Think of your standard email account. Sending a message with a typical free provider is like sending a postcard—the content is visible to anyone who handles it. Secure email services turn that postcard into a sealed, tamper-proof letter. These hosted email platforms use powerful tools like end-to-end encryption to shield your conversations from prying eyes, data miners, and surveillance.
The goal of a secure email service is to ensure only you and your intended recipient can read what’s inside, guaranteeing true email privacy.
What Makes a Hosted Email Platform Truly Secure?

When discussing a "truly secure" email service, we're looking beyond a strong password. It’s a fundamental shift in how the hosted platform itself is designed. This higher level of email security is built on a foundation of specific technologies and a privacy-first business philosophy.
The goal isn't just to add a lock to the door; it's to build a digital fortress around your communications, protecting them from the most common online threats and ensuring your email privacy is respected by the provider.
The Core Pillars of Email Privacy
At their heart, all genuinely secure email platforms are built on three non-negotiable principles. These are what separate them from the free, ad-supported services we’re all used to. Understanding these pillars is the first step toward reclaiming your digital privacy.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): This is the gold standard of email security. It means your message is scrambled into unreadable code on your device and can only be unscrambled on your recipient's device. No one in between—not even your email provider—can read it.
- Zero-Access Architecture: This goes hand-in-hand with E2EE. It's a design philosophy where the service provider builds their system so they physically cannot access or decrypt your emails stored on their servers. The encryption key belongs to you, and only you.
- Ad-Free, No-Tracking Business Model: Secure email providers charge a subscription fee, and that's a good thing. Their business model is simple: you pay for a private, hosted email platform. This ensures they work for you, not for advertisers who want to mine your data.
True email security isn't just about preventing hackers from accessing your account. It's about ensuring the hosted email platform itself is architected to respect and enforce your privacy by default, removing the provider from the circle of trust.
This move toward privacy isn't just a niche concern. As more people and businesses recognize the risks of unprotected digital conversations, the demand for email encryption is skyrocketing. The global market for email encryption is expected to jump from USD 9.30 billion in 2025 to USD 23.33 billion by 2030, a surge fuelled by rising cyber threats and tougher data privacy laws.
You can dive deeper into these global email security trends and their drivers to see the full picture. This powerful momentum confirms that secure email is no longer a luxury—it’s essential infrastructure for anyone serious about email security.
The Building Blocks of Email Privacy and Security
To understand what makes a secure email service effective, you have to look at the technologies that power it. Your standard email account is like sending a postcard. Anyone handling it—from your provider to the recipient's—can read the message.
Hosted email platforms like Gmail or Outlook are a step up, more like a letter in a sealed envelope. It’s private from casual observers, but the post office (the email provider) still has the ability to open it.
A truly private email service provides something far more robust. It's like writing a letter in a secret code, placing it in a tamper-proof vault, and having it delivered by a courier who has no idea what's inside. This level of email security is the result of specific design choices that put your privacy first.
Encryption: The Cornerstone of Secure Email
At its heart, email security comes down to encryption—the process of scrambling your message into gibberish that can only be unscrambled with a special key. Not all encryption is the same. The vast majority of hosted email platforms use something called Transport Layer Security (TLS).
TLS is a solid starting point. It protects your email as it travels from your computer to your provider's server, and then between different providers. The catch? Once the message arrives at its destination server, the provider can read it. Your emails are essentially sitting in their vault, fully accessible to them.
This is where the most critical feature of a secure email service comes into play: end-to-end encryption (E2EE).
End-to-end encryption means your message is locked on your device and can only be unlocked by the person you sent it to. The email provider can't read it because they never have the key. It's the gold standard for email privacy and secure communication.
With E2EE, your message is sealed before it even leaves your computer, and only your recipient holds the key. If you're curious about the technical details, this resource on What Is Encrypted Email is a great place to start. This single feature is what separates a truly private platform from the rest.
To help you see the difference at a glance, here’s a quick breakdown of how these encryption methods stack up.
Comparing Email Encryption Methods
| Encryption Type | What It Protects | Who Can Access Your Email | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport Layer (TLS) | The email in transit between servers. | Your email provider and the recipient's provider. | Standard on most major email services (Gmail, Outlook). |
| End-to-End (E2EE) | The email content from sender to recipient. | Only the sender and the intended recipient. | Secure email providers focused on maximum user privacy. |
| At-Rest Encryption | Stored emails on a provider's server. | The email provider (they hold the keys). | Most cloud services, to protect against server breaches. |
As the table shows, E2EE provides a level of email security that other methods can't match, ensuring your message content remains completely confidential.
Going Beyond the Message with Zero-Access Architecture
While E2EE locks down your email content, what about the provider's own access? A zero-access architecture is a system designed from the ground up to make it impossible for the service provider to access your stored messages. Your data is encrypted on their servers, but the encryption key belongs to you and you alone.
This means that even if a government served them a warrant for your inbox, the provider physically couldn't hand over your data because they don't have the means to decrypt it. They've intentionally built a system where they are blind to user content, a powerful statement that puts control back in your hands. For a deeper look at how this works, check out our complete guide to end-to-end email encryption.
Why Metadata Privacy Is Just as Important
Securing the message is one thing, but what about the information on the "envelope"? This metadata includes details like:
- Who sent the email (From:)
- Who received it (To:)
- The subject line
- Timestamps for when it was sent and received
- IP addresses of the sender and the servers involved
Even without reading your emails, this data paints an incredibly detailed picture of your communications. Many free hosted email platforms collect and analyze this metadata.
First-class secure email services go the extra mile to protect it, often by stripping identifying details like your IP address from email headers. Protecting metadata is the final piece of the email privacy puzzle, ensuring not only the letter’s content is secret, but the details of its journey are shielded as well.
How to Choose the Right Secure Email Platform
Picking the right secure email service can feel overwhelming, but it boils down to asking a few key questions. By focusing on what truly keeps your communications private, you can find a hosted email platform that genuinely protects your interests.
It’s not about finding the service with the longest feature list; it’s about finding one built on the right principles of email security and privacy.
This hierarchy shows the different tiers of protection available, from basic security measures up to the gold standard: zero-access encryption.
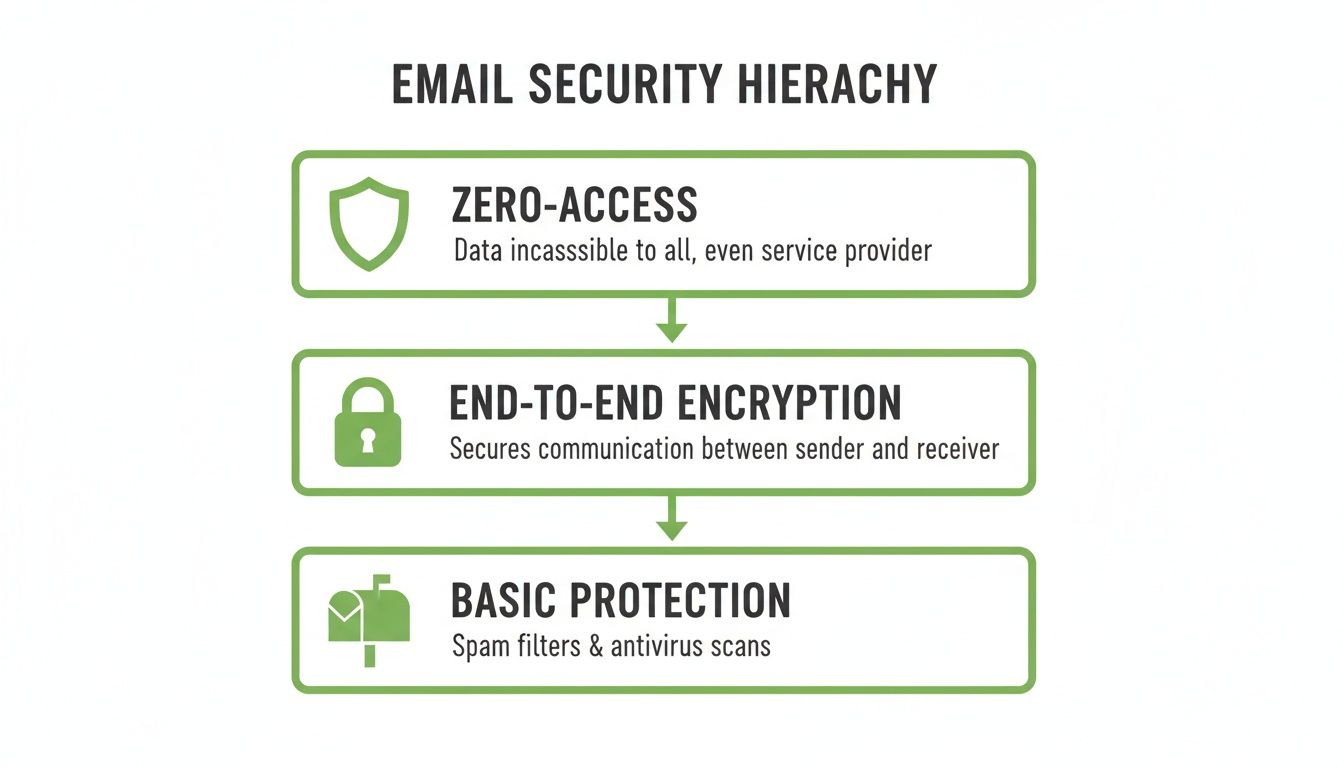
As you can see, each level offers more protection. Zero-access architecture sits at the very top because it represents the ultimate commitment to privacy—it makes your data impossible for even the service provider to read.
Where Is Your Data Physically Stored?
One of the first questions you should ask is simple: where will my emails actually live? The physical location of the servers storing your data dictates which country's laws apply to your email privacy. This has a massive impact on who can legally access your information.
For instance, a service with servers in a country part of a broad surveillance alliance could be forced to hand over your data. On the flip side, providers located in countries with strong privacy laws give you a powerful legal shield.
This is why data residency is a cornerstone of email security. Choosing a hosted email platform based in a privacy-friendly jurisdiction like Canada means your communications are protected by robust federal laws designed to defend personal information.
What Is the Provider’s Business Model?
Figuring out how an email provider makes money is the fastest way to understand their priorities. If the service is free, you can be certain that you are the product. These platforms typically rely on data mining, scanning your emails and metadata to build profiles for advertisers.
A genuinely secure email service will always have a straightforward business model: you pay them for a service.
When you pay for an email service, you are the customer, not the product. This simple exchange aligns the provider’s interests with yours, ensuring their primary goal is to protect your email privacy, not to monetize your data for advertisers.
This commitment to a user-funded model is a clear sign of a platform's dedication to your privacy. An ad-free, no-tracking policy should be a deal-breaker, as it's the only way to guarantee the provider has no financial incentive to scan your inbox.
Essential Features for Secure Communications
Beyond the foundational pillars of jurisdiction and business model, a few key features separate the best secure email services. These capabilities are crucial for making email security practical for both individuals and businesses.
- Custom Domain Support: For any professional, using your own domain (like
you@yourbusiness.ca) is non-negotiable. A good secure provider should make it simple to set this up without sacrificing any security features. - Centralized User Management: Businesses need an easy way to handle employee accounts. Look for a platform with a central admin dashboard to add or remove users, set permissions, and manage billing.
- Privacy by Default: Top-tier services don’t make you dig through settings to turn on security. Features like blocking spy pixels—invisible tracking images in marketing emails—should be enabled out of the box, protecting you automatically.
This growing demand for robust security is reflected in market trends. Canada's email encryption market is poised for significant growth, projected to expand from USD 3.41 billion in 2025 to USD 7.86 billion by 2031. This trend highlights that Canadian businesses see secure email as a fundamental operational need. You can learn more about the drivers behind Canada's email encryption growth.
By carefully evaluating these core areas, you can confidently choose a secure email platform that truly safeguards your digital life.
Why Canadian Data Residency Is a Privacy Game Changer

When you're looking at secure email services, it's easy to get lost in features like encryption. But one of the most fundamental questions is often missed: where on earth does your data actually live? The physical location of a hosted email platform's servers determines which country's laws have the final say over your private communications. It’s the legal bedrock of your email privacy.
Storing your data in a country with flimsy privacy rules or one that’s part of a broad international surveillance network can render even the best encryption pointless. Your information could be legally compelled and handed over to authorities, creating a backdoor that sidesteps all your security efforts.
This is exactly why data residency—the physical and legal home of your data—is such a game changer. Choosing a service hosted in a country with strong privacy laws gives you a powerful legal shield.
The Canadian Advantage in Data Sovereignty
Canada has carved out a reputation as a safe harbour for data, offering a protective legal climate. A huge part of this is thanks to our federal privacy law, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA).
PIPEDA isn't just a list of polite suggestions. It lays down clear, enforceable rules for how private companies must handle personal information, giving individuals real rights over their data.
Data sovereignty is the idea that your information is subject to the laws of the nation where it's stored. For your email, picking a Canadian provider puts your data squarely under the protection of Canadian law, keeping it out of the reach of foreign legal systems and their surveillance programs.
So, when you choose an email provider hosted in Canada, you're making a deliberate choice to put your data under this protective legal umbrella. It ensures your private conversations are governed by some of the world's most robust privacy regulations. If you want to dive deeper, our guide on Canadian data privacy laws explained breaks it all down.
Escaping the Reach of Big Tech and Foreign Laws
Many hosted email platforms, even secure ones, cut corners by using massive, third-party cloud infrastructure from giants like Amazon, Google, or Microsoft. This often means your data gets shipped to data centres in jurisdictions with weaker privacy laws, like the United States.
This can leave your information vulnerable to laws that give government agencies sweeping powers to access data on U.S. servers. A truly Canadian provider avoids this trap by owning and operating its own infrastructure, exclusively on Canadian soil.
This approach gives you two clear wins:
- Legal Insulation: Your data stays firmly under Canadian jurisdiction, protected by PIPEDA and shielded from foreign legal demands.
- Infrastructure Control: Owning the hardware means no dependency on Big Tech clouds, which closes another potential door for data access or vulnerabilities.
The growing demand for these safeguards is clear in the market. North America's email encryption market is booming, making up 34.24% of the global revenue share in 2025. Within this market, Canada is a standout because our strict regulations have turned secure email from a "nice-to-have" into a business necessity.
At the end of the day, picking a Canadian-hosted secure email service isn't just about geography. It’s a strategic move to lock down your digital sovereignty and ensure your private conversations stay private.
Making the Switch to a Secure Email Service

Deciding to take your email privacy seriously is a fantastic first step. But the idea of moving years of emails, contacts, and calendar events can feel overwhelming.
The good news? Most modern secure email services have made this process surprisingly painless. Whether you’re moving your personal account or migrating an entire small business to a new hosted email platform, there’s a clear path forward.
Having a simple, step-by-step plan makes all the difference. It ensures nothing critical gets lost, from that one important archived message to your entire address book.
Planning Your Migration Strategy
Before you begin, think about the move in a few distinct phases. This breaks down a big project into a series of small, manageable tasks.
First, take a quick inventory. What actually needs to come with you? For most people, it's a combination of emails, contacts, and calendars. If you're a business, you'll also need to migrate your custom domain. A well-planned move takes far less time than you imagined.
The entire point is to get you up and running in your new, private inbox without missing a beat.
Transferring Your Existing Data
Once you’ve picked your new provider, it's time to move your data. The best secure email services have built-in migration tools that do the heavy lifting for you. They connect to your old account—like Gmail or Outlook—and pull everything over automatically.
This usually covers all the essentials:
- Importing Emails: The tool will copy your folders and every message inside them, preserving your existing organization.
- Migrating Contacts: Your entire address book is transferred, saving you from hours of manual data entry.
- Syncing Calendars: Any appointments or events you have scheduled can be imported, keeping your schedule intact.
The real beauty of these tools is that they work quietly in the background. You can start exploring your new secure inbox right away while your old data is safely copied over. Crucially, this process is non-destructive—your original data is left completely untouched in your old account.
This automated approach takes the hassle out of the process. For a much more detailed breakdown, our complete guide to switching email providers walks you through every single step.
Migrating a Custom Domain for Your Business
For any business, the custom domain is the most important piece of the puzzle. The goal here is a zero-downtime migration. Your team needs to keep sending and receiving emails without any interruption.
This is done by updating your domain's DNS settings—specifically, the MX records—to point to your new secure email provider. Any reputable provider will give you clear, easy-to-follow instructions and have support on standby to help.
Once you flip the switch, all new emails start flowing directly to your new secure platform. From there, you can use the migration tool to import all historical emails, ensuring a complete archive and seamless business continuity.
After the technical side is sorted, let your key clients and partners know you’ve moved. A quick heads-up helps ensure your emails don't get accidentally flagged. The last step is setting up your new account on all your devices so you can enjoy better email security wherever you are.
How Typewire Puts Secure Email into Practice
It's one thing to talk about the theory of secure email, but another to see how it works in the real world. This is where a provider’s philosophy truly shows. Is email security just a feature, or is it the bedrock the entire service is built on?
At Typewire, we believe email privacy isn't an option—it's the whole point. That commitment starts with a fundamental decision: how and where your data is stored. Instead of renting space from a Big Tech cloud provider, we built our own infrastructure from the ground up. This gives us total control over the entire system, from the physical servers to the software that runs on them.
Keeping Your Data in Canada, on Our Own Hardware
We’ve already touched on why the physical location of your data matters so much. For us, the choice was clear. All Typewire data lives exclusively on our privately owned and operated servers right here in Vancouver, Canada. This isn't just a geographical preference; it's a legal one. Your communications are shielded by one of the world's most robust privacy laws: the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA).
Choosing to keep everything on Canadian soil provides a powerful legal buffer. It means your data is subject to Canadian law, keeping it safely out of the grasp of far-reaching foreign surveillance programs that can impact providers who rely on U.S.-based cloud infrastructure.
When your email is hosted on privately owned Canadian hardware, you get something called data sovereignty. This means your emails are protected by predictable Canadian laws, not the shifting policies of massive cloud corporations or foreign governments.
Because we control the physical hardware, we can guarantee your data never crosses the border. That's a level of certainty that hosted email platforms built on globally distributed, third-party clouds just can't offer.
Privacy Isn't an Opt-In, It's the Default
You shouldn’t have to dig through settings menus to protect yourself. Real email security should be baked into the experience from the moment you sign up. Think about all the marketing emails you get. Many contain invisible spy pixels—tiny trackers that report back to the sender when, where, and even how many times you've opened their message.
Typewire automatically blocks these trackers for you. No toggles to flip, no settings to find. This is a perfect example of what "privacy by default" looks like. We're proactively shielding you from this quiet surveillance because we believe your inbox should work for you, not for data miners.
This practical mindset also extends to the professional features businesses need to operate securely.
- Use Your Own Domain: Set up your email with your own domain (like
you@yourbusiness.ca) to build your brand, and all of Typewire’s security features are automatically applied. - Straightforward Team Management: From a single, clean dashboard, you can easily add and remove users, adjust permissions, and manage billing for your entire organisation.
This is how secure email goes from an abstract idea to a tangible tool. It’s the sum of deliberate choices—from owning our Canadian servers to blocking trackers by default—that creates an inbox where you can be confident your conversations are kept private.
Common Questions About Secure Email
Switching to a secure email service is a big step, and it’s normal to have questions about how it all works. Let's clear up some of the most common concerns about email privacy and security.
Many people worry that "secure" means "complicated." The reality is different. Modern secure email platforms are built to feel just as familiar as the big-name services you're used to. All the heavy lifting for email security happens behind the scenes, so you can focus on your messages.
What about emailing friends or colleagues on Gmail or Outlook? No problem. You can send and receive emails from anyone. The key difference is that when you email someone on a non-secure service, the message won't be end-to-end encrypted once it leaves your provider. But your own inbox, drafts, and sent messages are always protected on your secure server.
Do I Really Need End-to-End Encryption?
This question comes up a lot. Is end-to-end encryption overkill if you aren't sending classified secrets? Think of it this way: privacy shouldn't be a switch you flip only when you think something is important. It should be the default for everything you do online.
Choosing a secure email provider is about making privacy your baseline. It means your conversations—both personal and professional—are automatically shielded from data mining, surveillance, and ad-driven business models, not just when you remember to be careful.
Technology is only half the battle. Your own habits play a massive role in keeping your account safe. Knowing how to spot phishing attempts and using strong, unique passwords are vital skills. When you make privacy the default by choosing a secure hosted email platform, you start building smarter security habits that protect you from all sorts of online threats.
Ready to put real privacy at the core of your communications? Typewire offers a truly private email experience, hosted on our own infrastructure in Canada and protected by strong privacy laws. Start your free trial and take back your inbox today. Learn more at Typewire.