Is Your Email Fort Knox? 7 Must-Checks for 2025
Email remains a primary attack vector. This email security audit checklist provides seven crucial steps to bolster your email defenses. This list covers essential security measures from authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to data loss prevention (DLP) and recovery procedures. Following this email security audit checklist will help identify vulnerabilities and implement robust protection. Whether you're a business owner or an IT professional, these checks are vital for secure communication. For a platform already built with these principles, consider Typewire—designed with privacy as its core.
1. Email Authentication Protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Email authentication protocols are crucial for a robust email security audit checklist. These protocols verify the legitimacy of email senders, bolstering your defenses against spoofing attacks, a common tactic used in phishing campaigns. Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is essential for protecting your organization and users from malicious emails. These protocols work together to provide a layered defense, ensuring that emails purporting to come from your domain are genuinely originating from authorized sources.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) specifies which IP addresses are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain. Think of it as a whitelist of approved senders. By publishing an SPF record in your DNS, you declare which servers are authorized to send emails using your domain name, making it harder for spammers to forge your identity. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a digital signature to your outgoing emails, verifying their integrity and authenticity. This cryptographic signature, attached to the email header, allows receiving mail servers to confirm that the message hasn't been tampered with during transit. Finally, DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) acts as the overarching policy, instructing receiving mail servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks. DMARC allows you to specify whether these emails should be quarantined, rejected, or delivered, giving you control over how your domain's email is handled.
The benefits of implementing these protocols are significant. They drastically reduce spoofing and phishing attacks, protecting your brand reputation and users from falling victim to scams. By enhancing your email deliverability rates, legitimate messages are more likely to reach their intended recipients' inboxes, rather than being flagged as spam. Furthermore, DMARC provides valuable reports, offering visibility into potential email abuse attempts, allowing you to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Successful implementation of these protocols can be seen across various organizations. Microsoft's implementation of DMARC across all Outlook.com domains resulted in an 85% reduction in phishing emails. PayPal employs strict DMARC policies to protect its users from brand impersonation attacks. Even government agencies like the FBI and IRS mandate DMARC implementation, recognizing its critical role in secure communications.
While these protocols are essential, there are some challenges to consider. The initial setup and configuration can be complex, requiring technical expertise. Ongoing maintenance and monitoring are also necessary to ensure effectiveness. Misconfiguration can lead to legitimate emails being blocked, so careful attention to detail is paramount. Coordination with third-party email services might also be required, adding another layer of complexity.
Here are some practical tips for implementing these protocols:
- Start with Monitoring: Begin with a DMARC policy set to 'none' to monitor email traffic and identify legitimate sending sources before enforcing stricter policies.
- Gradual Rollout: Implement stricter DMARC policies gradually, using a percentage rollout to avoid sudden disruptions to email flow.
- Regular Review: Regularly review DMARC reports to identify legitimate email sources and adjust policies accordingly.
- Coordination: Coordinate with your marketing team and any third-party email service providers to ensure seamless integration and avoid unintended consequences.
The following infographic visualizes the core concepts of email authentication protocols and how they relate to each other. The central concept, "Email Authentication Protocols," is connected to three key components: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
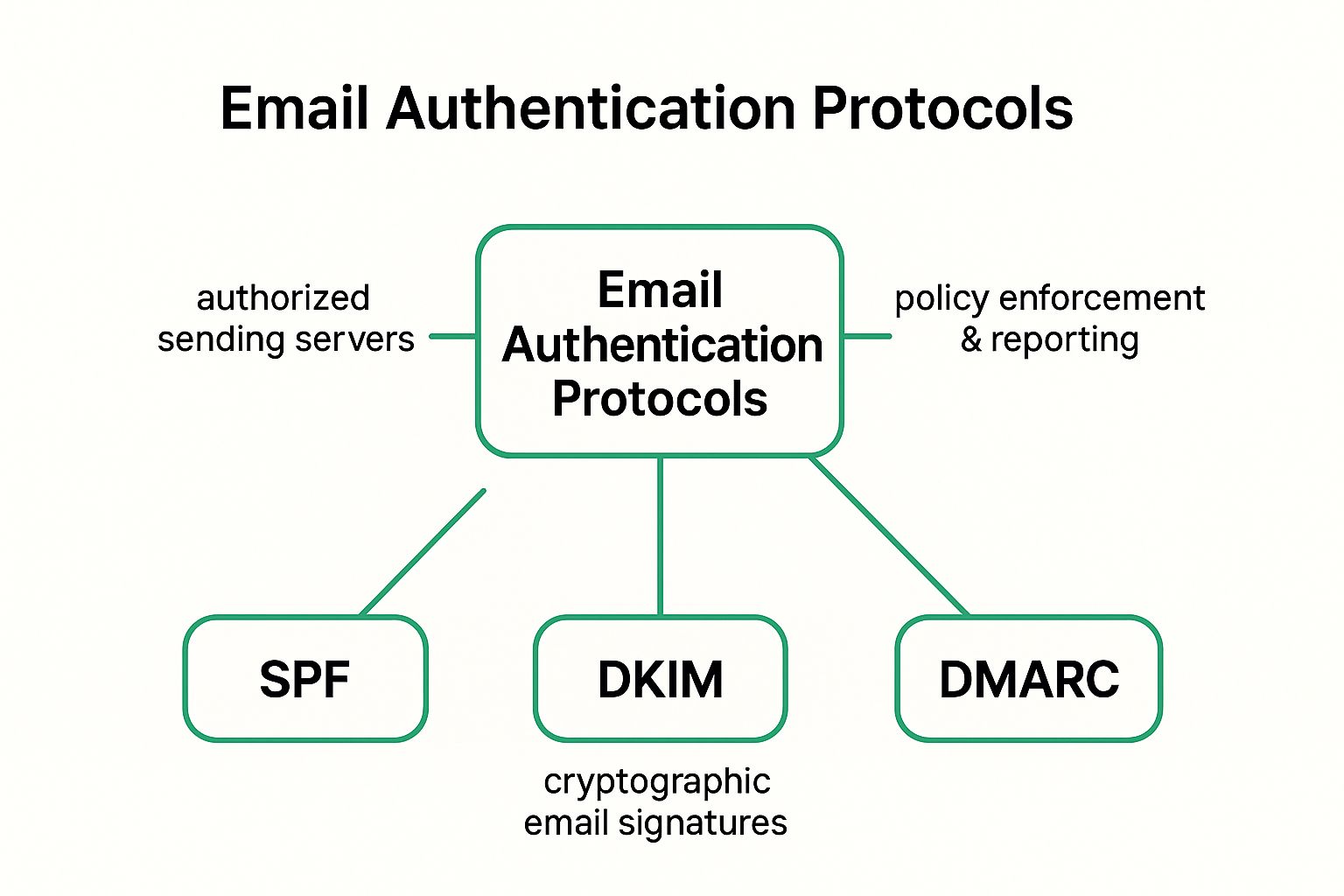
The infographic clearly illustrates how SPF, DKIM, and DMARC work together to form a comprehensive email authentication system, with SPF authorizing senders, DKIM verifying integrity, and DMARC enforcing policies.
In conclusion, implementing email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) is a non-negotiable aspect of a comprehensive email security audit checklist. While the initial setup may require some effort, the long-term benefits in terms of enhanced security, improved deliverability, and protection against spoofing and phishing attacks make it a worthwhile investment for any organization. These protocols are critical for protecting your organization, your users, and your brand reputation in today's complex threat landscape.
2. Encryption in Transit and at Rest
A crucial aspect of any robust email security audit checklist is verifying the presence and effectiveness of encryption both in transit and at rest. This dual approach forms the bedrock of protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality, and maintaining compliance with data protection regulations. Failing to adequately address email encryption leaves your organization vulnerable to data breaches, reputational damage, and potential legal repercussions. This section will delve into the mechanics of email encryption, outlining its benefits, potential drawbacks, and actionable steps for implementation.
Encryption in transit refers to the protection of email data as it travels across networks. This is primarily achieved using Transport Layer Security (TLS), a protocol that establishes a secure, encrypted connection between the sending and receiving mail servers. Think of it as a secure tunnel through which your emails travel, preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks where malicious actors intercept data mid-transmission. Without TLS, your emails are essentially postcards, open to anyone who might intercept them along the way.
Encryption at rest, on the other hand, focuses on protecting email data while it's stored on servers. This involves encrypting the email content itself, ensuring that even if a server is compromised, the stored data remains unreadable without the decryption key. Various encryption methods are employed for this purpose, including server-side encryption and client-side encryption.
A comprehensive email encryption strategy incorporates several key features:
- TLS encryption for email transmission: The foundation of secure email delivery, ensuring data confidentiality during transit.
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) for sensitive communications: Offers the highest level of protection by encrypting emails on the sender's device and only decrypting them on the recipient's device. This means that even the email provider cannot access the message content.
- Server-side encryption for stored emails: Protects data stored on email servers, mitigating the risk of data breaches in case of server compromise.
- Certificate-based authentication: Verifies the identity of the communicating parties, preventing spoofing and phishing attacks.
- Forward secrecy protection: Ensures that even if a current encryption key is compromised, past communications remain secure.
Implementing a robust email encryption strategy offers several advantages:
- Protects against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks: Secures email content from unauthorized access during transmission.
- Ensures compliance with data protection regulations: Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA, GDPR, and others.
- Maintains confidentiality of sensitive business communications: Protects proprietary information, client data, and internal discussions.
- Prevents unauthorized access to stored email archives: Safeguards historical email data even in the event of a server breach.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- May impact email delivery speed: The encryption and decryption process can introduce minor delays in email delivery.
- Requires proper certificate management: Maintaining and updating encryption certificates is essential for ensuring ongoing security.
- Can complicate email troubleshooting: Encrypted emails can be more challenging to troubleshoot in case of delivery issues.
- May require user training for end-to-end encryption tools: E2EE tools often require user setup and understanding, which can necessitate training for some users.
Several real-world examples highlight the importance and successful implementation of email encryption: Gmail enforces TLS encryption for all email transmission by default, providing a baseline level of security for its users. ProtonMail goes a step further, providing zero-access encryption for all stored emails, meaning even ProtonMail cannot access the content of user emails. Healthcare organizations routinely use encrypted email to comply with HIPAA requirements, protecting sensitive patient information.
To effectively integrate encryption into your email security audit checklist, consider these actionable tips:
- Enable opportunistic TLS and require encryption for sensitive domains: Maximize TLS usage by enabling opportunistic TLS and mandating encryption for communications with specific domains handling sensitive data.
- Implement certificate pinning for critical email communications: Enhance security for crucial communications by pinning certificates, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks that rely on fraudulent certificates.
- Use S/MIME or PGP for highly sensitive email exchanges: Leverage S/MIME or PGP for end-to-end encryption of highly confidential emails, ensuring maximum protection.
- Regularly audit and update encryption certificates: Establish a routine for auditing and updating encryption certificates to maintain their validity and prevent security vulnerabilities.
Learn more about Encryption in Transit and at Rest
Implementing a comprehensive email encryption strategy is not just a technical necessity; it is a fundamental component of a responsible security posture. By understanding the nuances of encryption in transit and at rest, and by implementing the tips outlined above, organizations can significantly bolster their email security, protect sensitive data, and maintain the trust of their users and clients. This proactive approach ensures a safer and more secure email environment, minimizing risks and maximizing confidentiality.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation
A crucial element of any robust email security audit checklist is the implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This security mechanism adds an extra layer of protection to email accounts by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access. Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA typically combines something the user knows (like a password), something they have (like a mobile device or security token), and/or something they are (like a fingerprint or facial recognition). This multifaceted approach significantly reduces the risk of account compromise, even if passwords are stolen through phishing attacks or data breaches.

MFA works by requiring users to present multiple credentials, making it exponentially harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. For example, a user might enter their password (something they know) and then receive a prompt on their smartphone (something they have) requiring them to approve the login attempt. This second factor ensures that even if an attacker obtains the user's password, they would still need access to the user's device to compromise the account. More advanced MFA implementations can also incorporate biometric factors, such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition (something they are), further strengthening security.
Several features enhance the effectiveness and flexibility of MFA. These include:
- Multiple Authentication Factors: Combining passwords with options like one-time passcodes (OTPs) delivered via SMS, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens.
- Adaptive Authentication: This risk-based approach analyzes login attempts for suspicious activity (like unfamiliar locations or devices) and triggers additional authentication challenges only when necessary.
- Hardware Token Support (FIDO2/WebAuthn): Providing support for physical security keys offers the strongest form of MFA, resistant to phishing and malware attacks.
- Biometric Authentication Options: Integrating fingerprint or facial recognition offers a convenient and secure authentication method.
- Conditional Access Policies: Granular control over access based on various factors, such as user role, device type, or location.
Implementing MFA offers several significant advantages:
- Dramatically Reduces Risk of Account Takeover Attacks: MFA is remarkably effective at preventing unauthorized access, even in the event of password breaches.
- Provides an Additional Security Layer Beyond Passwords: Recognizing that passwords alone are vulnerable, MFA bolsters security by adding layers of defense.
- Helps Meet Compliance Requirements: Many industry regulations and data privacy standards mandate MFA for sensitive data access.
- Can Prevent Lateral Movement in Network Breaches: By requiring MFA for access to critical systems, organizations can limit the damage caused by attackers who have gained initial access to the network.
While the benefits are undeniable, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- May Impact User Experience and Convenience: Requiring multiple authentication steps can add friction to the login process.
- Requires Backup Authentication Methods for Device Loss: Users need alternative ways to access their accounts if they lose their primary authentication device.
- Can Increase IT Support Burden: Implementing and managing MFA can require additional resources and training for IT staff.
- May Face User Resistance to Adoption: Some users may find MFA cumbersome and resist its implementation.
Numerous examples demonstrate the effectiveness of MFA. Microsoft reports a 99.9% reduction in account compromise with MFA enabled. Google's Advanced Protection Program utilizes hardware security keys for high-risk users. Banking institutions mandate MFA for all email access to protect sensitive financial information. These examples underscore the importance of MFA in a comprehensive email security strategy.
To effectively implement MFA within your organization as part of your email security audit checklist, consider these tips:
- Prioritize App-Based Authenticators Over SMS: Authenticator apps provide better security than SMS-based OTPs, which are vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks.
- Implement Risk-Based Authentication to Balance Security and Usability: This approach minimizes user disruption by only requiring additional authentication when suspicious activity is detected.
- Provide Multiple Backup Authentication Methods: Ensure users have alternative access options in case they lose their primary device.
- Conduct User Training and Awareness Programs: Educating users about the importance of MFA and how to use it correctly is essential for successful adoption.
MFA solutions are widely available from various providers, including Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, RSA SecurID, and Duo Security. Choosing the right solution depends on your specific needs and budget. Including MFA in your email security audit checklist is not just a best practice—it's a necessity in today's threat landscape. By implementing MFA, you significantly strengthen your email security posture and protect your organization from costly data breaches and reputational damage.
4. Email Gateway and Anti-Malware Solutions
A crucial component of any robust email security audit checklist is the implementation of a comprehensive Email Gateway and Anti-Malware solution. This critical security layer acts as the first line of defense against a multitude of email-borne threats, protecting your organization from malware, viruses, phishing attacks, spam, and other malicious content. As part of your email security audit, verifying the effectiveness and configuration of this gateway is paramount. This section explores the intricacies of these solutions and provides actionable advice for incorporating them into your security posture.
Email gateways function as a central filtering point for all incoming and outgoing email traffic. Before a message reaches a user's inbox, it passes through the gateway where it is subjected to a series of security checks. These checks utilize a combination of advanced detection techniques to identify and neutralize threats. Signature-based scanning detects known malware signatures, while behavioral analysis identifies suspicious patterns and anomalies in email content and attachments. Sandboxing isolates potentially harmful attachments in a secure environment to observe their behavior before delivery, and machine learning algorithms are employed to identify new and evolving threats based on vast datasets of known malicious activity. This multi-layered approach ensures a high level of protection against a broad spectrum of attacks.
Features of a robust email gateway and anti-malware solution include:
- Real-time threat detection and blocking: This feature provides immediate protection by identifying and blocking malicious emails as they arrive, preventing them from reaching user inboxes.
- Sandboxing for suspicious attachments: By isolating attachments in a controlled environment, sandboxing allows the gateway to analyze their behavior and detect malicious code that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- URL rewriting and safe browsing: This feature rewrites URLs in emails to pass through a security check before redirecting users to the intended website, protecting them from phishing and malicious websites.
- Advanced threat protection with AI/ML: Artificial intelligence and machine learning enhance threat detection by identifying new and evolving threats based on patterns and anomalies.
- Quarantine management and reporting: A centralized quarantine allows administrators to review and manage suspicious emails, while detailed reporting provides insights into threat trends and gateway performance.
The benefits of implementing such a solution are numerous:
- Blocks the majority of email-based threats before user interaction: This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of users falling victim to phishing scams or downloading malware.
- Reduces risk of malware infections and data breaches: By preventing malicious content from reaching user endpoints, email gateways minimize the potential for widespread infections and costly data breaches.
- Provides centralized security management and reporting: Centralized management simplifies security administration and provides valuable insights into threat activity.
- Can integrate with other security tools and SIEM systems: Integration with other security tools enhances overall security posture and streamlines incident response.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- May produce false positives blocking legitimate emails: Overly aggressive filtering can sometimes lead to legitimate emails being blocked, requiring manual intervention and policy adjustments.
- Requires ongoing tuning and maintenance: To maintain optimal performance and accuracy, email gateways require regular updates and policy tuning.
- Can introduce email delivery delays: While typically minimal, the scanning process can sometimes introduce slight delays in email delivery.
- Advanced solutions can be expensive: The cost of advanced email security solutions can be a barrier for some organizations.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of these solutions. Barracuda Email Security Gateway reported blocking 1.5 billion email threats in 2023, highlighting the sheer volume of malicious emails circulating. Proofpoint’s strong market presence, protecting over 87% of Fortune 100 companies, underscores the reliance on such solutions by large organizations. Microsoft Defender for Office 365, integrated with Exchange Online, offers a comprehensive solution for businesses utilizing Microsoft's ecosystem.
Learn more about Email Gateway and Anti-Malware Solutions
To maximize the effectiveness of your email gateway and anti-malware solution during your email security audit, consider the following tips:
- Implement layered security with multiple detection engines: Combining multiple detection techniques provides a more comprehensive defense against a wider range of threats.
- Regularly update threat intelligence feeds: Keeping threat intelligence up-to-date ensures that the gateway is equipped to identify the latest threats.
- Configure user-friendly quarantine notifications: Clear and concise quarantine notifications empower users to manage potentially legitimate emails that have been flagged.
- Monitor false positive rates and adjust policies accordingly: Regularly reviewing and adjusting filtering policies minimizes the impact of false positives while maintaining a high level of security.
Including Email Gateway and Anti-Malware solutions in your email security audit checklist is not merely a best practice; it's a necessity in today's threat landscape. By diligently implementing and maintaining these solutions, you can significantly reduce the risk of email-borne threats and protect your organization's valuable data and resources.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies are a crucial component of any robust email security audit checklist. They form a security framework designed to detect and prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data through email channels. This is achieved by monitoring email content, attachments, and metadata to identify confidential information. Such information can include anything from personally identifiable information (PII) like credit card numbers and social security numbers to proprietary business data, intellectual property, and regulated data like protected health information (PHI). Upon detection, a DLP solution can automatically take action, such as blocking the email, quarantining it for review, or encrypting it before transmission. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with various data protection regulations.

DLP solutions leverage a combination of techniques to effectively identify sensitive data. Content inspection and classification analyze the actual text within emails and attachments, looking for patterns and keywords indicative of confidential information. Policy-based automated responses then dictate the action taken when a match is found. These policies can be customized based on the sensitivity level of the data, the recipient, and other contextual factors. Integration with data classification systems allows for a more granular approach, leveraging existing data tags and labels to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, incident reporting and forensics capabilities provide valuable insights into data handling practices, enabling organizations to identify vulnerabilities and improve their security posture. Many DLP solutions also offer support for regulatory compliance templates, making it easier to adhere to industry-specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
DLP policies are essential for organizations of all sizes, but particularly beneficial for those handling large volumes of sensitive data. Financial institutions, for example, rely on DLP to prevent PCI DSS violations by monitoring and blocking emails containing credit card information. Healthcare organizations utilize DLP to protect PHI in email communications, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations. Government agencies employ DLP solutions to prevent the leakage of classified information, safeguarding national security. These examples illustrate the wide-ranging applicability and effectiveness of DLP in diverse sectors.
Implementing DLP policies offers several significant advantages. It prevents both accidental and intentional data breaches, protecting sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. It ensures compliance with data protection regulations, minimizing legal and financial risks. DLP provides detailed audit trails for data handling, enabling organizations to track the flow of sensitive information and demonstrate accountability. Finally, it can automatically encrypt or block sensitive emails, proactively mitigating risks before they materialize.
However, DLP implementation does come with its challenges. Overly restrictive policies can impact legitimate business communications, leading to frustration and delays. Careful policy tuning is required to minimize false positives and ensure that legitimate emails are not inadvertently blocked or quarantined. Implementing DLP across diverse data types can be complex, requiring significant initial configuration effort.
To effectively implement DLP policies, start with a monitoring mode before enforcing blocking policies. This allows you to observe email traffic, identify potential issues, and fine-tune your policies without disrupting business operations. Create user-friendly policy violation notifications with clear guidance on how to handle sensitive data appropriately. Regularly review and update data classification rules to reflect evolving data protection needs and best practices. Finally, provide comprehensive user training on data handling policies to raise awareness and promote a culture of security.
By incorporating DLP policies into your email security audit checklist, you can significantly enhance your organization's ability to protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and maintain a strong security posture. While implementation requires careful planning and ongoing management, the benefits far outweigh the challenges, making DLP an indispensable tool in today's increasingly complex threat landscape.
6. Access Controls and Privilege Management
Access controls and privilege management are critical components of any robust email security audit checklist. This crucial aspect of email security focuses on establishing a comprehensive framework for managing user permissions, roles, and access rights within your email systems. By implementing a well-defined access control system, organizations can significantly bolster their defenses against data breaches, insider threats, and unauthorized access, thereby ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information transmitted via email. When conducting an email security audit, thoroughly examining your current access control policies and procedures is paramount.
A key element of access control is the implementation of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). RBAC simplifies user management by assigning permissions based on predefined roles within the organization. Instead of granting individual permissions to each user, RBAC allows administrators to assign roles (e.g., "Sales," "Marketing," "Human Resources") and then assign permissions to those roles. This approach streamlines administration, ensures consistency in access levels, and simplifies audits by providing a clear overview of who has access to what.
Furthermore, a robust access control framework should incorporate automated user provisioning and deprovisioning. This automation ensures that new employees are granted the necessary access rights upon joining the organization and that those rights are revoked immediately when they leave, minimizing the risk of orphaned accounts and potential security vulnerabilities. Privileged Access Management (PAM) adds another layer of security by controlling and monitoring access to sensitive accounts with elevated privileges, such as administrator accounts. By implementing PAM, organizations can limit the potential damage caused by compromised administrator credentials.
Regular access certification and reviews are vital for maintaining the effectiveness of access control policies. Periodically reviewing user access rights helps ensure that access is still appropriate and aligned with job responsibilities. This process helps identify and rectify any discrepancies, such as users having access they no longer need, preventing potential security breaches. Additionally, audit logging of administrative activities provides a detailed record of all changes made to access control policies, enabling organizations to track and investigate any suspicious activity.
Implementing a strong access control and privilege management system offers numerous advantages. It significantly reduces the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access by ensuring that users only have the necessary permissions to perform their job functions. This adheres to the principle of least privilege, a fundamental security best practice. Moreover, robust access controls facilitate regulatory compliance and auditing, enabling organizations to demonstrate their commitment to data security and meet regulatory requirements. Streamlining user lifecycle management through automated provisioning and deprovisioning further enhances efficiency and reduces administrative overhead. Learn more about Access Controls and Privilege Management
However, implementing and maintaining an effective access control system can also present challenges. In large organizations with complex hierarchies and numerous users, implementing RBAC can be intricate. Overly restrictive access controls can negatively impact user productivity, hindering their ability to perform their tasks efficiently. Ongoing maintenance and review processes are necessary to ensure the continued effectiveness of the system, requiring dedicated resources and expertise. Integration with legacy systems can also pose challenges, requiring careful planning and execution.
Successful implementations of access controls are seen in platforms like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. Microsoft 365 uses conditional access policies based on user risk, dynamically adjusting access based on factors like location and device. Google Workspace leverages context-aware access controls, providing granular control over data access based on the user's context. Many enterprise organizations are also adopting zero-trust email access models, which verify every access request, regardless of the user's location or network.
To maximize the effectiveness of your access control policies during an email security audit, consider these tips: Implement automated access reviews and recertification processes to streamline regular reviews. Use group-based permissions rather than individual assignments whenever possible to simplify management. Monitor and alert on privilege escalation attempts to detect and respond to potential security breaches. Finally, maintain detailed documentation of all access control policies to facilitate audits and troubleshooting. By addressing access controls and privilege management effectively, organizations can strengthen their email security posture and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
7. Email Backup and Recovery Procedures
A crucial component of any comprehensive email security audit checklist is evaluating your email backup and recovery procedures. This process involves establishing a comprehensive strategy to protect email data through regular backups, robust disaster recovery planning, and effective business continuity measures. In today's threat landscape, a strong backup and recovery system is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for maintaining business operations and safeguarding sensitive information. This aspect of your email security directly influences your ability to restore email services swiftly and efficiently in the event of system failures, cyberattacks (including ransomware), or natural disasters. A weak or non-existent backup strategy can lead to significant data loss, financial repercussions, and reputational damage. Therefore, incorporating this element into your email security audit checklist is paramount.
A successful email backup and recovery strategy typically includes the following features:
- Automated Daily/Continuous Backup Processes: Automated systems eliminate human error and ensure consistent backups, allowing you to recover data from very recent points in time. Continuous backups offer the highest level of protection, capturing changes almost instantaneously.
- Multiple Backup Locations (On-site, Off-site, Cloud): The 3-2-1 backup rule is highly recommended here. This rule suggests having three copies of your data, stored on two different media, with one copy located off-site. This redundancy protects against a single point of failure and minimizes the risk of complete data loss.
- Point-in-Time Recovery Capabilities: This feature allows you to restore your email system to a specific point in time before a failure or attack occurred, minimizing data loss and disruption.
- Granular Recovery Options: The ability to recover individual emails or mailboxes, rather than the entire system, provides flexibility and efficiency in restoring specific data as needed.
- Backup Encryption and Integrity Verification: Encryption safeguards backup data from unauthorized access, while integrity verification ensures the backups remain unaltered and usable during recovery.
The benefits of a robust email backup and recovery strategy are numerous:
- Protection against data loss from various threat vectors: From hardware failures to ransomware attacks, a well-designed backup system provides a safety net for your email data.
- Enables quick recovery from ransomware attacks: With backups readily available, you can restore your email system without paying ransom demands, minimizing downtime and financial losses.
- Supports compliance with data retention requirements: Many industries have stringent data retention regulations. Email backups help organizations meet these requirements by preserving email data for specified periods.
- Provides business continuity assurance: In the event of a disaster, a strong backup and recovery strategy ensures that your email communication channels can be restored quickly, minimizing disruption to business operations.
However, implementing and maintaining such a system comes with certain challenges:
- Requires significant storage resources and costs: Storing multiple copies of email data can consume considerable storage space and incur associated costs.
- Backup and recovery processes can be time-consuming: Depending on the size of your email system, backup and recovery operations can take time, requiring careful planning and execution.
- May face challenges with large-scale email systems: Backing up and restoring massive email systems can be complex and require specialized solutions.
- Requires regular testing to ensure recovery effectiveness: Regular testing is essential to verify that the backup and recovery processes work as expected and that data can be restored successfully.
There are numerous real-world examples demonstrating the critical importance of email backup and recovery:
- The City of Atlanta successfully recovered from a crippling ransomware attack by utilizing their email backups, minimizing the impact on city services.
- Financial services firms are often required to maintain email archives for seven years or more to comply with regulatory requirements. Robust backup systems are essential for achieving this.
- Healthcare organizations rely on backup solutions to ensure HIPAA compliance and protect sensitive patient information.
To ensure your email backup and recovery procedures are effective, consider the following tips:
- Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: Create three copies of your data, store them on two different media types, and keep one copy off-site.
- Regularly test recovery procedures with various scenarios: Simulate different failure scenarios to validate the effectiveness of your recovery plan.
- Implement backup monitoring and alerting systems: Automated monitoring and alerts can help identify potential issues with the backup process and allow for prompt corrective action.
- Document and train staff on recovery procedures: Ensure that your staff is well-trained and aware of the recovery procedures to minimize confusion and delays during an emergency.
Implementing a comprehensive email backup and recovery procedure is a critical aspect of your email security audit checklist. It provides a vital safety net for your organization, protecting against data loss, ensuring business continuity, and supporting compliance requirements. By incorporating these strategies, you can significantly strengthen your email security posture and safeguard your valuable data.
7-Point Email Security Audit Checklist Comparison
| Security Measure | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Email Authentication Protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) | Medium to High Requires DNS and policy setup |
Moderate Coordination with email providers |
Strong spoofing/phishing reduction Improved deliverability |
Organizations sending bulk email Brand protection |
Industry standard Visibility into abuse Boosts sender reputation |
| Encryption in Transit and at Rest | Medium Needs certificate and key management |
Moderate to High Certificate and tool management |
Confidentiality protection Compliance with data regulations |
Sensitive communications Regulated industries |
Protects data in transit & storage Prevents interception |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation | Medium Requires integration and user adoption |
Moderate Authentication apps/devices and support |
Drastic reduction in account compromises Additional security layer |
User account access High-risk environments |
Significantly enhances account security Compliance support |
| Email Gateway and Anti-Malware Solutions | High Complex configuration and tuning |
High Ongoing threat intelligence and infrastructure |
Block malware, phishing, spam before delivery Centralized management |
Enterprises with high email volume Threat-prone environments |
Blocks majority of threats Integrates with security tools |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies | High Complex rule creation and tuning |
High Content inspection engines and monitoring |
Prevents data leaks Regulatory compliance enforcement |
Protecting sensitive data Regulated industries |
Automated data protection Audit trails and reporting |
| Access Controls and Privilege Management | Medium to High Requires RBAC and monitoring |
Moderate User and system administration |
Reduces insider threats Enforces least privilege |
Organizations with sensitive data Regulated sectors |
Controls user access Facilitates compliance audits |
| Email Backup and Recovery Procedures | Medium Setup of backup schedules and tests |
High Storage, testing, and monitoring resources |
Data loss protection Business continuity assurance |
Organizations requiring data retention Disaster recovery planning |
Fast recovery from attacks Supports compliance needs |
Email Security: It's a Marathon, Not a Sprint
Implementing a robust email security posture isn't a one-time fix; it requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation. This email security audit checklist, covering crucial areas from email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) to data loss prevention (DLP) policies and access controls, provides a strong foundation for protecting your valuable data and communications. Mastering these concepts—encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), robust gateway solutions, and comprehensive backup and recovery procedures—is paramount to minimizing the risk of phishing attacks, data breaches, and other email-borne threats. Regularly reviewing and updating your email security practices, informed by your email security audit checklist, is the key to staying ahead of evolving threats and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your email communications. This proactive approach translates directly to enhanced business continuity, stronger client trust, and peace of mind knowing your sensitive information remains secure.
Ready to simplify your email security journey? Typewire is built with security and privacy at its core, handling many of the complex aspects of email security discussed in this email security audit checklist. Explore a more secure email experience by visiting Typewire today.

