, helping you find the right fit for your specific needs. We'll explore the two main categories of free services: dedicated hosted mailboxes and simple email forwarding. For each of the top platforms, we provide a detailed review, complete with screenshots, direct links, and step-by-step setup instructions to get you started quickly.
Our goal is to give you clear, actionable insights so you can elevate your business communications without spending a dime. Securing your email is a crucial first step, and it pairs well with implementing strong website security best practices to protect your entire digital footprint. Let's dive into the platforms that will give your business the professional edge it deserves.
1. Typewire
Typewire distinguishes itself as a premier choice for businesses and individuals who prioritize data sovereignty and security above all else. While many platforms offer free services by monetizing your data, Typewire operates on a fundamentally different, privacy-first model. It provides a secure, ad-free, and no-tracking email environment, making it an exceptional option for those looking for free business email hosting without compromising on privacy.
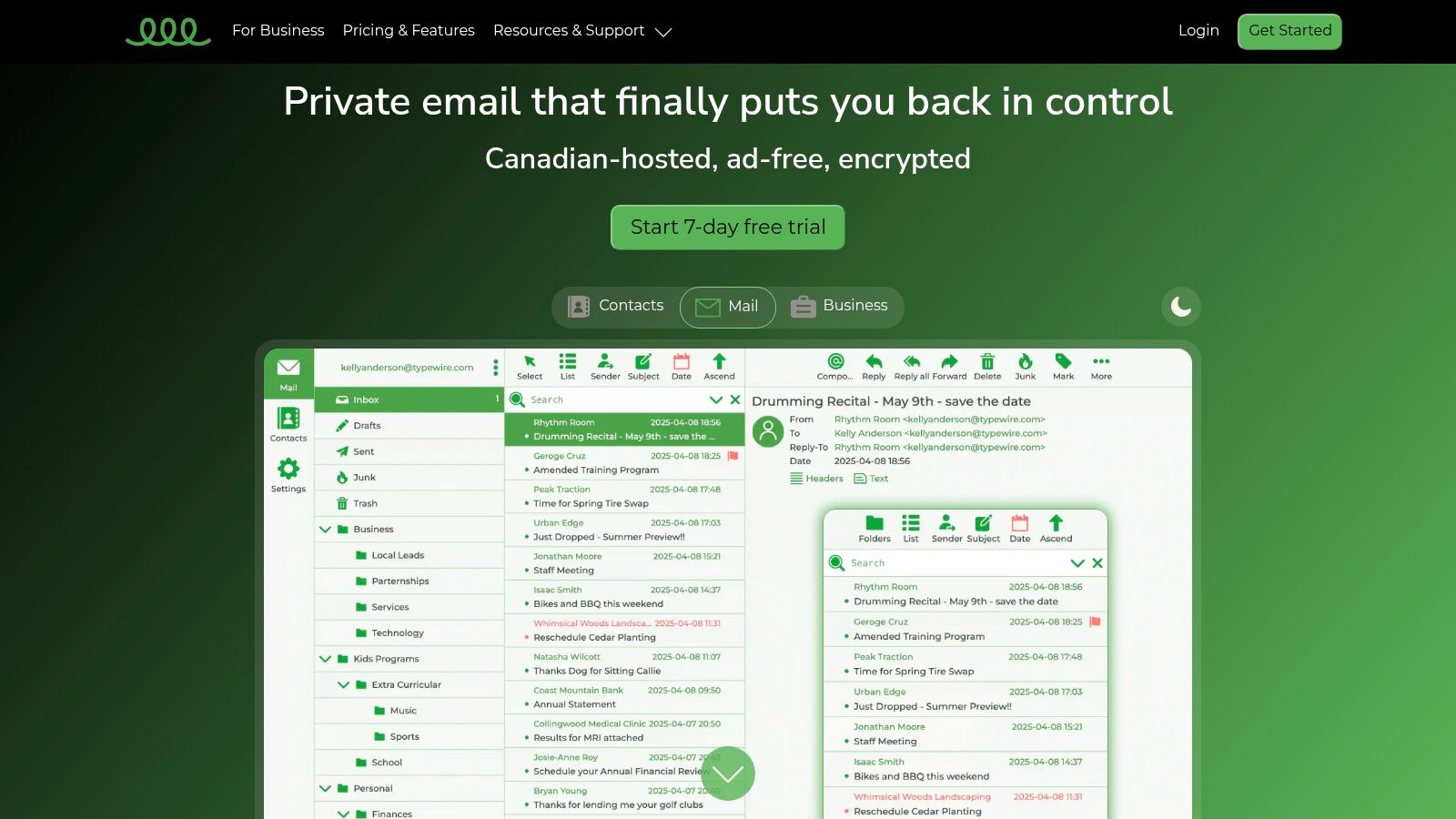
The platform's core strength lies in its commitment to data protection, with all infrastructure located in Canadian-owned and operated data centers. This ensures your communications are shielded by robust Canadian privacy laws like PIPEDA, giving you full ownership and control over your information. This is a critical differentiator for businesses handling sensitive client data or anyone wary of the data-mining practices common with mainstream email providers.
Key Features and Capabilities
Typewire’s platform is engineered for security and ease of use, providing a robust suite of tools even within its introductory offerings.
- Privacy and Security: At its foundation, Typewire provides end-to-end encryption alongside advanced anti-spam and virus protection. This multi-layered defense system ensures your inbox remains clean and your communications are secure from unauthorized access.
- User-Friendly Interface: The webmail client is fast, intuitive, and modern, featuring both light and dark modes. The user management dashboard is streamlined, making it simple for IT administrators or business owners to add users, manage permissions, and oversee accounts without a steep learning curve.
- Seamless Migration: For businesses moving from another provider, Typewire offers straightforward migration tools to transfer existing emails, contacts, and calendars securely, minimizing downtime and data loss.
- Custom Domain Hosting: While the free plan is excellent for individual use, premium plans unlock the ability to use your own domain name (e.g.,
contact@yourbusiness.com). This feature is essential for establishing a professional brand identity.
Ideal Use Cases
Typewire is particularly well-suited for specific types of users:
- Small to Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs): Companies that need a professional, secure email solution without the complexity and overhead of managing their own servers. The ability to scale from a free trial to premium plans with custom domains provides a clear growth path.
- Privacy-Conscious Professionals: Freelancers, consultants, and legal or healthcare professionals who handle confidential information will find the platform's commitment to data sovereignty and encryption indispensable.
- IT Administrators: The centralized management tools and robust security features make it an attractive option for administrators tasked with deploying and managing a secure communication infrastructure for their teams.
Plan Breakdown and Access
Typewire offers a tiered pricing structure that includes a free option, making its high-security features accessible.
| Plan Tier | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Free | Secure, ad-free email with basic features. | Individuals and users testing the platform. |
| Basic | More storage and enhanced support. | Power users and small teams. |
| Premium | Custom domain support, up to 50 aliases per user. | Businesses needing professional branding. |
To get started, you can sign up for a 7-day free trial to experience the premium features firsthand, although a credit card is required for verification. This risk-free trial allows you to fully evaluate the platform’s capabilities before committing.
Learn more at Typewire.com
2. Zoho Mail
Zoho Mail stands out by offering one of the few truly free business email hosting services that includes full-featured, hosted mailboxes on your own custom domain. While many "free" options are simply forwarding services, Zoho provides a comprehensive email solution with an admin console for user management, making it an ideal starting point for small businesses and startups. The "Forever Free Plan" is specifically designed for small teams, supporting up to five users on a single domain.
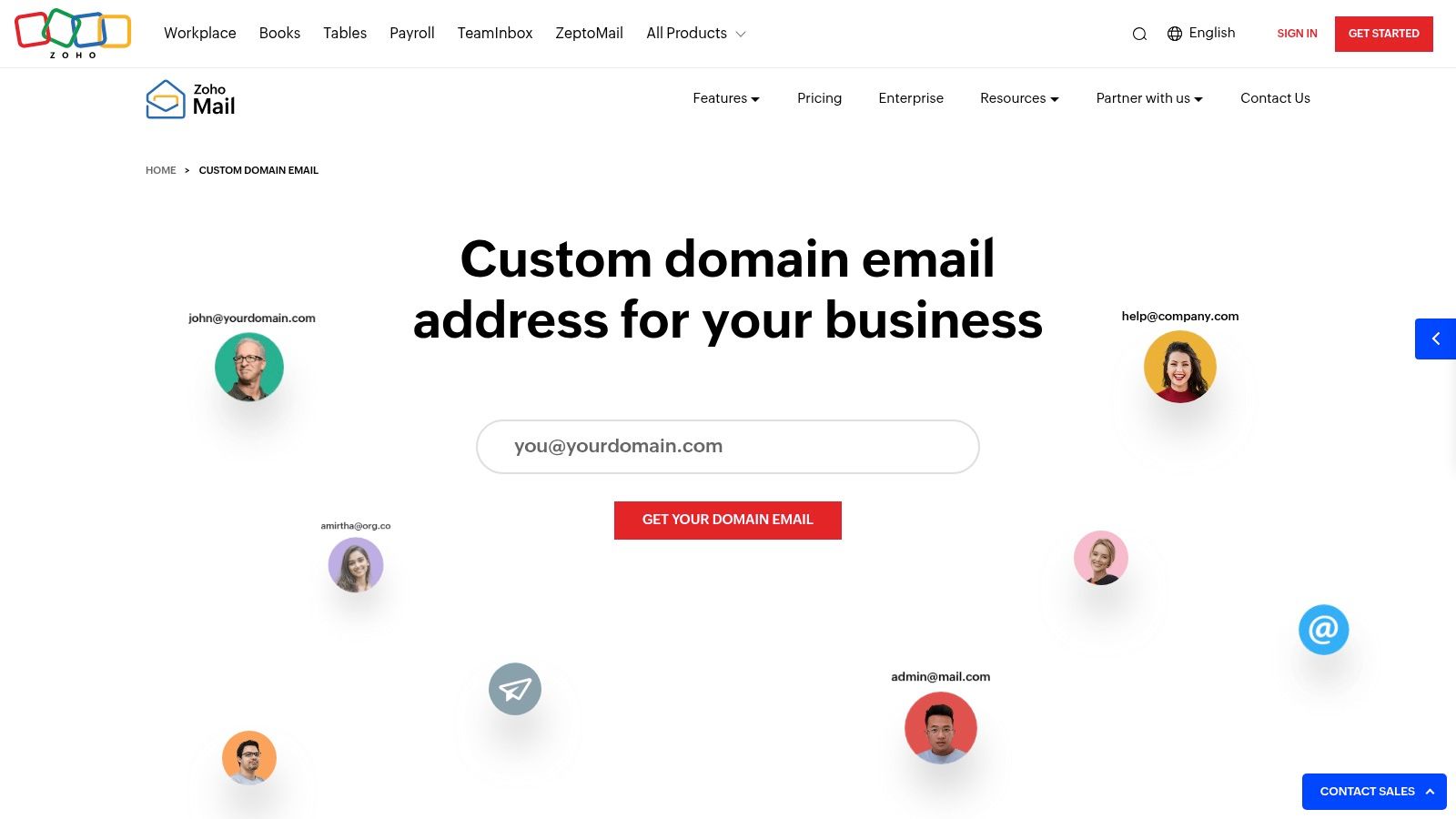
This plan allocates a generous 5 GB of storage per user, which is ample for most new businesses. The administrative panel simplifies the technical setup process, providing clear, step-by-step instructions for verifying your domain and configuring the necessary MX, SPF, and DKIM records to ensure email deliverability and security.
Key Features and User Experience
The user interface for both the admin console and the webmail client is clean and intuitive. Admins can easily add or remove users, create group aliases (like info@yourdomain.com), and set up policies. The webmail-only access on the free tier is a notable limitation, but the web client itself is robust, offering a modern, ad-free experience with features like conversation views, folders, and filters.
Here's a breakdown of what the free plan includes:
- Custom Domain: Host email for one domain (e.g.,
you@yourbusiness.com). - User Accounts: Supports up to 5 user mailboxes.
- Storage: 5 GB of mailbox storage per user.
- Admin Console: A dedicated portal for domain verification and user management.
- Security: Strong spam filtering and essential security protocols.
Expert Tip: While the free plan's availability can vary by region, it remains one of the best options for true free business email hosting. Before committing, verify its availability in your data center region during signup.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Truly Free Mailboxes: Not just a forwarder. | Regional Availability: Free plan not offered everywhere. |
| Generous Limits: 5 users and 5 GB storage each. | Webmail Only: No IMAP/POP access on the free tier. |
| Reputable Provider: Part of the larger Zoho ecosystem. | Limited Integrations: Lacks some advanced features. |
For businesses that anticipate needing more advanced tools, Zoho offers clear upgrade paths. However, as a starting point, it provides unmatched value. If you want to explore how Zoho stacks up against other options, check out this comprehensive comparison of small business email service providers.
Website: https://www.zoho.com/mail/custom-domain-email.html
3. Cloudflare Email Routing
Cloudflare Email Routing is a powerful and entirely free solution for anyone whose domain already uses Cloudflare's DNS. Unlike services that host mailboxes, Cloudflare provides a sophisticated forwarding system. This allows you to create unlimited professional email addresses on your custom domain (e.g., contact@yourbusiness.com or sales@yourbusiness.com) and have all incoming mail routed to an existing personal inbox, like your Gmail or Outlook account.
The primary advantage is its simplicity and integration within the Cloudflare ecosystem. If your domain is managed by Cloudflare, setting up email routing takes just a few clicks to add the necessary MX and TXT records. This approach is perfect for solopreneurs, freelancers, or small projects that need a professional appearance without the overhead of managing separate inboxes.
Key Features and User Experience
The setup process is famously straightforward within the Cloudflare dashboard. Users can quickly create custom addresses and define destination inboxes. The platform provides analytics and logs, giving you visibility into your email traffic. A standout feature is its integration with Cloudflare Workers, which allows for advanced, programmable routing rules for developers who need more control.
Here’s a breakdown of what Cloudflare Email Routing offers:
- Custom Domain: Use any domain managed with Cloudflare DNS.
- Unlimited Addresses: Create as many custom email aliases as you need.
- Forwarding Only: Routes incoming mail to one or more destination inboxes.
- Easy Setup: Automatic DNS record configuration for a quick start.
- Advanced Control: Integrates with Email Workers for custom routing logic.
Expert Tip: While you can receive emails at your custom address, you cannot send replies from it directly. To send emails, you'll need to configure your destination email client (like Gmail) with an SMTP service to "Send Mail As" your custom domain address.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Completely Free: No cost for unlimited aliases. | Forwarding Only: Does not host mailboxes or sent mail. |
| Simple Configuration: Ideal for existing Cloudflare users. | No Outbound SMTP: Requires a separate service for sending. |
| Advanced Programmability: Integrates with Cloudflare Workers. | Requires SPF/DKIM: Stricter rules for forwarding are being enforced. |
For businesses that simply need to manage inbound inquiries professionally, Cloudflare offers an unbeatable free solution. It provides a clean way to get started with free business email hosting by leveraging infrastructure you may already be using.
Website: https://developers.cloudflare.com/email-routing/
4. Forward Email
Forward Email is an open-source, privacy-focused service that redefines what a forwarding solution can be. While it's not a traditional hosted mailbox on its free tier, it offers an incredibly powerful and flexible system for managing unlimited domains and aliases. This makes it an excellent choice for solopreneurs, developers, or small businesses that want to use a familiar interface like Gmail to manage their custom domain email without the cost.
The service works by forwarding incoming mail from your custom domain (e.g., contact@yourbusiness.com) to a personal email address (e.g., you@gmail.com). What sets it apart is its support for unlimited domains, catch-all addresses, and multi-recipient aliases even on the free plan. Setup involves adding a few DNS records to your domain registrar, and the platform provides clear instructions for doing so.
Key Features and User Experience
Forward Email's strength lies in its simplicity and advanced rule-based system. There is no new webmail client to learn; you continue using your existing inbox. The setup is entirely DNS-based, which might feel slightly technical but is well-documented. Once configured, you can set up powerful rules using regular expressions to direct emails based on the sender or recipient.
Here's a breakdown of what the free plan includes:
- Custom Domain: Use unlimited custom domains.
- User Accounts: Create unlimited aliases and forwarding rules.
- Storage: Relies on the storage of your destination mailbox (e.g., Gmail's 15 GB).
- Advanced Aliasing: Supports catch-all addresses, regex, and webhooks for developers.
- Security: Open-source and privacy-first, with no logs or tracking.
Expert Tip: To send emails from your custom domain alias, use Gmail's "Send mail as" feature. This requires an SMTP server, which you can get with Forward Email's affordable paid plans or by using Gmail's own SMTP servers, making it a fully functional free business email hosting solution.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unlimited Domains & Aliases: Extremely generous free tier. | Forwarding Only: No native mailbox or storage on the free plan. |
| Open-Source & Privacy-First: Transparent and secure. | Technical Setup: Requires DNS record configuration. |
| Powerful Routing Rules: Flexible for complex needs. | Sending Requires Paid Plan: Outbound SMTP is a premium feature. |
For those who just need to receive email at a professional address and are comfortable with a DNS-based setup, Forward Email offers unparalleled flexibility. It’s a lean, powerful alternative to a full-fledged hosting service.
Website: https://forwardemail.net/
5. ImprovMX
ImprovMX offers one of the most straightforward and user-friendly solutions for free email forwarding on a custom domain. Unlike services that provide full mailboxes, ImprovMX specializes in creating aliases that redirect all incoming mail from your professional address (e.g., contact@yourbusiness.com) to a personal inbox you already use, like Gmail or Outlook. This approach is perfect for solopreneurs and small projects that need a professional email presence without the complexity of managing a separate inbox.
The setup process is exceptionally fast, requiring only the addition of MX records to your domain's DNS settings. The platform's dashboard provides clear, step-by-step instructions and even includes helpful guides for popular domain registrars. The free tier is generous, allowing unlimited forwarding aliases for a single domain, making it an excellent choice for anyone prioritizing simplicity and speed.
Key Features and User Experience
The ImprovMX dashboard is clean, modern, and highly intuitive. Users can add, edit, and delete forwarding rules with just a few clicks. While the free plan is forwarding-only, paid plans unlock SMTP credentials, which allow you to send emails from your custom domain address directly within clients like Gmail. This hybrid model offers a practical upgrade path for users who eventually need sending capabilities.
Here’s a breakdown of what the free plan includes:
- Custom Domain: Supports unlimited email aliases for one domain.
- Simple Forwarding: Redirects all incoming mail to your designated personal email address.
- Easy Setup: A streamlined process focused on adding MX records.
- User-Friendly Dashboard: A clean interface for managing your forwarding rules.
- Strong Documentation: Excellent help guides and support materials.
Expert Tip: To maintain a professional appearance, configure your personal email client (like Gmail) to send mail through ImprovMX's SMTP servers (a paid feature). This ensures your outgoing emails also come from your custom domain, not your personal address.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Extremely Fast and Simple Setup: Ideal for beginners. | Forwarding Only on Free Tier: Cannot send from your domain. |
| Unlimited Aliases: No limit on forwarding rules. | Sending Requires Paid Plan: SMTP access is a premium feature. |
| Strong Documentation: Excellent help center and guides. | No Mailbox Storage: It's not a hosted email service. |
For those wanting a quick and effective way to establish a professional email front, ImprovMX is a top-tier option. If you want to dive deeper into how this works, you can explore this guide to an email alias service.
Website: https://improvmx.com/
6. Namecheap
Namecheap offers one of the most straightforward and cost-effective solutions for businesses that only need professional-looking email addresses without the overhead of full mailboxes. Included with any domain registered with them or using their free DNS service, Namecheap provides a robust email forwarding service. This allows you to create up to 100 custom email aliases (like contact@yourbusiness.com) that automatically redirect incoming messages to an existing personal inbox, such as a Gmail or Outlook account.
This forwarding-only approach is ideal for solopreneurs, freelancers, or micro-businesses looking to establish a professional presence at no extra cost beyond their domain registration. The setup is managed directly from the Namecheap dashboard and doesn't require complex MX record configuration, making it accessible even for non-technical users. It’s a powerful tool for centralizing communications without paying for hosted email services.
Key Features and User Experience
The primary benefit of Namecheap's offering is its simplicity and integration within its domain management panel. Setting up forwarding rules is a matter of a few clicks. The control panel is intuitive, allowing you to quickly add, edit, or delete aliases as needed. The high limit of 100 aliases provides immense flexibility for creating department-specific addresses (sales@, support@) or temporary addresses for projects.
Here's a breakdown of what the free forwarding service includes:
- Custom Domain: Create aliases for any domain using Namecheap's DNS.
- User Accounts: Up to 100 forwarding aliases per domain.
- Catch-All Functionality: Option to set a "catch-all" address to receive any email sent to a non-existent alias at your domain.
- Free DNS Service: The feature works even if you only use their FreeDNS service without registering the domain with them.
- Simple Management: Easy-to-use interface for managing all your forwarding rules.
Expert Tip: To ensure emails you send from your personal account (like Gmail) on behalf of your custom domain alias are delivered reliably, you must correctly configure your personal account's "Send Mail As" settings with the proper SPF and DKIM records for your domain.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| No Extra Fee: Included with domain registration. | Forwarding Only: No hosted mailboxes or storage. |
| High Alias Limit: Create up to 100 aliases. | No Outbound SMTP: Cannot send email directly from the alias. |
| Simple Setup: Easy for beginners to configure. | Deliverability Concerns: Relies on proper sender configuration. |
For businesses that just need to receive emails at a professional address, Namecheap provides a perfect, no-cost solution. It's an excellent first step before committing to a paid plan. If you're starting from scratch, you can get a complete guide on how to set up a custom email domain to walk you through the process.
Website: https://www.namecheap.com/
7. Squarespace Domains
For businesses already invested in the Squarespace ecosystem or those who prioritize a unified management experience, Squarespace Domains offers a compelling email forwarding solution. While not a hosted mailbox service, it provides free email forwarding for up to 100 aliases when you register or transfer a domain to Squarespace. This allows you to create professional addresses like contact@yourdomain.com that automatically redirect messages to your existing personal inbox, such as a Gmail or Outlook account.
This service is ideal for solopreneurs and small businesses who need a professional front without the complexity of managing separate inboxes. The setup is handled directly within the Squarespace dashboard, making it incredibly straightforward for users who are not technically inclined. DNS and forwarding rules are managed in the same place as your website, creating a seamless workflow.
Key Features and User Experience
The primary benefit of using Squarespace for email forwarding is its simplicity and integration. The domain management panel is clean, intuitive, and comes with excellent documentation to guide you through the process. Instead of navigating complex cPanel settings, you can configure forwarding addresses with just a few clicks.
Here's what you get with a Squarespace domain:
- Custom Domain Forwarding: Create up to 100 email aliases for your domain (e.g.,
info@,support@,sales@). - Unified Dashboard: Manage your website, domain, and email forwarding all in one place.
- Bundled Security: Includes free WHOIS privacy and an SSL certificate for your connected website.
- Premium DNS: Reliable and secure DNS services are included with the domain registration fee.
Expert Tip: To maintain a professional appearance, set up your personal email client (like Gmail) to "Send mail as" your custom domain address. This allows you to reply to forwarded emails using your
you@yourbusiness.comaddress, completing the professional loop.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| No Extra Cost: Included with domain fee. | Forwarding Only: No hosted mailboxes or sent items folder. |
| Simple, Unified Management: Ideal for Squarespace users. | Propagation Delays: DNS changes can take time to activate. |
| Generous Alias Limit: Up to 100 forwards per domain. | Requires Upgrade: Full email requires a paid Google Workspace plan. |
While Squarespace provides an excellent and streamlined forwarding service, it’s important to remember its limitations. This solution is a great starting point for establishing a professional presence, but businesses that need dedicated inboxes and advanced email features will eventually need to upgrade to a paid hosting plan.
Website: https://domains.squarespace.com/
Free Business Email Hosting Comparison of Top 7 Providers
| Service | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typewire | Moderate: requires subscription setup and migration tools | Moderate: Premium plans needed for custom domain hosting | High: Secure, privacy-first email with full hosting and encryption | Privacy-conscious individuals and SMBs needing full control and security | Strong privacy, Canadian data centers, end-to-end encryption, easy migration |
| Zoho Mail | Low to Moderate: simple setup with domain verification | Low: free tier supports up to 5 users | Moderate: Basic hosted mailboxes with admin controls | Very small teams needing free business email with custom domains | Free hosted mailbox, straightforward setup, reputable provider |
| Cloudflare Email Routing | Low: simple DNS MX/TXT configuration | Low: requires Cloudflare DNS | Basic: free unlimited forwarding only | Users wanting free professional email forwarding without hosting | Free unlimited forwarding, Cloudflare ecosystem integration |
| Forward Email | Low to Moderate: forwarding setup, alias rules configuration | Low: free forwarding, paid sending/storage | Moderate: Flexible email forwarding, SMTP with paid plans | Developers and privacy-focused users preferring open-source and aliasing | Open-source, flexible aliasing, Gmail integration |
| ImprovMX | Low: quick setup with clear guides | Low: free forwarding, SMTP on premium | Basic to Moderate: forwarding with SMTP sending option | Users needing fast forwarding setup with optional SMTP sending | User-friendly, fast configuration, SMTP option on paid plans |
| Namecheap | Low: straightforward DNS and control panel setup | Low: bundled with domain registration | Basic: free email forwarding only | Small businesses wanting cost-effective email forwarding with many aliases | Free forwarding, high alias limit, no extra fees |
| Squarespace Domains | Low: included with domain registration | Low: bundled with domain purchase | Basic: forwarding with domain management dashboard | Squarespace users needing simple email forwarding with domain | No extra cost, integrated with Squarespace, easy domain/email management |
Choosing the Right Free Email Host for Your Business Growth
Navigating the landscape of free business email hosting reveals a clear trade-off: you can opt for a complete, albeit limited, mailbox solution or embrace the powerful flexibility of email forwarding. Your ideal path depends entirely on your current operational needs, technical comfort level, and long-term vision for your brand's communication strategy.
Deciphering Your Immediate Needs
For businesses that require a dedicated inbox from the start, a provider like Zoho Mail offers an impressive suite of tools, essentially a microcosm of a premium email suite. It's a fantastic, self-contained option for solopreneurs or micro-businesses needing a functional mailbox without an initial investment. However, its regional availability can be a significant hurdle.
For the majority of new businesses, email forwarding presents a more universally accessible and streamlined solution. Tools like Cloudflare Email Routing, Forward Email, and ImprovMX excel at this, allowing you to project a professional image with a custom domain (you@yourcompany.com) while centralizing all communications in a personal inbox you already use, like Gmail or Outlook. This approach is efficient, cost-effective, and surprisingly robust for handling initial business inquiries.
Planning for Future Growth and Security
The term "free" is often a starting point, not a final destination. As your business scales, so will your requirements for security, storage, and advanced collaboration features. The initial convenience of a free plan can become a bottleneck if it doesn't offer a clear and secure upgrade path. This is where a forward-thinking strategy becomes critical.
Consider these key factors as you make your decision:
- Scalability: Does the provider offer a seamless transition to a paid plan? A service that grows with you, like Typewire, prevents the future headache of a complex migration.
- Privacy and Security: Free services often come with compromises. Prioritize providers that are transparent about their data policies and offer advanced security features, even in their introductory tiers. Your business communications are sensitive assets that deserve protection.
- Feature Set: While forwarding is great, will you eventually need shared mailboxes, calendars, or enhanced spam filtering? When evaluating different providers, consider their comprehensive approach to supporting small business email solutions to ensure long-term growth.
Ultimately, the best free business email hosting solution is one that solves today's problems without creating tomorrow's obstacles. By starting with a provider that aligns with your privacy values and offers a scalable infrastructure, you build your professional communications on a foundation of security and foresight. You get the immediate benefit of a professional email address while ensuring your setup can evolve as your business succeeds.
Ready to establish your professional presence with an emphasis on privacy and security? Typewire offers a robust, privacy-first email hosting platform. Start with our free trial to experience a secure, ad-free environment and see how easily you can scale your business communications.