Email is the digital backbone of our personal and professional lives, yet we often settle for services that treat our data as a commodity. The default options from big tech companies frequently come with a hidden cost: invasive ad tracking, data mining, and security vulnerabilities. Choosing from the best webmail clients is no longer just about storage space or a slick interface; it’s a critical decision for protecting your privacy and securing your communications. This guide is designed to help you navigate the complex world of hosted email platforms, moving beyond the familiar names to uncover services that put your security first.
We’ve compiled a comprehensive resource list that cuts through the marketing fluff to deliver an honest assessment of each provider. You will find a detailed breakdown of top-tier services focused on privacy, security, and user control. We analyze key features like end-to-end encryption, data sovereignty, and robust anti-phishing measures. To truly safeguard your email communications, it's essential to understand strategies to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks that can compromise your data, a concept central to many of the secure providers we'll cover.
This article provides everything you need to make an informed choice. Each entry includes:
- A concise overview of what makes the service unique.
- In-depth analysis of its security and privacy features.
- Clear pros and cons based on real-world usage.
- Practical use cases for individuals, teams, and businesses.
- Transparent pricing details.
Our goal is to equip you with the information necessary to select a webmail client that aligns with your specific needs, whether you're a privacy-conscious individual, a small business owner, or an IT professional. Let's find the right hosted email platform to protect your digital correspondence.
1. Typewire
Best for Privacy-First Business & Personal Email
Typewire establishes itself as a premier choice among the best webmail clients by championing an uncompromising privacy-first architecture. It’s an ideal solution for individuals and businesses seeking to reclaim control over their digital communications, free from the pervasive data mining, tracking, and advertising that define many mainstream services. By owning its entire infrastructure, Typewire ensures all user data is hosted exclusively on private servers in Vancouver, Canada, and protected under strong Canadian privacy laws (PIPEDA).
The platform’s commitment to email security is evident in its robust feature set. Every message benefits from end-to-end encryption, and the client automatically blocks tracking pixels by default, preventing senders from monitoring your activity. This core focus on user protection makes it an exceptional hosted email platform for IT administrators, SMBs, and remote teams who handle sensitive information. You can learn more about Typewire’s dedicated privacy features on their site.
Key Features & User Experience
Typewire’s web interface is clean, fast, and responsive, with both light and dark modes available to suit user preferences. For teams, the service simplifies administration with unlimited users per account, easy migration tools, and support for up to five custom domains on its premium plan. Each user can also create up to 50 aliases, adding a layer of flexibility for managing different communication channels.
- Pros:
- Privacy-Centric Design: No ads, data mining, or tracking pixels.
- Canadian Data Sovereignty: All data is stored on privately owned Canadian infrastructure.
- Comprehensive Security: End-to-end encryption plus advanced anti-spam and phishing defenses.
- Business-Ready Tools: Straightforward user management and custom domain support.
- Cons:
- Paywalled Features: Custom domains and high alias counts require a premium subscription.
- Limited Geographic Redundancy: Hosting is exclusively in Canada, which may not suit all global data residency needs.
- Trial Requires Card: A credit card is needed for verification to start the 7-day free trial.
Website: https://typewire.com
2. Gmail (Google)
As arguably the most dominant force in consumer email, Gmail’s place as one of the best webmail clients is secured by its sheer ubiquity and powerful features. However, its business model for the free tier is a significant trade-off for privacy. The service relies on data collection from your inbox to personalize advertising across Google's ecosystem. While conversations are encrypted in transit (TLS), this does not prevent Google from scanning email content for various purposes, a critical distinction from zero-knowledge providers.
For users concerned about this level of data access, it is possible to add stronger protections. This guide to enabling end-to-end encryption in Gmail shows how to layer on security, though it isn't a native, default feature. On the security front, Gmail offers robust spam filtering and phishing detection, but the platform's core architecture is not built for user privacy. It excels as a powerful, feature-rich service, but not as a secure, hosted email platform for sensitive communications.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 15 GB of storage (shared across Google services) with ads and data scanning.
- Paid Plans: Google One (starting at $1.99/month) or Google Workspace (starting at $6/user/month) for more storage, no ads, and business features like custom domains.
- Best For: Individuals and businesses deeply embedded in the Google ecosystem who prioritize features over email privacy.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Exceptional search and organization tools, reliable infrastructure and high deliverability rates, and strong spam filtering.
- Cons: Not a privacy-first service; scans email content for ad personalization, and lacks default end-to-end encryption.
Website: https://mail.google.com/
3. Outlook.com (Microsoft)
As Microsoft's flagship webmail service, Outlook.com has evolved into a modern platform with a strong security footing, especially for users within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. Its spam and phishing protection are built on Microsoft's enterprise-grade infrastructure, offering a reliable defense against common threats. However, like Gmail, the free version of Outlook.com operates on a business model that includes targeted advertising, which means your data is used for commercial purposes.
The true security and privacy benefits of Outlook are unlocked with a paid Microsoft 365 subscription. This removes ads, provides message encryption options, and includes advanced threat protection that scans attachments and links for malware. For a detailed walkthrough of its security options, you can consult this guide to securing your Outlook emails. While it’s a more secure hosted email platform than many free alternatives, its privacy posture is not as strict as zero-knowledge services like Proton Mail or Tuta, as Microsoft can still access user data under certain conditions.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 15 GB of mailbox storage and 5 GB of OneDrive cloud storage with ads.
- Paid Plans: Microsoft 365 (starting at $1.99/month for Basic) provides 50 GB of ad-free email and enhanced security features.
- Best For: Individuals and businesses invested in the Microsoft ecosystem who need strong, enterprise-level security features and are comfortable with a corporate privacy policy.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Strong spam and phishing defenses, advanced security features in paid tiers, and excellent integration with Microsoft 365 apps.
- Cons: The free tier includes advertisements and is not privacy-focused; the strongest security tools are paywalled.
Website: https://outlook.live.com/
4. Yahoo Mail
As one of the original major players in the webmail space, Yahoo Mail has modernized its interface but remains a choice for users where advanced privacy and security are not top priorities. Its history of significant data breaches makes it a difficult recommendation for anyone handling sensitive information. While the service offers basic security features like spam filtering and virus protection, it lacks the advanced privacy tools that define the best secure webmail clients, such as end-to-end encryption or tracking pixel blocking.
The platform's business model is ad-supported, and its privacy policy allows for the scanning of emails to personalize those ads and other content. This practice is in direct contrast to privacy-first hosted email platforms. Yahoo Mail’s key differentiators are its generous free storage and organizational tools, like the "Subscriptions" view for managing newsletters. These features make it a practical choice for a secondary, non-critical email account, but it is not suitable for users seeking genuine email privacy or robust security.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 20 GB of storage with ads and email scanning.
- Paid Plans: Yahoo Mail Plus (starting at $5/month) offers an ad-free experience, 500 disposable email addresses, and premium support.
- Best For: Casual users who need a free, high-storage account for non-sensitive communications and managing subscriptions.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Excellent tools for managing subscriptions, user-friendly mobile apps, and a low-cost plan to remove ads.
- Cons: A history of major security breaches, scans emails for advertising, and lacks advanced privacy features like end-to-end encryption.
Website: https://mail.yahoo.com/
5. Proton Mail
For users who prioritize privacy and security above all else, Proton Mail has established itself as a leading choice among the best webmail clients. Built by former CERN scientists, the service is based in Switzerland, a country renowned for its strong privacy laws. Its core feature is automatic end-to-end encryption for all messages exchanged between Proton users, meaning not even the company can read your emails. This privacy-first approach is extended through its open-source applications and a strict no-logs policy, making it a fortress for sensitive communications.
Unlike mainstream providers that rely on advertising, Proton Mail is funded by its users, ensuring its business model aligns with user privacy. The platform offers advanced features like self-destructing messages and password-protected emails for communicating securely with non-Proton users. As a hosted email platform, all data is stored on secure, company-owned servers in Switzerland. While its free plan is limited, it serves as an excellent entry point into a more secure and private email experience.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 1 GB total storage, 150 messages per day limit, and 1 email address.
- Paid Plans: Mail Plus (starting at €3.99/month) or Proton Unlimited (starting at €9.99/month) for more storage, custom domains, unlimited messages, and access to the full Proton ecosystem (VPN, Calendar, Drive).
- Best For: Privacy-conscious individuals, journalists, activists, and businesses that handle sensitive data and require legally protected communications.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: True end-to-end encryption by default, Swiss jurisdiction provides strong legal privacy protections, and a transparent, open-source security posture.
- Cons: The free plan is quite restrictive, advanced features are paywalled, and encrypted workflows can have a learning curve when interacting with non-Proton recipients.
Website: https://proton.me/mail
6. Zoho Mail
Zoho Mail carves out its niche as a powerful, ad-free webmail client that prioritizes business functionality and user privacy over data monetization. Positioned as a direct competitor to Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, it provides a comprehensive suite of applications while maintaining a firm no-ads policy, ensuring that your email content is never scanned for advertising purposes. For small businesses and individuals wanting to use a custom domain, Zoho Mail is an exceptionally compelling hosted email platform, offering a generous free-forever plan that includes support for one domain.
The platform is built for professional use, with robust administrative controls and easy migration tools. Email security is a key focus, with features like S/MIME message encryption, two-factor authentication, and data retention policies available to protect sensitive business communications. Its data centers are geographically distributed, offering redundancy and compliance with various regional regulations. This commitment to security without ad-based revenue makes it one of the best webmail clients for organizations looking for a unified, private productivity suite.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: Ad-free email for up to 5 users, 5 GB/user storage, and single custom domain support.
- Paid Plans: Mail Lite starts at $1/user/month for more features. Workplace plans (starting at $3/user/month) bundle the full suite of Zoho apps.
- Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses needing affordable custom-domain email hosting, and privacy-conscious users seeking an ad-free experience.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Very competitive pricing for business email, strong admin and security controls, and a strict no-ads privacy policy.
- Cons: The most advanced security and compliance tools (like e-discovery) are locked behind higher-tier plans, and the user interface can feel less modern than some competitors.
Website: https://www.zoho.com/mail/pricing.html
7. Fastmail
For users prioritizing speed, privacy, and an ad-free experience, Fastmail stands out as a premium, independent choice. Unlike free services that monetize user data, Fastmail is a paid hosted email platform focused entirely on providing a fast, reliable, and secure email service. It is independently owned and operates its own servers, ensuring that your data isn't being handled by a third-party cloud provider. Fastmail never scans your content for advertising or tracks your behavior.
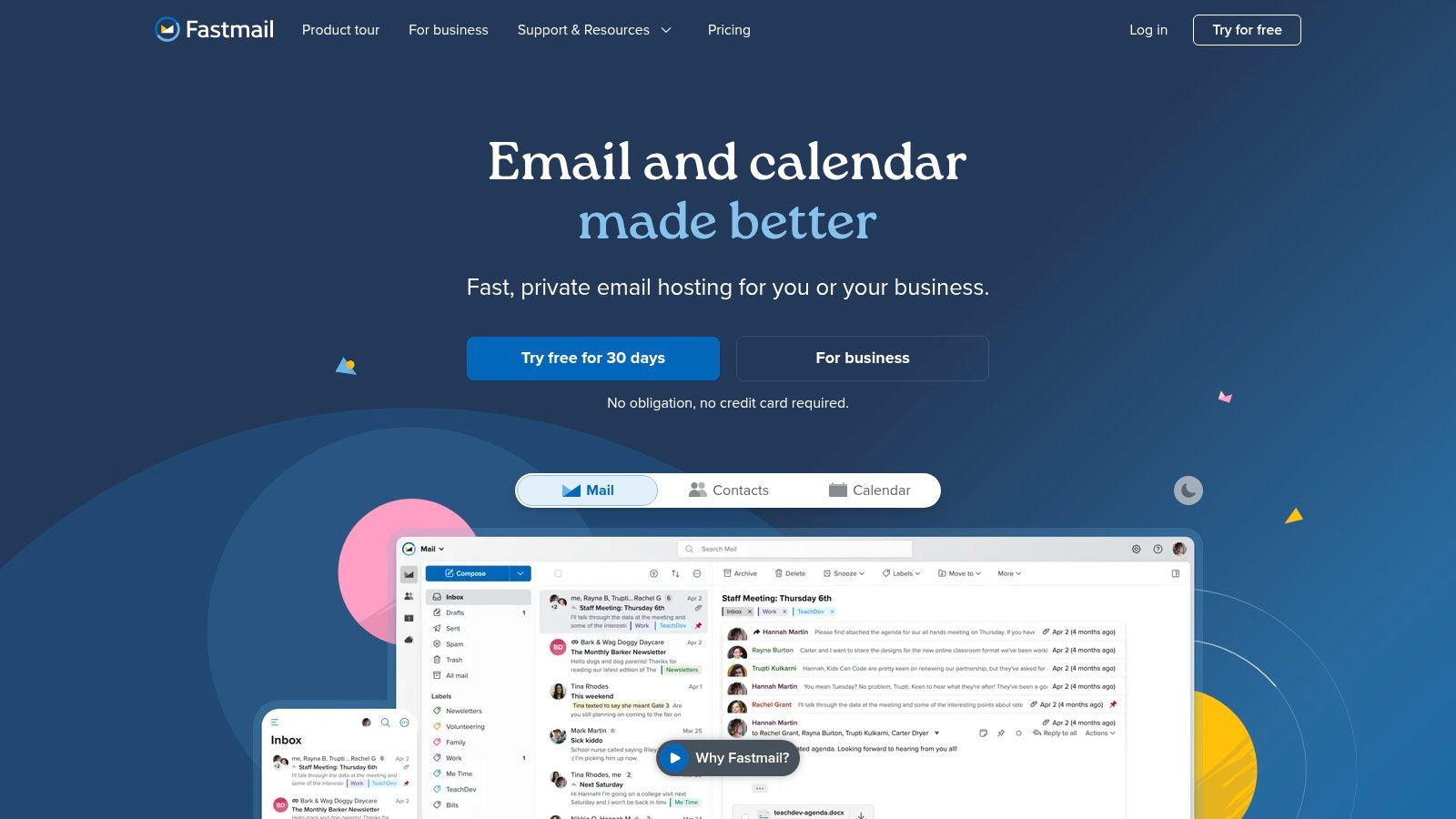
Its reputation for excellent deliverability and robust custom domain support makes it one of the best webmail clients for professionals and privacy-conscious individuals. A standout feature for email privacy is its native integration with 1Password for Masked Email, allowing users to generate unique, anonymous email aliases on the fly to protect their real address from spam and data breaches. This commitment to user privacy and control, combined with responsive customer support, justifies its place as a top-tier email provider.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: No free tier available (offers a 30-day free trial).
- Paid Plans: Start at $3/user/month for Basic, with Standard ($5/user/month) and Professional ($9/user/month) tiers offering more storage (from 2 GB up to 100 GB per user), custom domains, and more.
- Best For: Privacy-focused individuals, families, and small businesses who need a reliable, ad-free email host with strong custom domain features.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Fast, clean, and ad-free web UI, excellent deliverability and custom domain tools, and a strong commitment to privacy and open standards.
- Cons: No free tier available after the trial period, and lacks built-in end-to-end encryption like Proton Mail or Tuta.
Website: https://www.fastmail.com/
8. Tuta (formerly Tutanota)
For users who demand uncompromising privacy, Tuta stands out as one of the best webmail clients available. Built from the ground up on a foundation of end-to-end encryption, the German-based platform ensures that not even the company can read your emails or access your calendar events. This zero-knowledge architecture extends to its search functionality, which encrypts your search index and allows you to search your mailbox locally on your device without compromising your data privacy. Tuta’s commitment to transparency is further reinforced by its open-source clients, which allow for independent security audits.
This makes Tuta an excellent choice for journalists, activists, and any business handling sensitive information. Unlike mainstream providers whose business models rely on data scanning for advertising, Tuta is entirely funded by its users, ensuring its interests remain aligned with protecting privacy. The service operates on 100% renewable energy, adding an ethical dimension to its strong privacy stance. As a hosted email platform, it is an excellent alternative to big tech ecosystems.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 1 GB of storage with limited search and a Tuta domain.
- Paid Plans: Start at €3/month for personal use (Revolutionary plan) with 20 GB storage, 15 email aliases, and 3 custom domains. Business plans offer more advanced user and alias management.
- Best For: Privacy-conscious individuals, security professionals, and businesses that require a hosted email platform with uncompromising end-to-end encryption.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Strong privacy and security defaults with automatic encryption, open-source clients enhance trust, and no tracking or ads.
- Cons: The strict focus on encryption means it cannot integrate with third-party email clients like Thunderbird or Outlook via IMAP/POP3, and its ecosystem is smaller than mainstream competitors.
Website: https://tuta.com/
9. Mailfence
Mailfence offers a privacy-first email service from Belgium, a country known for its strong data protection laws. As a secure alternative to mainstream providers, it positions itself as one of the best webmail clients for users who prioritize confidentiality without sacrificing essential productivity tools. The platform integrates end-to-end encryption using the open-standard OpenPGP, making it straightforward for users to send and receive fully encrypted messages, even to recipients who don't use Mailfence.
Beyond its core email security, Mailfence provides a full suite of tools, including a calendar, document storage, and contact management, all protected under the same privacy-focused philosophy. This makes it an excellent choice for individuals and businesses seeking a cohesive, ad-free digital workspace. Unlike many free providers, Mailfence does not track user behavior or scan emails to serve ads, ensuring user communications remain private. Its business model is based purely on paid subscriptions, aligning its interests directly with its users' privacy.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: Includes 500 MB of email storage and 500 MB for documents, with no ads or tracking.
- Paid Plans: Entry plan starts at €3.50/month for 10 GB email storage, custom domain support, and IMAP/POP3/ActiveSync access. Business plans add comprehensive admin controls and more storage.
- Best For: Privacy-conscious individuals, journalists, and small businesses needing an affordable, secure, and ad-free email suite with integrated encryption.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Strong focus on privacy with built-in OpenPGP encryption, operates under strong Belgian privacy laws, and offers a complete suite of productivity tools.
- Cons: The free plan lacks IMAP/SMTP access, limiting its use with third-party desktop clients, and its ecosystem is smaller compared to major providers.
Website: https://mailfence.com/
10. GMX Mail
GMX Mail, originating from Germany, operates under strong European data protection laws (GDPR) but positions itself as a feature-rich free service rather than a dedicated privacy platform. Its standout feature is the massive 65 GB of free email storage, which is appealing for users with high storage needs. The service includes built-in antivirus and spam protection and allows users to create up to 10 alias addresses, which can help protect one's primary email address from spam.
However, GMX Mail's free tier is ad-supported, which means it doesn't align with the principles of the most secure, privacy-first webmail clients. While its security features are adequate for a casual user, it lacks advanced privacy tools like end-to-end encryption or tracking-pixel blocking. It is a functional and generous free hosted email platform, but users seeking true confidentiality for their communications should consider a paid, privacy-focused alternative.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 65 GB of mailbox storage, 50 MB attachment limit, 2 GB of cloud storage, and is ad-supported.
- Paid Plans: GMX does not have a widely available premium tier in all regions; the free service is its primary offering.
- Best For: Individuals who need a large amount of free email storage and are not primarily concerned with advanced email privacy.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Extremely generous 65 GB of free mailbox storage, large 50 MB attachment limit, and operates under GDPR.
- Cons: The free tier is supported by advertisements, lacks advanced security and privacy features, and the interface feels less modern than competitors.
Website: https://www.gmx.com/mail/
11. iCloud Mail (Apple)
For users deeply embedded in the Apple ecosystem, iCloud Mail presents a seamless and increasingly privacy-focused experience. It offers a clean, ad-free interface, and Apple’s business model does not rely on selling user data for advertising. This positions it as a more private alternative to services like Gmail or Yahoo. Its primary strength lies in its perfect synchronization across Apple devices.
A paid iCloud+ subscription significantly enhances its security and privacy credentials. The Hide My Email feature generates unique, random email addresses to protect your personal address from spam and data brokers. Mail Privacy Protection hides your IP address and prevents senders from seeing if you’ve opened their email. While Apple does perform server-side scanning for security threats and spam, and does not offer zero-knowledge encryption for mail, these features make it one of the best webmail clients for privacy-conscious Apple users.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: 5 GB of storage (shared across all iCloud services).
- Paid Plans: iCloud+ (starting at $0.99/month for 50 GB) adds more storage and powerful privacy features like Hide My Email and Mail Privacy Protection.
- Best For: Individuals and families heavily invested in the Apple ecosystem who value seamless integration and strong privacy features.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Excellent privacy features with iCloud+ subscriptions (Hide My Email, Mail Privacy Protection), ad-free, and exceptional integration with Apple devices.
- Cons: The best experience is tied to Apple’s ecosystem, lacks zero-knowledge encryption, and the free storage tier is a restrictive 5 GB.
Website: https://www.icloud.com/mail
12. HEY (by 37signals/Basecamp)
HEY is an innovative and opinionated take on email that prioritizes user privacy and control. It fundamentally changes how you interact with messages through its unique workflow, which starts with "The Screener." This feature acts as a gatekeeper, letting you decide if you ever want to hear from a sender again, effectively blocking unwanted mail before it hits your inbox. HEY is built for those seeking to escape email overload within a secure, private environment.
Its commitment to privacy is a core tenet. HEY actively blocks spy pixels and tracking scripts by default, preventing senders from knowing when or where you opened their messages. This privacy-first approach is central to its appeal, offering a secure and ad-free hosted email platform without scanning your emails for marketing purposes. While it does not offer end-to-end encryption, its default privacy settings are a significant step up from mainstream providers, making it one of the best webmail clients for those who value both workflow innovation and privacy.
Pricing and Key Details
- Free Plan: No ongoing free tier; a 30-day free trial is available.
- Paid Plans: HEY for You is $99/year for a personal @hey.com address with 100 GB of storage. HEY for Domains is $12/user/month for businesses using a custom domain.
- Best For: Individuals overwhelmed by inbox clutter and businesses seeking a privacy-focused, workflow-driven email solution.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Strong default privacy features like spy-pixel blocking, innovative workflows that actively reduce email overload, and a clean, ad-free user interface.
- Cons: Does not offer end-to-end encryption, the opinionated design requires a significant adjustment, and there is no free plan after the initial trial period.
Website: https://www.hey.com/
Top 12 Webmail Clients Comparison
| Product | Core features | Security & Privacy ★ | Pricing / Value 💰 | Target audience 👥 | Unique selling point ✨ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typewire 🏆 | End‑to‑end encryption, advanced anti‑spam, custom domains, unlimited users, responsive web & apps | ★★★★★ Canada‑hosted, no trackers, no 3rd‑party cloud | Free / Starter / Premium — 7‑day trial 💰 | Privacy‑conscious individuals, SMBs, IT admins 👥 | ✨ Canadian‑owned infra, in‑house dev, 24/7 support |
| Gmail (Google) | 15 GB shared storage, powerful search, labels, Drive/Meet integration | ★★☆ Scans email for ads; strong spam filters | Free; Workspace paid upgrades 💰 | General consumers, G Suite users 👥 | ✨ Deep Google ecosystem & search |
| Outlook.com (Microsoft) | Modern web app, Calendar & OneDrive sync, mobile apps | ★★★☆ Good phishing/spam defenses; ads on free tier | Free; Microsoft 365 adds storage/AI 💰 | Microsoft users, families, businesses 👥 | ✨ Advanced security in paid tiers |
| Yahoo Mail | 20 GB free, subscription view, disposable/alias addresses | ★☆☆ History of breaches; scans email for ads | Free w/ ads; Plus for ad‑free & more storage 💰 | Casual users, newsletter managers 👥 | ✨ One‑tap unsubscribe & alias support |
| Proton Mail | E2E encryption, open‑source clients, custom domains, bridge app | ★★★★★ Swiss jurisdiction, privacy‑first | Free + paid (EUR) tiers for advanced features 💰 | Privacy‑first power users & activists 👥 | ✨ Open‑source, strong jurisdictional privacy |
| Zoho Mail | Ad‑free mail, custom domains, workplace suite integration | ★★★★ Business controls, S‑MIME on premium | Free for small teams; competitive paid plans 💰 | SMBs and teams using Zoho apps 👥 | ✨ Affordable custom-domain email & admin tools |
| Fastmail | Paid plans, generous storage, IMAP/open standards, fast UI | ★★★★ No tracking, excellent deliverability | Paid only; per‑user plans 💰 | Professionals wanting speed & deliverability 👥 | ✨ Strong privacy policy & domain tools |
| Tuta (Tutanota) | E2E by default, zero‑knowledge search, aliases, shared calendar | ★★★★★ Default encryption, open‑source clients | Free + paid tiers for domains & aliases 💰 | Privacy advocates & secure communicators 👥 | ✨ Zero‑knowledge search, strong defaults |
| Mailfence | OpenPGP built‑in, calendar, docs, groups, 2FA | ★★★★ OpenPGP & 2FA; balanced privacy | Free 1GB; affordable paid business tiers 💰 | Users wanting integrated OpenPGP & tools 👥 | ✨ Built‑in OpenPGP suite with docs/calendar |
| GMX Mail | Very large free mailbox (65 GB), cloud, online office | ★★☆ GDPR compliant; ad-supported model | Free w/ ads; extras included 💰 | Users needing large free storage 👥 | ✨ Huge free mailbox + cloud tools |
| iCloud Mail (Apple) | Aliases, rules, Hide My Email, iCloud+ storage | ★★★★ Strong within Apple ecosystem | Free; iCloud+ paid storage tiers 💰 | Apple device users & families 👥 | ✨ Hide My Email & family sharing benefits |
| HEY (37signals) | Opinionated inbox workflows (Screener, Set Aside), 100 GB | ★★★★ Spy‑pixel blocking & privacy defaults | Paid flat pricing; 30‑day trial only 💰 | Users wanting inbox re‑design & focus 👥 | ✨ Unique workflows to tame inbox overload |
Making the Final Call: Your Privacy is Worth It
Navigating the crowded market of webmail clients can feel overwhelming, but our deep dive into the top contenders reveals a clear and crucial trend. The era of passively accepting data-mining in exchange for a "free" inbox is ending. The modern digital landscape demands a more deliberate, security-conscious approach to our most fundamental communication tool: email.
As we've explored, the distinction between ad-supported giants like Gmail and Outlook and privacy-first platforms like Proton Mail, Tuta, and Fastmail is not just about features; it's a fundamental difference in philosophy. One model treats you as the product, analyzing your conversations to sell ads. The other treats you as the customer, offering a robust, secure service in exchange for a fair price. This shift is at the heart of finding the best webmail clients for your needs.
Key Takeaways: From Free to Sovereign
The most important takeaway from this comprehensive review is that you have a choice. You are not locked into a system that compromises your privacy for convenience. Secure, hosted email platforms provide a viable, and often superior, alternative that puts you back in control of your digital identity.
Remember these core principles as you make your decision:
- Zero-Knowledge Encryption is the Gold Standard: Services like Proton Mail and Tuta use end-to-end and zero-access encryption, meaning not even the provider can read your emails. This is the highest level of privacy available.
- Custom Domains Build Professionalism: For small businesses or professionals, a service like Zoho Mail or Fastmail that seamlessly integrates custom domains is essential for brand identity and credibility.
- Jurisdiction Matters: The legal jurisdiction where a provider is based (e.g., Switzerland for Proton Mail, Germany for Tuta) has significant implications for data privacy laws and government surveillance.
- A Small Price for Priceless Privacy: Investing a few dollars a month in a premium email service is a direct investment in your own security, digital freedom, and an ad-free experience.
Your Action Plan for Choosing the Right Webmail Client
So, how do you move forward? Don't let analysis paralysis stop you. Follow these actionable steps to select and implement the right service.
First, define your non-negotiables. Is end-to-end encryption your top priority, or is it a polished user interface with advanced calendar and contact management? Are you a solo user, or do you need to manage a team with shared inboxes and administrative controls? Create a short list of your must-have features.
Next, leverage the free trials. Nearly every premium service we've covered offers a free tier or a trial period. Use this opportunity to test the real-world experience. Import a few contacts, send some test emails, and see how the interface feels during daily use. Is it intuitive? Is it fast? Does it meet your expectations?
Finally, plan your migration. Switching email providers can seem daunting, but modern tools make it simpler than ever. Look for built-in import tools that can transfer your old emails, contacts, and calendar events. Set up email forwarding from your old account for a few months to ensure you don't miss anything. Announce your new address to your key contacts and methodically update your online accounts.
Choosing one of the best webmail clients is more than just a technical decision; it's a declaration of your digital independence. By opting for a secure, user-funded platform, you not only protect your own sensitive communications but also support a healthier, more private internet ecosystem for everyone. The peace of mind that comes from knowing your inbox is truly yours is an invaluable asset in today's digital world.
If your priority is a streamlined, privacy-focused experience that combines powerful features with an intuitive design, consider Typewire. It was built from the ground up to provide a secure and productive environment, making it an excellent choice among the best webmail clients for users who value both security and usability. Explore how it reclaims your inbox at Typewire.