Choosing an email host goes far beyond simply getting a custom you@yourdomain.com address. It's a critical decision for protecting your most sensitive communications from surveillance, data mining, and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Standard "free" email services often treat your data as the product, scanning your private messages to fuel advertising algorithms. For businesses and privacy-conscious individuals, this trade-off is unacceptable. A dedicated hosted email platform provides the essential control and security needed to maintain confidentiality.
This guide cuts through the marketing noise to deliver a detailed analysis of the best email hosting providers, with a sharp focus on their privacy architecture, security features, and operational integrity. We will dive into crucial details like end-to-end encryption, data residency policies, two-factor authentication methods, and advanced anti-spam and anti-phishing capabilities.
Our goal is to help you find a hosted email platform that truly safeguards your digital correspondence, whether you're a small business owner, an IT administrator, or simply someone fed up with invasive ads. While this article focuses specifically on email, securing your inbox is just one part of a larger digital safety strategy. We recommend also reviewing general website security best practices to ensure comprehensive protection. Each option below includes screenshots, direct links, and a practical breakdown to help you make an informed choice.
1. Typewire
Best for Privacy-Focused Businesses and Canadian Data Residency
Typewire stands out as one of the best email hosting providers for users who prioritize data sovereignty, privacy, and operational independence. Its entire infrastructure is built on privately owned data centers in Vancouver, Canada, completely avoiding third-party cloud vendors like AWS or Google Cloud. This structure ensures your data remains on Canadian soil, governed by PIPEDA protections, and is never mined, sold, or scanned for advertising purposes. For businesses and individuals concerned with data residency and escaping the reach of US cloud legislation, this is a critical security advantage.
The platform is engineered for security and ease of use, making it ideal for SMBs, IT administrators, and remote teams. The user management dashboard is straightforward, and the service provides fast migration tools to simplify the transition from other hosted email platforms. With a strict ad-free, zero-tracking policy, Typewire delivers a clean, private, and focused communication experience.
Key Features and Analysis
Typewire’s feature set is built on a foundation of robust security and practical business tools.
- Privacy and Data Sovereignty: The commitment to Canadian-only, privately owned hardware is its most significant differentiator. This architecture provides a strong legal and technical shield for your data's privacy.
- Default Security Protocols: End-to-end encryption and advanced anti-spam and virus filters are enabled by default, not as optional add-ons. This proactive security approach ensures high deliverability and protects users from threats out of the box.
- Business-Centric Tools: Premium plans support up to 5 custom domains and 50 aliases per user, offering excellent flexibility for managing multiple brand identities or team roles without extra cost.
Onboarding and Support
Typewire simplifies the switching process with a 7-day free trial for up to five users, allowing teams to test the platform thoroughly. For larger teams, a 7-day refund guarantee is available. Their 24/7 support and clear migration guides are designed to help new users set up their custom domains and transfer existing emails with minimal disruption, making it a reliable choice for businesses that cannot afford downtime.
| Feature Highlights | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Data Hosting | Exclusively Canadian, privately owned data centers. |
| Primary Focus | Privacy, data sovereignty, security. |
| Custom Domains | Supported on premium plans. |
| Onboarding | 7-day free trial or refund guarantee. |
| Support | 24/7 customer support. |
Pros:
- Strict privacy-first architecture with Canadian data residency.
- Security features like E2EE and advanced spam filtering are standard.
- Business-ready with multi-domain support and generous aliasing.
- Low-friction onboarding with a free trial and migration support.
Cons:
- Detailed per-user pricing is not immediately visible on the website.
- The most valuable features, like custom domains, are limited to premium plans.
2. Google Workspace (Gmail for Business)
Google Workspace bundles business-grade Gmail with a full productivity suite, making it one of the best hosted email platforms for organizations that prioritize integration and user familiarity. It leverages Google's robust infrastructure to deliver exceptional uptime, best-in-class spam filtering, and near-perfect email deliverability. While the consumer version of Gmail has privacy trade-offs, the business version provides stronger protections and a commitment against using your data for ad targeting.
From a security standpoint, Workspace provides strong administrative controls, including two-factor authentication enforcement, user activity logs, and email routing rules. Higher-tier plans add advanced security features like Google Vault for eDiscovery and archiving, plus Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to prevent sensitive information from being shared externally. This makes it a solid choice for businesses needing to meet specific compliance standards. The platform's main privacy consideration is its US-based hosting, which subjects data to US laws.
Key Features:
- Integrated Suite: Seamlessly combines custom domain email with Drive, Docs, Sheets, and Meet.
- Advanced Security: Offers robust admin controls, with options for Vault, DLP, and advanced security center on higher tiers.
- Excellent Uptime & Deliverability: Backed by Google's global network, ensuring reliable service.
Pricing:
- Business Starter: $6 per user/month
- Business Standard: $12 per user/month
- Business Plus: $18 per user/month
Best For: Businesses of all sizes seeking a powerful and highly integrated hosted email platform with top-tier reliability and strong security controls.
3. Microsoft 365 for Business (Exchange Online)
Microsoft 365 stands as a titan among the best email hosting providers, bundling its enterprise-grade Exchange Online email with the familiar Office productivity suite. It is the go-to solution for organizations deeply integrated into the Windows ecosystem, offering a mature and secure hosted email platform ideal for businesses with stringent regulatory and security requirements.
From an administrative perspective, the platform’s strength lies in its highly granular controls over email security and data governance. Administrators can enforce multi-factor authentication, configure sophisticated mail flow rules, and leverage Microsoft Defender for advanced threat protection against phishing and malware. Higher-tier plans include powerful eDiscovery and archiving tools, crucial for legal and compliance needs. While the licensing structure can be complex, its deep security controls and seamless Office integration provide significant value for businesses prioritizing robust data protection policies.
Key Features:
- Deep Office Integration: Unparalleled synergy with Outlook, Teams, OneDrive, and desktop Office applications.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Granular admin policies, MFA, and optional Microsoft Defender for advanced threat protection.
- Compliance & Archiving: Offers robust eDiscovery, litigation hold, and data retention tools on higher-tier plans.
Pricing:
- Business Basic: $6 per user/month
- Business Standard: $12.50 per user/month
- Business Premium: $22 per user/month
Best For: Organizations standardized on the Microsoft ecosystem that require a powerful, enterprise-level hosted email platform with top-tier security and compliance controls.
4. Zoho Mail (and Zoho Workplace)
Zoho Mail carves out its space among the best email hosting providers by offering a remarkably feature-rich and privacy-focused service at an aggressive price point. Unlike many competitors, Zoho’s hosted email platform is built around secure, ad-free communication, making it an excellent choice for startups and SMBs. Crucially, Zoho has a strong privacy policy, guaranteeing it will never scan user data for advertising purposes, a key differentiator from many US-based tech giants.
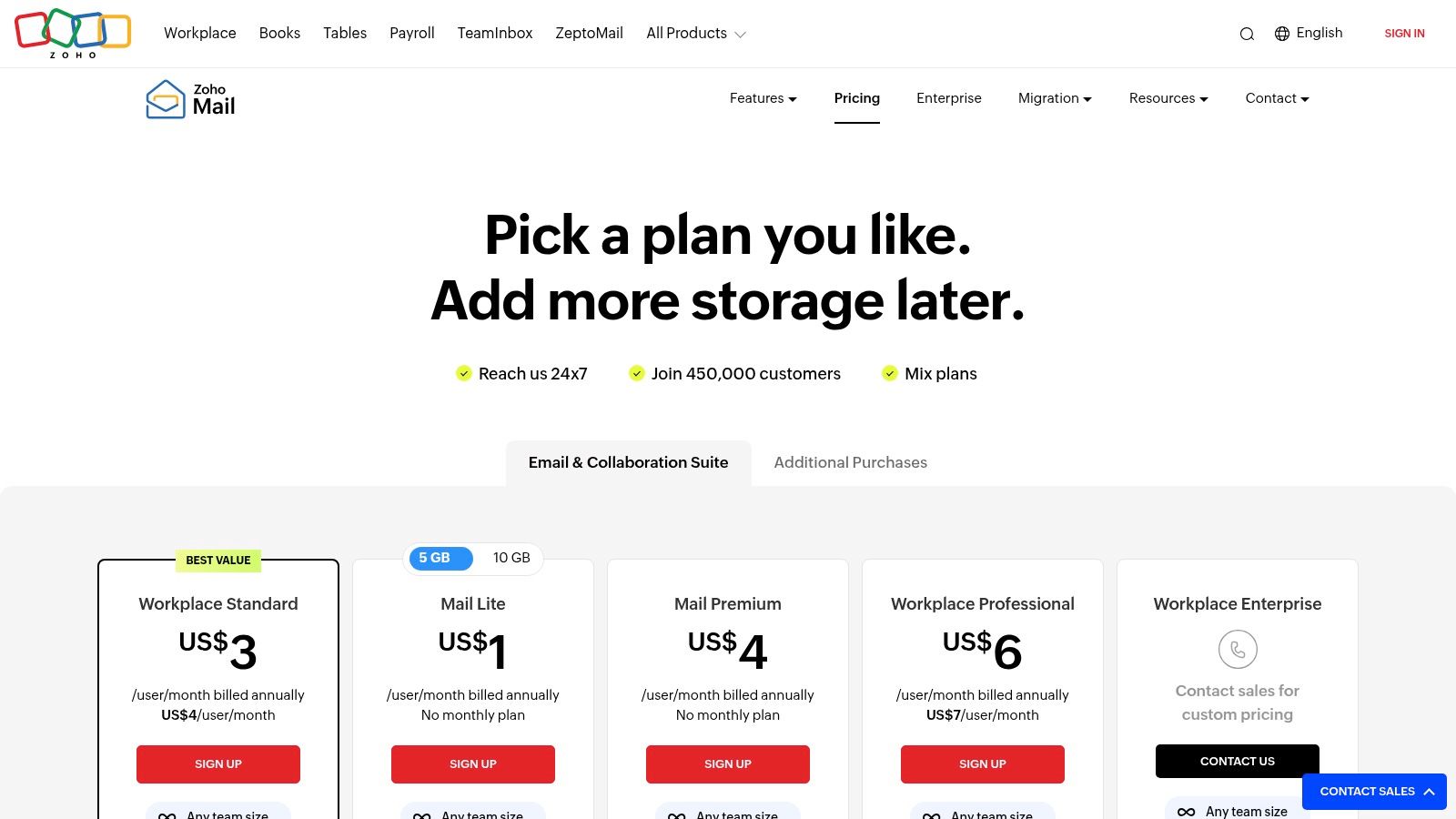
The platform’s flexibility allows businesses to choose data centers in the US, EU, India, Australia, or China, giving organizations control over data residency. On the security front, Zoho supports S/MIME encryption, email retention policies, and eDiscovery on higher-tier plans, addressing critical compliance and data protection needs. The comprehensive admin panel offers granular control over security policies, user permissions, and email routing, making it a powerful and private email hosting solution.
Key Features:
- Data Residency Options: Allows customers to choose their data center location for compliance and privacy.
- Strong Admin Controls: Provides comprehensive tools for user management, security policies, and anti-spam configurations.
- Privacy-First Approach: Guarantees an ad-free experience with a commitment to never scan emails for data mining.
Pricing:
- Mail Lite: Starts at $1 per user/month (billed annually)
- Mail Premium: Starts at $4 per user/month (billed annually)
- Workplace Standard: Starts at $3 per user/month (billed annually)
Best For: Startups, SMBs, and privacy-conscious businesses seeking an affordable, secure, and scalable email hosting solution with powerful administrative capabilities and data residency options.
5. Proton for Business
Proton for Business is a premier hosted email platform for organizations that place the highest value on privacy and security. Hosted in Switzerland under strict privacy laws, it offers end-to-end encryption for all emails by default, meaning not even Proton can read your messages. This zero-access architecture makes it a powerful choice for businesses handling sensitive client data, legal communications, or proprietary information where data privacy is a non-negotiable requirement.
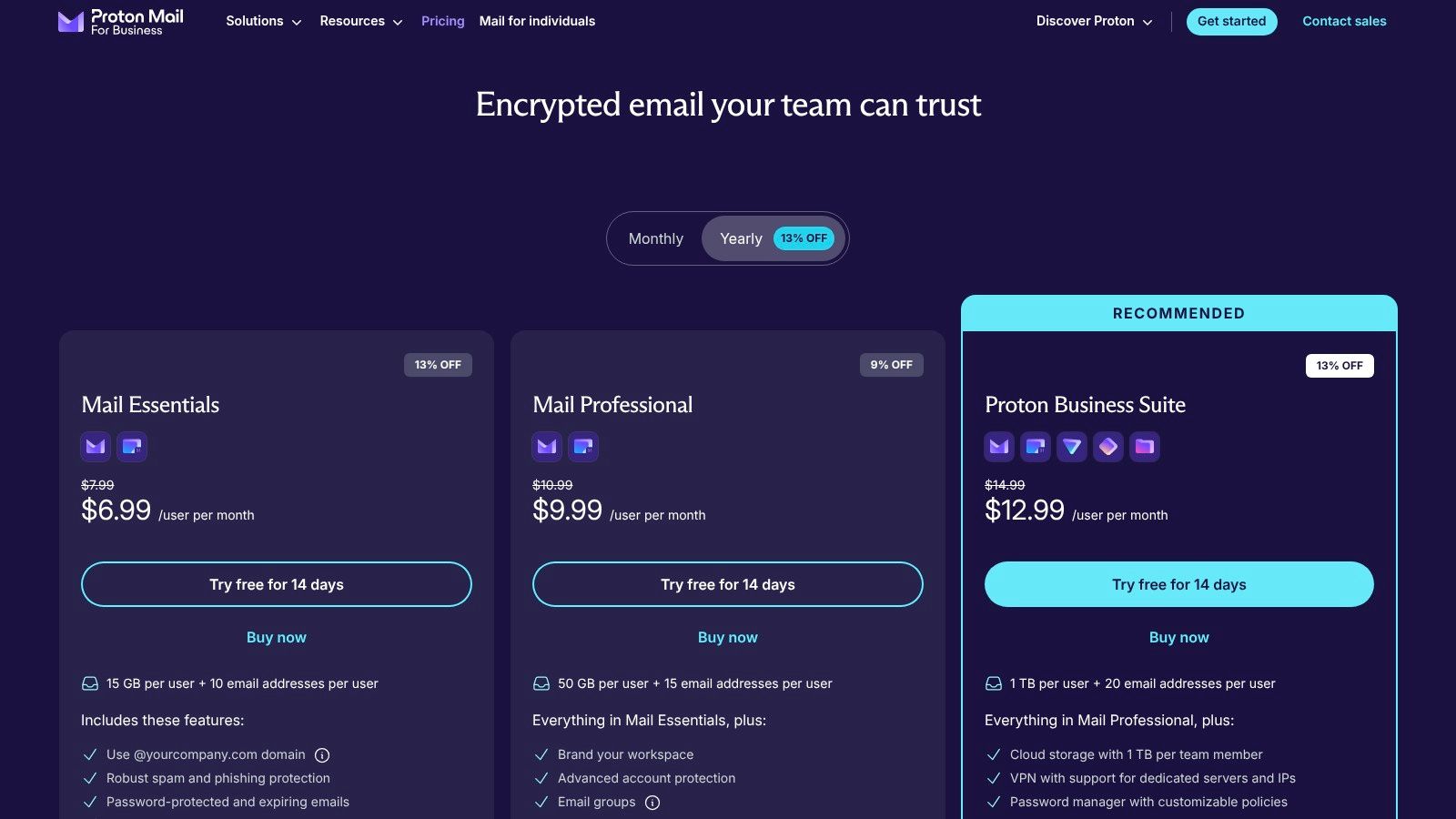
The platform bundles Proton Mail with its secure ecosystem, including Calendar, Drive, and VPN, creating a complete, privacy-focused productivity suite. Administrators have access to essential controls for user management, custom domain configuration, and organizational security policies. While its third-party integration capabilities are not as extensive as Google's or Microsoft's, Proton’s unwavering commitment to email security and privacy makes it a standout. For those specifically seeking the best hosted email for privacy, Proton is a leader.
Key Features:
- Zero-Access Encryption: End-to-end encryption is automatically applied, ensuring maximum message privacy.
- Integrated Secure Suite: Includes encrypted Calendar, Drive, and VPN in business plans.
- Swiss Privacy: All data is protected by strict Swiss privacy laws, outside of US and EU jurisdiction.
Pricing:
- Mail Essentials: €6.99 per user/month
- Business: €10.99 per user/month
Best For: Healthcare providers, legal firms, journalists, and any business prioritizing data sovereignty and default end-to-end encryption for their communications.
6. Fastmail (Business)
Fastmail is an independent, privacy-focused email hosting provider that delivers a fast, clean, and ad-free experience. Based in Australia, it has a long-standing reputation for robust performance and a strong commitment to user privacy, making it a top choice for those looking to de-google their business communications. As a dedicated hosted email platform, it avoids the data-mining business models of larger competitors.
From a security perspective, Fastmail offers strong phishing protection and mandatory two-factor authentication, along with robust administrative controls for user management. The platform is engineered for speed, with a highly responsive web interface and powerful search capabilities. While it lacks native document editors, its email-centric approach is a strength for businesses that have already established their own productivity stack and simply need one of the best and most private email hosting providers available.
Key Features:
- Privacy-Focused: An independent provider that does not scan emails for advertising purposes.
- Superior Performance: Extremely fast web and mobile applications with excellent search functionality.
- Strong Security Standards: Enforces 2FA and provides robust spam and phishing protection.
Pricing:
- Standard: $5 per user/month
- Professional: $9 per user/month
Best For: Privacy-conscious businesses and teams that need a reliable, high-performance, and secure email platform without a bundled office suite.
7. IONOS Email Hosting
IONOS Email Hosting provides an extremely budget-friendly entry point for individuals and small businesses needing professional, domain-based email. It stands out as one of the best email hosting providers for those prioritizing affordability and simplicity in a hosted email platform. The service focuses on core email functionality, offering ad-free webmail, robust spam filtering, and the essential security of TLS/SSL encryption for data in transit.
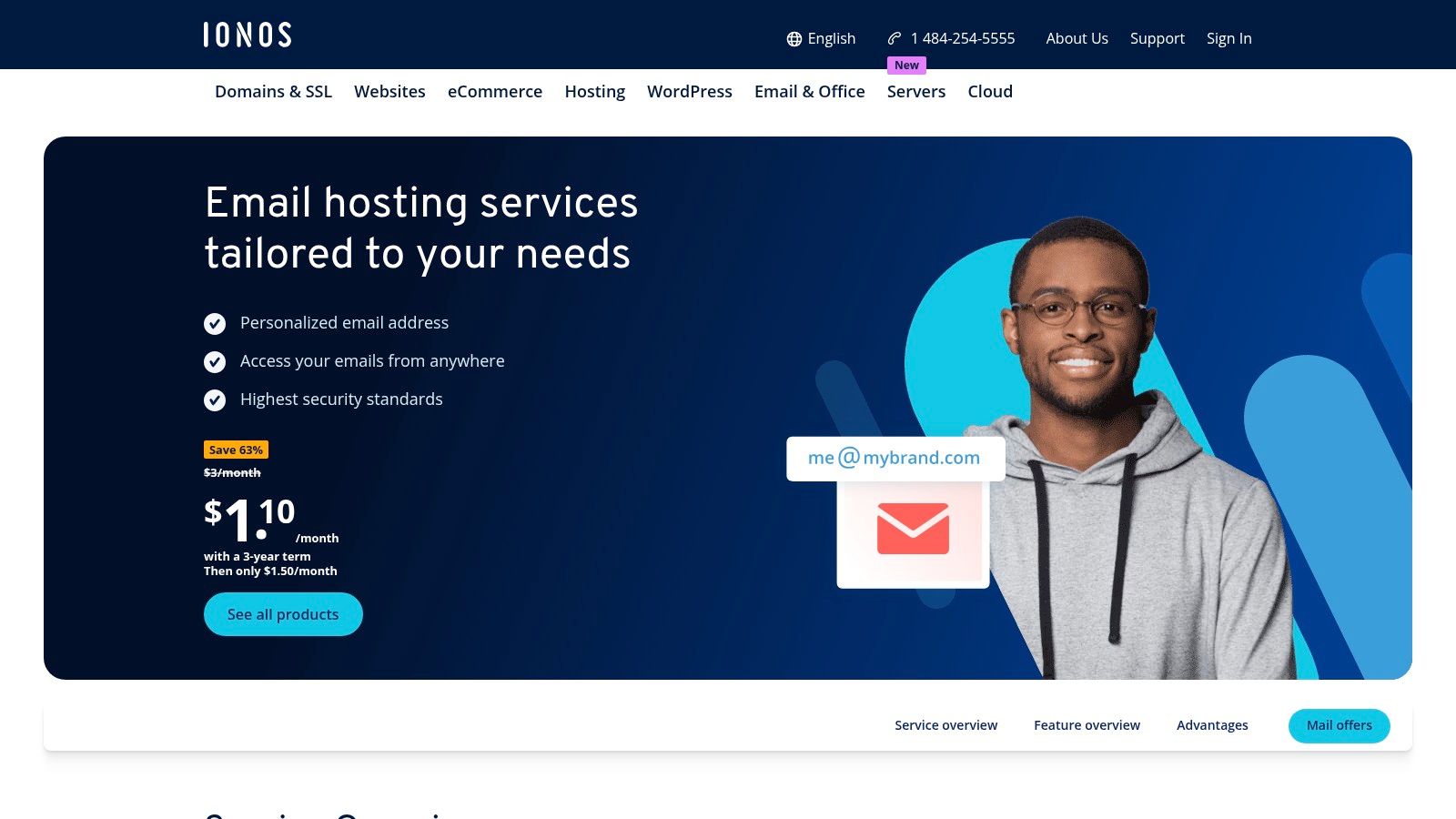
From a security perspective, IONOS includes automatic virus scanning on all incoming messages and provides server-side spam protection to keep inboxes clean. While it lacks the advanced security controls of enterprise-grade platforms, its straightforward management console makes it easy to set up mailboxes and aliases. The primary drawback is that its incredibly low introductory prices often require long-term commitments and increase significantly upon renewal. However, for a startup needing a secure, custom email address on a tight budget, it's a very compelling and accessible option.
Key Features:
- Ad-Free Webmail: Clean and professional webmail interface without intrusive advertising.
- Spam & Virus Protection: Built-in filters to protect mailboxes from common threats.
- Secure Data Centers: Operates ISO 27001-certified data centers, ensuring a high standard of physical and network security.
Pricing:
- Mail Basic 1: Starts at $1 per user/month
- Mail Business 25: Starts at $4 per user/month
Best For: Individuals, freelancers, and small businesses seeking a low-cost, secure, and no-frills professional email solution with a custom domain.
8. Rackspace Email (Hosted Email)
Rackspace Email offers a straightforward, business-class hosted email solution that prioritizes reliability and expert support. It is one of the best email hosting providers for teams that require dependable, secure email without the added complexity or cost of bundled applications. The platform is built on a foundation of strong uptime guarantees and robust, premium anti-spam and anti-virus protection, ensuring business communications remain secure and accessible.
The service provides generous 25 GB mailboxes and includes a free migration service managed by experts, a significant security advantage for businesses looking to switch providers with minimal risk of data loss. While it lacks the integrated collaboration tools of larger suites, its focused approach makes it a predictable and cost-effective option for core email security. The availability of 24x7x365 "Fanatical Experience" support is a key differentiator, offering direct access to email specialists for any technical issues. The optional archiving add-on helps businesses meet compliance and data retention requirements.
Key Features:
- Expert Migration & Support: Offers free, managed migrations and renowned 24x7x365 expert customer support.
- Security & Reliability: Includes premium spam/virus protection and a 100% uptime guarantee service level agreement (SLA).
- Focused Email Service: Provides a simple, powerful email solution with optional add-ons like archiving and mobile sync.
Pricing:
- Rackspace Email: $2.99 per user/month
- Rackspace Email Plus: $3.99 per user/month (adds 30 GB file storage and mobile sync)
- Archiving: Add $6.99 per user/month
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses that need a highly reliable, secure, and professionally supported hosted email platform without the overhead of a full productivity suite.
9. Namecheap Private Email (Professional Business Email)
Namecheap offers one of the most cost-effective entry points into professional hosted email, making it an excellent choice for freelancers and startups focused on security on a budget. The platform is built on Open-Xchange's modern webmail interface and is hosted in secure US-based data centers. It provides a simple, reliable service focused on delivering branded email (@yourdomain.com) securely.
From a security and privacy standpoint, Namecheap includes robust anti-spam protection and two-factor authentication (2FA) options to protect user accounts from unauthorized access. The service is ad-free and maintains a strong privacy policy. While it lacks the advanced security tools of larger providers like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, it covers the essentials effectively. Its primary strengths are its extremely low annual pricing and an exceptionally long 60-day free trial, giving users ample time to evaluate the security and performance.
Key Features:
- Affordable Pricing: Extremely competitive annual plans that are ideal for new businesses and sole proprietors.
- Generous Trial Period: A 60-day free trial allows for extensive testing of the platform's security features.
- Solid Security Basics: Includes 2FA, anti-spam protection, and is hosted on secure infrastructure.
Pricing:
- Starter: From $1.24 per month (1 mailbox, 5 GB storage)
- Pro: From $3.24 per month (3 mailboxes, 30 GB storage)
- Ultimate: From $5.24 per month (5 mailboxes, 75 GB storage)
Best For: Freelancers, solopreneurs, and small businesses needing a simple, low-cost, and secure branded email solution without bundled office apps.
10. DreamHost Professional Email
DreamHost offers a straightforward and affordable professional email hosting solution, making it one of the best email hosting providers for individuals and small businesses seeking simplicity and value. It's an excellent choice for those who already use DreamHost for web hosting, as it integrates seamlessly into their existing control panel. The hosted email platform focuses on core functionality without the complexity or cost of a full productivity suite.
From a security and privacy perspective, DreamHost provides robust spam, virus, and phishing filters to keep your inbox clean and secure. The company maintains a strong anti-spam policy and does not read or scan emails for advertising. Users get a generous 25 GB of storage per mailbox, which is substantial for the price point. The main trade-off is the lack of advanced enterprise security features like eDiscovery and archiving, making it less suitable for organizations with strict compliance needs. However, for a simple, private, and reliable email service, it excels.
Key Features:
- Generous Storage: Provides 25 GB of storage for each mailbox.
- Strong Security: Includes built-in spam, virus, and phishing filtering.
- Privacy Commitment: Ad-free service with a policy against scanning emails for advertising.
Pricing:
- Monthly Plan: $1.99 per mailbox/month
- Annual Plan: $1.67 per mailbox/month (billed annually)
Best For: Small businesses and website owners who need a cost-effective, no-frills hosted email platform with ample storage and solid security basics.
Visit DreamHost Professional Email
11. GoDaddy Microsoft 365 Email (with Advanced Email Security bundles)
GoDaddy offers a simplified path to Microsoft 365, making it one of the best email hosting providers for customers who value convenience and integrated security. It bundles Microsoft's powerful and secure Exchange email platform with its own streamlined management interface and support. This is particularly useful for small businesses that want a single point of contact for their domain and email security needs.
The primary security advantage is GoDaddy's curated packages, which include options for Advanced Email Security and Email Archiving. These add-ons provide enhanced protection against phishing, malware, and data loss, and can be purchased as part of a HIPAA-compliant plan, which is crucial for businesses in the healthcare sector. While this simplified bundling is convenient, it offers less granular control over licensing than purchasing directly from Microsoft. Furthermore, renewal rates can be significantly higher, which is a key consideration for long-term budgeting.
Key Features:
- Integrated Management: Simplifies purchasing and support for existing GoDaddy domain customers.
- Security & Compliance Bundles: Offers pre-packaged options for advanced security, email archiving, and HIPAA compliance.
- Microsoft 365 Foundation: Built on the reliable and feature-rich Microsoft Exchange platform, inheriting its enterprise-grade security.
Pricing:
- Email Essentials (Email Only): Starts at $1.99 per user/month (renews higher)
- Email Plus (Email & More Storage): Starts at $4.99 per user/month (renews higher)
- Business Professional (Full Office Suite): Starts at $8.99 per user/month (renews higher)
Best For: Small businesses and solo entrepreneurs who manage their domains with GoDaddy and prefer a simplified, one-stop-shop approach for professional email and security.
Visit GoDaddy Microsoft 365 Email
12. Bluehost Professional Email
Bluehost offers a highly affordable, Titan-powered email hosting solution designed for individuals and small businesses who already use its web hosting services. This makes it one of the best email hosting providers for those seeking a secure, budget-friendly hosted email platform. The service provides a professional email address at your custom domain, along with a modern webmail interface provisioned directly from the Bluehost dashboard.
While it lacks the advanced compliance tools of enterprise suites, Bluehost Professional Email focuses on core security features. Security is handled with standard anti-spam and anti-virus protection to safeguard your inbox from common threats. Its primary advantage is the seamless setup process for existing Bluehost customers and its extremely competitive introductory pricing. However, users should be mindful that it is an email-only service, and renewal rates are typically higher than the initial promotional price, a common practice in the hosting industry.
Key Features:
- Easy Provisioning: Simple, one-click setup for domains hosted with or purchased through Bluehost.
- Built-in Security: Includes standard anti-spam and virus protection for all mailboxes.
- Affordable Entry Point: Very low introductory pricing makes it accessible for new businesses and solopreneurs needing secure email.
Pricing:
- Professional Email: Starts around $2.99 per user/month (introductory)
- Professional Email Plus: Starts around $4.99 per user/month (introductory)
Best For: Existing Bluehost customers and small businesses needing a cost-effective, straightforward professional email solution with essential security features.
Visit Bluehost Professional Email
Top 12 Email Hosting Comparison
| Provider | Core features | UX & Reliability | Pricing & Value | Target & USP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typewire 🏆 | E2E encryption; advanced anti‑spam; custom domains (premium); Canadian‑hosted | Responsive web & mobile; fast; 24/7 support; ★★★★☆ | Transparent tiers; 7‑day free trial; 💰💰 | 👥 Privacy‑conscious users & SMBs; ✨ no tracking, privately owned Vancouver data centres |
| Google Workspace (Gmail for Business) | Custom‑domain Gmail; Drive/Docs/Meet; admin controls | Familiar UI; excellent uptime & deliverability; ★★★★★ | Per‑user pricing (scales); trials; 💰💰💰 | 👥 Teams needing collaboration & integrations; ✨ vast ecosystem |
| Microsoft 365 (Exchange Online) | Exchange email, Teams, Office apps; granular compliance | Deep Outlook & Office integration; enterprise security; ★★★★★ | Flexible SKUs; licensing complexity; 💰💰💰 | 👥 Enterprises/Windows shops; ✨ compliance & Defender integration |
| Zoho Mail (Workplace) | Mail‑only & Workplace suites; S/MIME; migration tools | Solid web/mobile; mature admin tools; ★★★★☆ | Aggressive pricing; regional plans; 💰 | 👥 Startups & SMBs on budget; ✨ mix‑and‑match plans |
| Proton for Business | Zero‑access E2EE; custom domains; Mail+VPN+Drive bundles | Privacy‑first apps; priority support; ★★★★☆ | Premium privacy pricing; trials/money‑back; 💰💰 | 👥 Privacy‑focused teams; ✨ Swiss hosting & end‑to‑end encryption |
| Fastmail (Business) | Custom domains; shared calendars/contacts; strong search | Very fast web & mobile; excellent support; ★★★★☆ | Email‑centric pricing; good value; 💰💰 | 👥 Teams wanting fast, focused email; ✨ best‑in‑class search |
| IONOS Email Hosting | Single or multi mailboxes; spam filtering; optional domain | Ad‑free webmail; basic features; ★★★☆☆ | Very low intro pricing (promos); 💰 | 👥 Small teams/individuals on budget; ✨ domain + email bundling |
| Rackspace Email (Hosted Email) | 25 GB mailboxes; premium spam/virus; archiving add‑ons | Strong SLAs & 24/7 support; ★★★★☆ | Competitive per‑mailbox pricing; predictable; 💰💰 | 👥 Teams needing reliable hosted email; ✨ SLAs & dedicated support |
| Namecheap Private Email | Starter/Pro/Ultimate mailboxes; anti‑spam; mobile sync | Modern webmail; long 60‑day trial; ★★★☆☆ | Very low annual pricing; 💰 | 👥 Freelancers & small businesses; ✨ long free trial & low cost |
| DreamHost Professional Email | 25 GB mailbox; IMAP/POP; spam & phishing filters | Simple setup; bundles with hosting; ★★★☆☆ | Low per‑mailbox price; flexible billing; 💰 | 👥 DreamHost users; ✨ generous entry‑level storage |
| GoDaddy Microsoft 365 Email | Resold M365 bundles; security & HIPAA options | Streamlined purchase & support; ★★★☆☆ | Convenient bundles; renewal variability; 💰💰 | 👥 GoDaddy domain customers; ✨ simplified purchase & add‑ons |
| Bluehost Professional Email | Titan webmail; 10–50 GB options; read receipts & mobile apps | Feature‑rich webmail; easy provisioning; ★★★☆☆ | Very low pricing for customers; 💰 | 👥 Bluehost customers & small businesses; ✨ smooth dashboard provisioning |
Making the Right Choice for Your Email Privacy
Navigating the landscape of the best email hosting providers can feel overwhelming, but the journey boils down to a clear assessment of your core needs for privacy and security. As we've explored, the market is broadly segmented, catering to distinctly different priorities. Your final choice hinges on which of these priorities you value most: comprehensive integration, budget-friendliness, or uncompromising privacy and security.
Aligning Your Choice with Your Priorities
For organizations needing deep integration, Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 offer unparalleled collaboration tools with robust, enterprise-grade security controls, making them the default for many businesses.
Conversely, if cost is your primary driver, providers like Zoho Mail, IONOS, and Namecheap deliver exceptional value. They provide secure, professional hosted email with custom domain support at a fraction of the cost, making them ideal for startups and small businesses prioritizing security on a budget.
However, for a growing number of users and businesses, privacy is the non-negotiable feature. This is where independent providers like Typewire, Proton for Business, and Fastmail truly shine. These hosted email platforms are architected from the ground up to protect user data, not monetize it. They offer features like end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge principles, and a commitment to data sovereignty that you simply won't find in the ad-driven models of big-tech competitors.
Actionable Steps to Your Final Decision
Before you commit to a hosted email platform, it is crucial to move from analysis to practical application. Here’s a simple framework to guide your final steps:
- Audit Your Security Needs: Identify the sensitivity of your data and any regulatory requirements (like HIPAA or GDPR). This will determine whether you need features like end-to-end encryption, data residency options, or advanced archiving. Check integrations with your existing top contact management software to ensure a secure, uninterrupted workflow.
- Leverage Free Trials: Words on a page are no substitute for hands-on experience. Almost every provider on our list offers a free trial or a money-back guarantee. Use this opportunity to test the user interface, configure security settings like 2FA, and assess the mobile app's performance.
- Evaluate the Migration Process: How easy will it be to move your existing emails, contacts, and calendar events securely? Some providers offer one-click migration tools or managed services, while others may require a more manual approach. Ensure the process aligns with your team's technical comfort level to avoid data loss.
Ultimately, your email is more than just a communication tool; it's a digital extension of your professional identity and a repository for sensitive information. Choosing a hosted email platform that respects and protects this critical asset is one of the most important investments you can make for your business or personal security. The right provider empowers you with control, security, and peace of mind.
Ready to prioritize privacy without sacrificing performance? Typewire is built for businesses and professionals who demand a secure, ad-free, and private email experience. Reclaim control over your most important communications with a platform designed to protect your data, not profit from it. Try Typewire today and experience email as it should be.