Why Your Email Needs Protection (And What Happens When It Doesn't)

This screenshot from Wikipedia's Email Security page gives us a glimpse into the many layers and protocols that go into protecting our email conversations. It's a bit like a complex engine, with different parts like TLS/SSL, S/MIME, and PGP all working together to ensure your messages are safe.
Think about it this way: imagine sending sensitive financial information through the mail. Without a secure envelope, it's like writing it on a postcard for everyone to see. This is the inherent vulnerability that cybercriminals exploit.
A compromised email account can be a gateway to all sorts of trouble: identity theft, financial losses, and damage to your reputation.
The Real Cost of Insecurity
The consequences of weak email security aren't theoretical. They're happening every day, impacting businesses of all sizes. Remember the 2019 phishing attack on Riviera Beach, Florida? A single phishing email opened the door for hackers, resulting in a $600,000 ransom payment.
Beyond the direct financial hit, there's also the long-term damage to a company's reputation. When customer data is compromised due to lax security, trust evaporates, impacting future business and potentially leading to expensive legal battles.
Why Traditional Email Falls Short
Traditional email systems weren't designed with today's cyber threats in mind. Often, they lack the basic security features needed to protect your sensitive data. This isn't to say that email is inherently bad, but rather that we need to bolster its defenses with strong protocols.
The growing demand for email security solutions speaks volumes. In 2024, the market was valued at $18.5 billion. By 2030, it's projected to reach $24 billion, growing at a CAGR of 4.4%. This upward trend highlights the increasing importance of email security in a world of ever-evolving cyber threats. You can learn more about this growth in the Email Security Solutions Market report.
Moving Beyond Assumptions
Many organizations operate under a false sense of security when it comes to email. Some think their antivirus software is enough, failing to realize that many email attacks are highly targeted. Others assume their employees are too smart to fall for phishing scams, underestimating the sophistication of these tactics.
These assumptions can leave your organization vulnerable. Implementing secure email protocols isn't just a technical chore; it's a crucial strategic move. It’s about protecting your reputation, your customer relationships, and your financial future. By understanding the risks and investing in robust security, you can build a strong defense against email-borne threats and ensure your communications remain confidential and secure.
Transport Layer Security: Building Your Email's Protective Shield
This screenshot from Wikipedia's Transport Layer Security page gives us a visual of how a secure channel is built between your computer and a server. See how TLS creates a protected connection, keeping the data safe from prying eyes? That's the core idea behind how TLS protects your email.
The main takeaway here is the secure channel. This prevents eavesdropping and tampering. Think of it like this: sending a postcard versus sending a sealed letter. TLS effectively transforms your email from that exposed postcard into a secure, sealed message. This leads us to how TLS actually works within the larger world of email security.
The TLS Handshake: A Secure Introduction
Imagine TLS as a secret knock. It's how both sides of an email exchange verify each other's identity before sharing sensitive information. This “secret knock” is technically known as the TLS handshake. It's a series of back-and-forth communications between your email program and the receiving server, all working together to establish a secure, encrypted connection.
Let's say you're sending an email through Gmail. Your email client starts this handshake with Google's servers. This process ensures that both your client and Google's server are who they say they are. It also lets them agree on the specific way they'll encrypt the email.
Spotting TLS in Action: Padlocks and Protocols
How can you actually see TLS working its magic? There are a couple of tell-tale signs within your email client. A padlock icon in your browser's address bar is one common indicator. You should also see https:// at the beginning of the web address instead of http://. That little 's' is short for 'secure', and it indicates that TLS is active.
But seeing a padlock isn't the whole story. For really strong security, you need to know which version of TLS is being used. Older versions like TLS 1.0 and 1.1 have known weaknesses. Modern email services use TLS 1.2 or later for the best protection. Let's take a closer look at the different TLS versions and their security features:
To understand these differences more clearly, let's look at a table summarizing the key aspects of each TLS version:
TLS Version Comparison for Email Security: This table compares different TLS versions and how they stack up in terms of security, how widely they're used, and whether they work well with various email systems.
| TLS Version | Security Level | Adoption Rate | Key Features | Email Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLS 1.0 | Low | Very Low (Deprecated) | Weak ciphers, known vulnerabilities | Limited, not recommended |
| TLS 1.1 | Low | Low (Deprecated) | Improved ciphers, but still vulnerable | Limited, not recommended |
| TLS 1.2 | High | High | Strong ciphers, widely supported | Excellent |
| TLS 1.3 | Very High | Increasing | Most secure, improved performance | Excellent, becoming the standard |
As you can see, TLS 1.2 and 1.3 provide the best security for email. While TLS 1.3 is the most modern and secure, TLS 1.2 is still widely used and provides strong protection. Older versions should be avoided due to known vulnerabilities.
TLS as the Foundation: Why It Matters
TLS isn't just one piece of the email security puzzle; it's the foundation. It establishes the secure channel, protecting the message as it travels from sender to receiver.
This means even if you're using other security measures like S/MIME or PGP, TLS is still critical. Think of it as a secure armored truck carrying a valuable package. Even if the package inside is well-protected, you still need that secure truck to get it safely to its destination. This makes TLS essential for any robust email security plan. Platforms like Typewire prioritize robust TLS implementation for users who want a more secure email experience, offering better protection and peace of mind. By understanding TLS, you can evaluate your own email security and make informed choices about your privacy online.
Email Authentication: Proving Your Messages Are Really From You
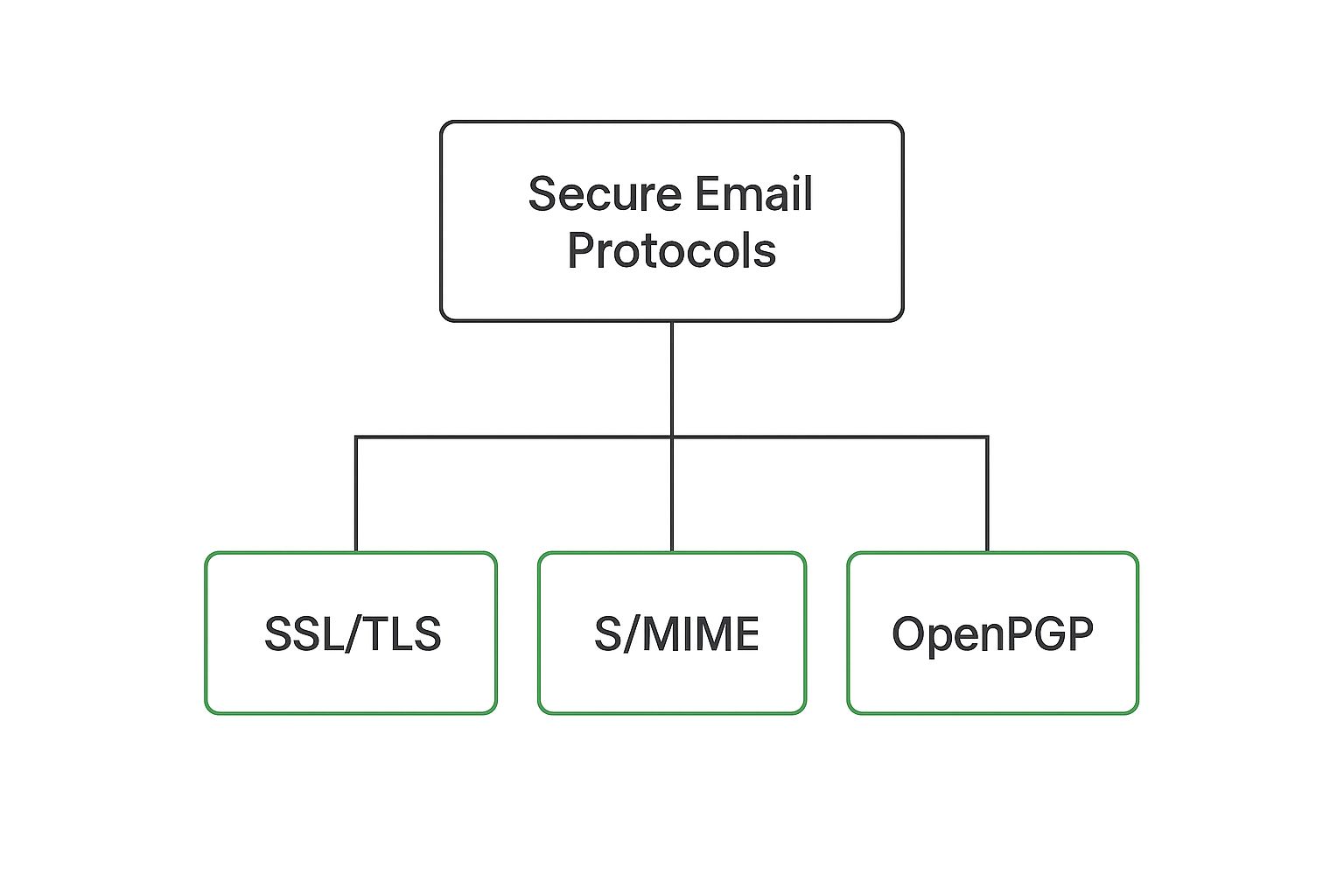
This infographic illustrates how different email security protocols fit together. It shows transport-level security (SSL/TLS), message-level encryption (S/MIME), and end-to-end encryption (OpenPGP) as distinct layers of protection. But what about verifying the sender? That's where email authentication comes in.
The Power Trio: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Imagine arriving at a secure building. You'd probably need multiple forms of ID to get in. Email authentication uses a similar approach, employing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify a sender's identity and protect against spoofing.
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is like the guest list at a party. It tells email servers which mail servers are permitted to send messages on behalf of a particular domain. This helps prevent impersonators.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is like a unique, unforgeable signature on your messages. It cryptographically signs your outgoing emails, verifying their origin and that they haven't been tampered with. This adds a strong layer of assurance for recipients.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is the enforcer. It instructs receiving email servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks. This might involve rejecting suspicious messages, quarantining them, or simply monitoring them for analysis.
Why Implementation Can Be Tricky
Setting up these protocols can be tricky. Configuring them correctly requires technical expertise. It also needs coordination between different teams, like IT, marketing, and security.

Services like EasyDMARC offer tools and support to help manage the complexities of DMARC. This screenshot shows an example of their interface. These resources can be invaluable in navigating the setup and ongoing management of email authentication.
Phishing remains a serious threat, with nearly 9 million attacks reported globally in 2023. While DMARC is increasingly important, adoption is still relatively low. Only about 33.4% of websites had a valid DMARC record, though this saw an 11% increase in 2024. For a deeper look at phishing trends, you can explore these phishing statistics.
Success Stories and Best Practices
Many organizations have successfully implemented these protocols and seen real benefits. Some have dramatically improved email deliverability, while others have thwarted potentially damaging spoofing attacks.
Let's look at a comparison of these key protocols:
Email Authentication Protocol Comparison
| Protocol | Primary Function | Implementation Difficulty | Attack Prevention | Industry Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPF | Specifies authorized mail servers for a domain | Relatively easy | Prevents unauthorized senders from using your domain | Moderate |
| DKIM | Cryptographically signs emails, verifying their origin and integrity | Moderate | Prevents email tampering and spoofing | Moderate |
| DMARC | Defines how receiving servers handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks | More complex | Enforces email authentication policies, strengthens protection against spoofing | Growing, but still relatively low |
This table summarizes the core functions, implementation challenges, and effectiveness of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. While DMARC offers the strongest protection, layering all three protocols provides a robust defense.
Want a more in-depth understanding? We've put together a comprehensive guide: What Is Email Authentication? Your Complete Security Guide. Implementing these protocols is more than just a technical task; it’s a crucial step in protecting your organization from email-based threats. By understanding how SPF, DKIM, and DMARC work, you can significantly bolster your email security. This helps build trust with your recipients and protect your organization’s reputation.
End-to-End Encryption: S/MIME vs. PGP in the Real World

This screenshot from Wikipedia's S/MIME page visually represents how S/MIME uses digital certificates and encryption to protect email messages. See how the sender's certificate encrypts the message? This ensures only the recipient with the right private key can unlock it, highlighting the core concept of public key cryptography used in S/MIME.
This reliance on digital certificates is key. Think of these certificates as digital passports, verifying the sender's identity and providing the cryptographic keys needed for secure communication. However, how these keys are managed is a core difference between S/MIME and its counterpart, PGP.
Key Management: The Heart of the Matter
If TLS is like securing the delivery truck, end-to-end encryption like S/MIME and PGP is like placing the valuable package inside a locked box. Only the recipient has the key.
S/MIME uses a centralized, certificate-based system to simplify key management. Imagine a company issuing employee ID cards. A trusted entity, a Certificate Authority (CA), issues these digital certificates. This simplifies key management, especially for larger organizations.
PGP, however, uses a decentralized, web-of-trust model. It's like exchanging keys directly with people you trust. This offers flexibility but can become complex as your network grows. The sheer volume of daily emails – about 333.2 billion in 2022 – underscores the importance of robust email security. And with about 90% of data breaches stemming from phishing and similar tactics, strong email security is more critical than ever. To explore this further, check out this resource: Learn more about email security protocols.
Usability: The Adoption Hurdle
Encryption is only effective if it's used. Usability often determines whether a secure email protocol is adopted.
S/MIME, with its centralized key management, is generally easier for users. Once a certificate is installed, encryption and decryption happen automatically.
PGP’s flexibility comes with added complexity. Users must grasp key generation, exchange, and management – a potential barrier for non-technical users.
S/MIME in the Corporate World
S/MIME's centralized nature makes it a popular choice for corporations. Imagine managing individual keys for thousands of employees – a logistical nightmare. S/MIME simplifies this with its certificate-based system.
For example, a financial institution might use S/MIME to secure internal emails containing sensitive client data. The CA ensures only authorized personnel can access these messages.
PGP for Enhanced Privacy
PGP's decentralized approach appeals to individuals and organizations prioritizing privacy. Journalists, activists, and whistleblowers often use PGP to protect their communications from prying eyes. This decentralized structure makes it difficult for any single entity to compromise the system.
Choosing the Right Protocol: Practical Considerations
Choosing between S/MIME and PGP depends on your needs and priorities. For large organizations requiring centralized control, S/MIME often makes more sense. For individuals and groups prioritizing privacy and flexibility, PGP might be the better fit.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the best protocol for your specific situation. By considering key management, usability, and practical applications, you can develop a robust email security strategy. Services like Typewire offer flexible options, allowing users to select the security level that best suits their individual or organizational requirements. This ensures your email remains confidential and secure, regardless of your needs.
Your Practical Roadmap to Implementation Success
Implementing secure email protocols can feel like a steep climb, but with a good plan, it's entirely manageable and brings a lot of value. This section offers practical advice for any organization, from small startups to larger companies. We'll also share some real-world experience from IT managers who've been through this process, including their lessons learned and best practices.
Phased Rollouts: Minimizing Disruption
Think about renovating your house all at once. Pretty overwhelming, right? Implementing email security is similar. A phased rollout helps avoid major disruption. Start with a small pilot group, like one team or department. This lets you test the new protocols, find any hiccups, and fine-tune your approach before going company-wide.
For instance, you could start by implementing SPF and DKIM for your marketing team. Once those are running smoothly, add DMARC. Later on, you might consider end-to-end encryption with S/MIME for your most sensitive communications. This step-by-step approach allows for flexibility and keeps your daily work flowing smoothly.
Getting Buy-In: From Leadership to End Users
Successful email security relies on everyone being on board. Start by explaining the importance of these protocols to your leadership team, focusing on the potential risks of not having them. Put those risks into concrete terms, like the cost of a data breach, the need to comply with regulations, or the value of protecting sensitive data. When talking to end-users, highlight the practical benefits, like less spam and fewer phishing attacks. Clear communication and training are essential for a smooth transition.
Measuring Success: The Metrics That Matter
So how do you know if your new email security is actually working? Keep an eye on some key metrics. Track your email deliverability rates, your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC pass rates, and the number of reported phishing attempts. Regular monitoring helps you spot any problems and see how well your efforts are paying off. This data-driven approach ensures your security measures are hitting the mark.
This screenshot shows a section of RFC 5321, the standard that defines the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). The technical details might look intimidating, but it highlights how important it is to follow established standards when setting up your email security. Understanding these standards helps ensure everything works together and strengthens your overall security posture.
Troubleshooting: Practical Guides for Common Issues
Even with the best planning, sometimes things go wrong. Be prepared for common problems like emails not arriving, authentication failures, or users being confused. Create easy-to-follow troubleshooting guides and offer support resources for your team and end-users. Being proactive like this means you can fix problems quickly and efficiently. For hands-on advice about setting up email data loss prevention, see our guide: Data Loss Prevention Email: Real-World Setup Guide.
Choosing the Right Path: Tailoring Your Approach
One size doesn't fit all when it comes to email security. The best approach depends on your organization's specific needs and resources. A small startup might focus on the basics like TLS, SPF, and DKIM. A larger company might need a more involved setup, like end-to-end encryption and more advanced authentication. Consider your budget, your team's technical skills, and your risk tolerance when choosing the best path forward.
Private Hosting: Taking Control of Your Email Security
This screenshot from Typewire’s website emphasizes their dedication to secure and private email. They highlight user control and robust security, showcasing a different approach than large email providers. Typewire clearly focuses on privacy, security, and giving you, the user, control – reflecting a growing demand for email solutions that prioritize these values.
Picking the right security protocols for your email is important, but it's only part of the picture. You also need the right environment. Think of it like building a house. You can have the strongest locks and a top-notch alarm system, but if the foundation is shaky, your security is still at risk. Secure email protocols are your locks and alarms, but private hosting is the solid foundation you need. It offers a level of control you just won’t find with typical email providers.
Enhanced Security Compliance and Customization
Private hosting lets you tailor your email security to fit your specific needs. This is especially important for industries with strict rules, like healthcare. For therapists navigating HIPAA compliance, this is a crucial consideration. Learn more in this guide: HIPAA Compliant Email for Therapists: Secure Practice Guide. With private hosting, you're in the driver's seat, implementing the exact protocols and configurations needed to meet these standards, something often impossible with shared hosting. This fine-grained control lets you create a truly secure email system designed for your specific compliance obligations.
For example, imagine a healthcare provider needing to ensure all internal communication is encrypted to protect patient data and comply with HIPAA. With private hosting, they can configure their server to enforce S/MIME encryption for all internal messages. Similarly, a financial institution could use private hosting to implement specific DMARC policies to defend against sophisticated phishing attacks aimed at their clients.
Improved Privacy Controls and Data Ownership
With private hosting, you own your email data. Unlike big email providers that might scan your emails for advertising or data analysis, private hosting platforms like Typewire put your privacy first. No ads, no tracking, and no data mining means your conversations stay private. This control is crucial for organizations handling sensitive information, providing much greater confidence that their data is safe from prying eyes.
Private hosting also lets you choose where your data lives. This could be your own data center, a specific geographic location, or even servers on your premises. This is essential for organizations with strict rules about where their data can be stored.
Advanced Security Features and Flexibility
Private hosting platforms can implement advanced security measures that aren’t readily available with shared hosting. Think intrusion detection systems, advanced spam filtering, and real-time malware scanning. This proactive approach to security goes beyond the basic email protocols, stopping threats before they even reach inboxes.
You also get more flexibility in how you configure email protocols. For example, you can customize TLS settings to use the strongest encryption and disable older, less secure versions. You can also implement custom DKIM signing policies to improve email authentication. This level of customization is vital for organizations that need tight control over their email security.
Balancing Convenience and Control: The Trade-offs
While private hosting offers significant security benefits, there are trade-offs. Managing a private email server takes technical know-how and resources. It’s definitely more involved than simply using a standard email service. You need to weigh the benefits of increased control against the added responsibility of managing your own email system. However, platforms like Typewire aim to simplify this by providing user-friendly interfaces and helpful support.
By understanding these trade-offs, you can decide if private hosting fits your needs and resources. Private hosting empowers organizations to take charge of their email security, boosting compliance, privacy, and overall protection. This approach allows for a more personalized and robust security strategy, ensuring confidential communication in a world of ever-changing threats.
Building an Email Security Strategy That Evolves
This screenshot from Wikipedia's Email Security page gives us a good bird's-eye view of how different security layers work together to protect emails. It shows how these layers are interconnected, reminding us that email security isn't about one single tool, but a combination of protocols and smart practices. The main takeaway? A multi-layered approach, like a castle with walls, a moat, and guards, offers the strongest protection.
Think about it: a castle with only a wall could be scaled. A castle with just a moat could be crossed with a bridge. But a castle with multiple defenses is far more secure. Email security works the same way.
Email security isn’t something you can set up once and then forget about. It's more like tending a garden. You can't just plant the seeds and walk away expecting a bountiful harvest. You need to water, weed, and adjust to changing weather. Similarly, your email security needs regular care and attention to stay effective against new and emerging threats.
Adapting to the Ever-Changing Threat Landscape
The world of cybersecurity is constantly changing. New phishing tricks, sneaky malware, and even AI-powered attacks pop up all the time. This means your email security has to be flexible and ready to adapt. Organizations that are truly on the ball don't just react to these threats; they try to anticipate them.
A good strategy is to set up a regular security assessment routine. Think of it like a regular health check-up for your email system. This involves reviewing your current security measures, spotting any potential weaknesses, and updating your defenses accordingly. For example, if you're using an older version of TLS (Transport Layer Security), you'll want to upgrade to the latest version for stronger protection.
The Power of Threat Intelligence
Staying one step ahead of these digital bad guys requires solid threat intelligence. This means gathering information about current and future cyber threats. It's like having a weather forecast for the digital world, letting you know when a storm is brewing.
There are many sources of threat intelligence available, but some are definitely better than others. Look for sources that give you practical information, like details about specific software vulnerabilities or new attack methods. Some organizations even share threat intelligence with each other, working together to defend against common enemies.
Monitoring and Response: The Dynamic Duo
Setting up secure email protocols like SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is essential, but it's not the whole story. You also need to keep a close eye on your email traffic for anything suspicious. This means looking for unusual activity, like a sudden increase in spam or phishing attempts.
Effective monitoring means having the right tools and processes in place. Some organizations use automated systems to scan emails for known threats, while others have security experts who manually review any messages that look suspicious.
When a threat is detected, you need to act fast. This could involve blocking suspicious emails, quarantining infected attachments, or even temporarily shutting down affected accounts. The key is to have a clear incident response plan, so you know exactly what to do when something goes wrong.
Building a Future-Proof Email Security Posture
A truly resilient email security strategy takes a holistic approach. It's not just about having the newest software; it's about creating a security-conscious culture throughout your organization. This means educating your employees about best practices, encouraging them to report anything suspicious, and building a sense of shared responsibility for protecting company data.
With AI-powered attacks on the rise, it’s wise to consider using AI-driven security tools. These tools use machine learning to detect and block malicious emails, even brand new ones that haven't been seen before. This adds an extra layer of defense against sophisticated threats.
Looking even further ahead, the development of quantum computing presents both opportunities and challenges. While quantum computers could potentially break our current encryption methods, they also open the door to new, quantum-resistant encryption. Organizations need to start preparing now by keeping up with these developments and exploring potential solutions.
By following these strategies, you can build an email security system that not only protects you today but also prepares you for the challenges of tomorrow. This proactive approach will help keep your email communications confidential, secure, and resilient in the face of ever-evolving threats.
Ready to take control of your email security? Explore Typewire's secure private email hosting platform and see how it can protect your communications. Start your free 7-day trial at https://typewire.com.

