If you’re wondering, "why am I getting so many junk emails," you're not just dealing with an annoyance; you're facing a symptom of a larger issue related to your email security and privacy. The short answer is that your email address has been exposed online. This isn't your fault—it's the consequence of a digital world where personal data is a commodity. Your address was likely harvested by bots, sold after a data breach, or shared when you signed up for a service, turning your inbox into a prime target.
Your inbox has essentially become a billboard for a massive, automated spam industry that thrives on weak email security.
Why Your Inbox Is a Constant Security Target

It helps to think of your email address not as a private mailbox, but as a digital identifier that spammers and cybercriminals actively hunt for. Every time you post it in a forum, list it on a social media profile, or sign up for a service with weak privacy policies, you increase your digital footprint. Spammers use automated bots that crawl the web 24/7, harvesting these addresses to build massive distribution lists.
Once your email is on one of these lists, it's sold and resold on shady online marketplaces. This is how a single data breach at a company you used years ago can suddenly open the floodgates to junk mail from countless sources, directly compromising your email security.
The Cycle of Data Exposure and Junk Mail
Here’s a breakdown of how your email privacy is breached, leading to an inbox full of spam.
Top Reasons Your Email Security Is Compromised
| Privacy Breach Source | How It Compromises Your Security | Typical Junk Mail You Receive |
|---|---|---|
| Data Breaches | A company's database is hacked, and your email is stolen along with other personal data. | Sophisticated phishing scams pretending to be from banks, fake invoices, or "urgent" security alerts designed to steal credentials. |
| Email Harvesting | Your email is publicly visible on a website or social media and is scraped by automated bots. | Unsolicited marketing, adult content spam, and fraudulent get-rich-quick schemes. |
| Unsecure List Sharing | You sign up for a service, and they sell or share your email with third-party "partners" without robust privacy controls. | Promotions from companies you've never heard of, often related to your interests or browsing history. |
| Unsafe Unsubscribe Links | Clicking "unsubscribe" on a malicious email confirms your address is active, validating you as a target for more spam. | A sudden spike in junk from various sources after you tried to opt out of a single list. |
Understanding this cycle is the first step toward strengthening your email privacy and security.
How Your Email Platform Impacts Your Security
The email platform you choose is your first line of defense. Many free email services offer basic spam filtering, but their business model often relies on data mining for advertising purposes. This focus on monetization can create fundamental privacy gaps that spammers exploit. Your inbox becomes a battleground where your provider’s filters are constantly trying to catch up with spammers' latest tactics.
In contrast, secure hosted email platforms are built on a foundation of privacy and security. Their business model is to protect your data, not profit from it. They provide a fortified environment designed to prevent junk mail from ever reaching you.
Your overflowing inbox is a direct symptom of your digital footprint and the security posture of your email provider. The more exposed your email is and the weaker your platform's privacy focus, the larger the target you become.
Getting a handle on these core security issues—data exposure, platform vulnerabilities, and the economics of spam—is crucial. It shifts the perspective from being a random victim to understanding you're up against an industrial-scale system. From here, you can implement strategies to truly secure your inbox and reclaim your digital privacy.
How Spammers Get a Hold of Your Email Address

Spammers employ systematic methods to acquire your email address. Think of your online activity as leaving a trail of digital breadcrumbs. Every public comment, forum post, or social media profile containing your email is a breadcrumb for their automated bots.
These email harvesting bots are relentless scripts that crawl the public internet with one simple goal: scrape any text that follows the name@domain.com format. The more places your address is publicly visible, the more likely it is to be captured and added to a spammer's database, undermining your email privacy.
The Dark Marketplace of Data Breaches
Even if you meticulously guard your email address from public view, your security is still at risk from third-party vulnerabilities. When a company you trust is hacked, cybercriminals steal entire user databases. These stolen lists—packed with email addresses, passwords, and other sensitive information—are then sold on the dark web.
This is a primary reason for sudden, overwhelming floods of junk email. A single data breach can distribute your email address to spammers globally, permanently compromising its security.
The moment your email appears in a data breach, it ceases to be private. It becomes a commodity—a product to be bought, sold, and exploited by any cybercriminal willing to pay for access to a validated target.
These lists are a goldmine for spammers because they contain verified, active email addresses. For them, buying a list from a recent breach is like acquiring a guaranteed roster of potential victims. To learn more about this process, our guide explains what data mining is and how it impacts your email privacy.
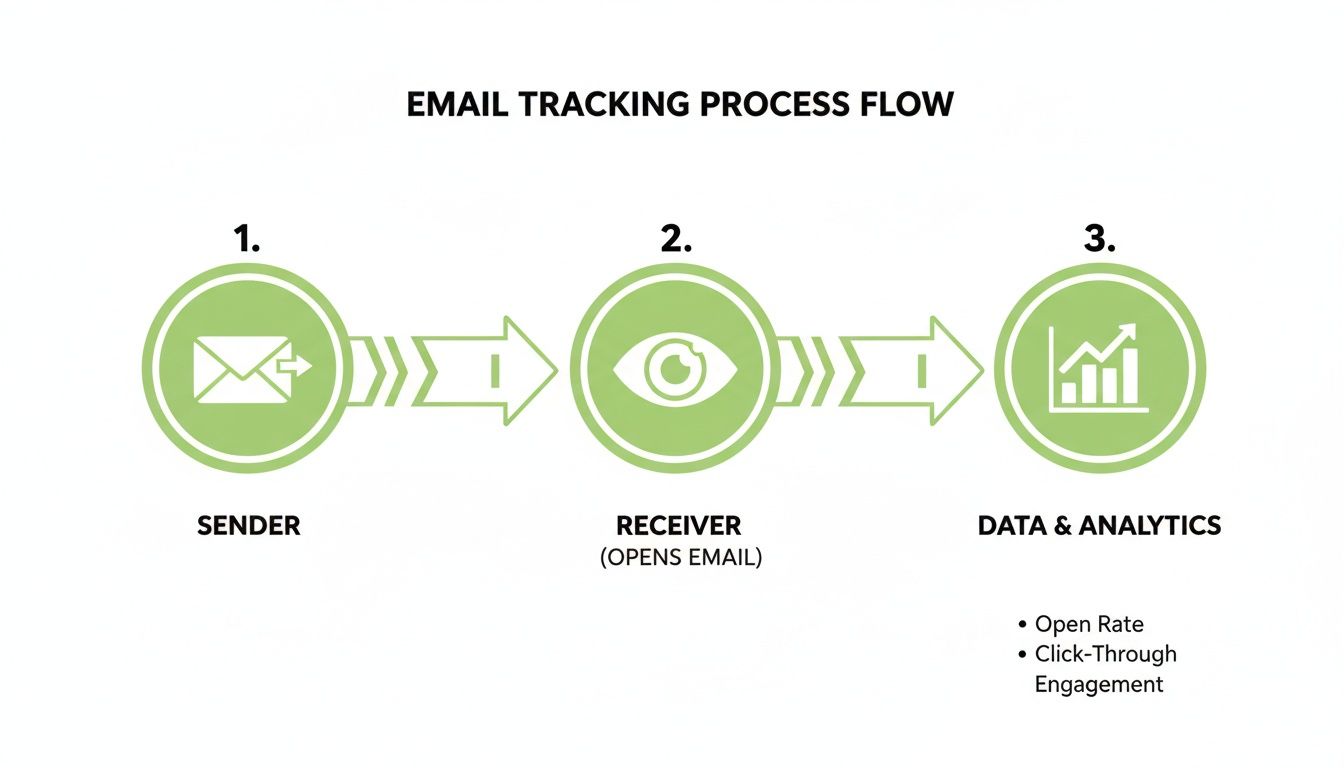
How Spammers Use Trackers to Violate Your Privacy
Once spammers have your address, they use invasive tracking techniques to confirm it's active and monitor your behavior. This validation makes your email address more valuable on the spam market.
These privacy-invading tools include:
- Spy Pixels: A tiny, invisible 1×1 pixel image is embedded in the email's HTML code. When you open the message, your email client loads this pixel from the spammer's server, sending a signal that confirms your email is active and you've opened their message.
- Tracking Links: Every link in a spam email is unique to you. Clicking any link—even the "unsubscribe" button—alerts the spammer that your account is active and you are an engaged user.
Any interaction with junk mail often confirms your status as a live target, leading to your address being sold to more spammers and resulting in even more junk mail. This vicious cycle highlights the security limitations of many free email platforms.
The Hidden Dangers Lurking in Your Junk Folder
Not all junk mail is a simple annoyance; a significant portion is a direct threat to your email security. While much of it is aggressive marketing, a dangerous subset is engineered to deceive you into surrendering sensitive personal information. This is where the problem escalates from inbox clutter to a serious security risk.
These malicious emails have become incredibly sophisticated, often impersonating trusted brands like your bank, Canada Post, or even a government agency. They are designed to create a sense of urgency, pressuring you to act impulsively before you can scrutinize the message.
From Annoyance to Active Security Threat
The real danger lies in how convincing these scams can be. An email with the subject "Action Required: Your Account Has Been Suspended" can look completely official, with legitimate logos and branding. This is a classic phishing attack.
The link in the email leads not to the real website, but to a pixel-perfect fake login page. The moment you enter your credentials, you have handed them directly to a criminal. This can lead to financial theft, identity fraud, or the takeover of your online accounts.
The core of a phishing email is manipulation. It preys on trust and urgency, bypassing technical defences by targeting human psychology. Protecting your email security means learning to spot these emotional triggers.
Phishing is one of the most dangerous forms of junk mail, and its prevalence is rising in Canada. Stealing credentials has become the preferred method for cybercriminals. In fact, phishing campaigns targeting Canadian organizations shot up by 27% from 2023 to 2024 alone. You can dig deeper into the rise of these threats by exploring the latest Canadian phishing statistics.
Common Disguises for Malicious Emails
To protect your email security, you must learn to recognize the common tactics cybercriminals use:
- Fake Delivery Notifications: An email from "Canada Post" claims a package could not be delivered and asks you to click a link to reschedule or pay a small fee, which is a ploy to steal your credit card details.
- Fraudulent Bank Alerts: A message that appears to be from your bank warns of suspicious activity and directs you to a counterfeit site designed to capture your banking credentials.
- Urgent Password Resets: An unexpected email from a service like Netflix or Amazon claims you must reset your password, leading you to a malicious link that compromises your account.
These examples underscore why robust email security is non-negotiable. It's about building a solid defense for your finances and digital identity, starting with your choice of email provider and your own security habits.
Proven Strategies to Reclaim Your Inbox
Feeling overwhelmed by junk mail is more than frustrating—it's a security risk and a drain on your productivity. The good news is that you can fight back effectively. By implementing a layered defense strategy, you can significantly reduce spam and enhance your overall email security.
It starts with handling existing junk mail correctly to avoid making the problem worse.
Your first instinct may be to click "unsubscribe." For legitimate newsletters, this is safe. However, for suspicious emails from unknown senders, clicking "unsubscribe" is a critical mistake. It confirms to spammers that your email address is active, making you a more valuable target and inviting even more junk.
A much safer approach is to use your email client’s built-in security tools. “Block Sender” and “Mark as Spam” are essential. Blocking prevents that specific address from reaching you again, while marking as spam trains your email provider’s filters to better identify and stop similar threats in the future.
Building a Stronger Defence System
While blocking and reporting are reactive, a truly secure inbox requires a proactive strategy. The goal is to prevent your primary email address from being exposed and to automate the filtering of incoming mail.
Here are two highly effective email security strategies:
-
Use Email Aliases: An alias is a disposable, forwarding email address that directs mail to your main inbox. Create unique aliases for different services, like
shopping.username@email.comornewsletters.username@email.com. If an alias starts receiving spam, you know exactly which company had a data leak or sold your information. You can then simply delete that alias to cut off the spam instantly. -
Create Custom Filters and Rules: Set up rules in your email platform to automatically manage messages. For example, create a filter that sends any email containing spammy keywords like "crypto" or "limited time offer" directly to the trash. This ensures the most obvious junk never distracts you. For more advanced protection, explore some of the top email spam filters available to protect your inbox.
As the chart below illustrates, effective filtering is your first line of defense against serious online threats.

This visual highlights how a poorly managed junk folder can be a gateway to significant security risks, including phishing, financial fraud, and identity theft.
Understanding Email Authentication Protocols
A more advanced layer of email security involves authentication protocols that operate behind the scenes. These technical standards help your email provider verify a sender's identity, making it much harder for spammers to impersonate legitimate brands.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) are the three pillars of email authentication. They function like a digital passport system, validating a sender's credentials to confirm they are authorized to send from a specific domain.
You don't need to be a technical expert to benefit from these. Your responsibility is to choose a hosted email platform that enforces these standards rigorously. A secure provider will have strict authentication checks built-in, automatically rejecting fraudulent emails before they can compromise your inbox. This is a cornerstone of modern email security.
Choosing a Secure Hosted Email for Lasting Privacy
To stop junk mail for good, the most impactful step is to choose a secure email platform. The problem with most free email providers is their business model: you are the product. They profit by scanning your data to serve targeted ads, creating a fundamental conflict of interest between their profits and your privacy.
A paid, secure hosted email service operates on a different principle. You pay a fee for the service, and in return, their entire business is dedicated to safeguarding your data and privacy, not monetizing it.
The Fortress Model of Email Security
A secure email service functions less like a public mailbox and more like a private vault. It is engineered from the ground up with features designed to defeat the tools spammers and cybercriminals rely on.
These platforms are a core part of your digital defense system. Key privacy and security features include:
- Automatic Tracker Blocking: These services automatically strip out invisible spy pixels that spammers use to track when you open their emails, cutting off their validation feedback loop.
- Zero-Access Encryption: Your messages are encrypted so that not even the email provider can read them. In the event of a data breach, your information remains unreadable and secure.
- Ad-Free Environments: With no advertisers to please, the provider has no incentive to scan your emails or monitor your behavior, ensuring true email privacy.
By design, these platforms create a hostile environment for spam and a secure one for your communications.
Why Data Residency Matters for Email Privacy
Where your email data is physically stored has significant privacy implications. Choosing a hosted email provider in a country with strong privacy laws, like Canada, adds a robust layer of legal protection. Canadian data residency means your information is governed by regulations like the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), which provides legal safeguards against unauthorized access.
A private, hosted email service flips the power dynamic. Instead of your data being a commodity for advertisers, it becomes a protected asset that the provider is paid to secure. This alignment of interests is the cornerstone of lasting email privacy and security.
Ultimately, tackling junk email effectively means making secure data practices a priority. To learn more about selecting the right platform, check out our guide to secure email services.
For instance, a provider like Typewire keeps its entire infrastructure within Canada, ensuring all your communications benefit from these stringent privacy standards. This commitment to a secure foundation is the real answer to "why am I getting so many junk emails?"—it stops the problem at its source.
The Sheer Scale of the Junk Mail Problem
If you're wondering why your inbox is constantly flooded with junk, the first thing to realise is that you're not just up against a few annoying marketers. You're facing a highly organised, industrial-scale operation. The sheer volume of spam hitting Canadian inboxes has reached staggering levels, making it a daily battle to find your important messages.
This isn't a personal issue; it's a global tidal wave. In 2025, estimates show that a mind-boggling 160 billion spam emails are sent across the world every single day. That accounts for nearly half of all email traffic. The problem is especially bad here at home, with Canada ranking as one of the top spam-generating countries, contributing around 6.9 billion spam messages daily. If you want to dive deeper into these numbers, the latest statistics on global spam traffic paint a pretty clear picture.
This massive, automated assault is exactly why trying to block senders one by one feels like trying to bail out the ocean with a thimble. The scale of the problem demands a defence that's just as powerful and automated.
This is where a privacy-first, secure email hosting platform changes the game entirely. It moves your defence from a frustrating, manual chore to a proactive, professional-grade shield built to fight this industrial-sized threat head-on.
Your Junk Email Questions, Answered
Let's cut through the noise. When it comes to junk mail, there's a lot of conflicting advice out there. I've broken down some of the most common questions to give you clear, actionable answers for keeping your inbox clean and secure.
Will Unsubscribing from Junk Email Just Make It Worse?
This is the big one, and the answer is: it depends entirely on who sent it.
If the email is from a legitimate business you know—a newsletter you signed up for, a store you shopped at—then hitting "unsubscribe" is exactly what you should do. It’s the proper way to tell them you’re no longer interested, and they’re legally obligated to honour it.
But what about that sketchy email from a sender you’ve never heard of? Clicking anything in that message, especially the unsubscribe link, is a mistake. It’s like raising your hand and telling the spammer, “Yep, this email is active!” That confirmation makes your address a more valuable target, and they'll likely sell it to other spammers, unleashing an even bigger wave of junk.
My Rule of Thumb: If you recognise the sender, unsubscribe. If it looks like a random scam, just mark it as spam and delete it. Don't engage.
How Can I Find Out If My Email Was Part of a Data Breach?
Understanding where you’ve been exposed is a massive step towards better security. Thankfully, there are free and trusted services that can help. My go-to recommendation is always “Have I Been Pwned?”.
It’s simple. You just pop your email address into their secure site, and it cross-references it against a massive database of known data breaches. If your address shows up, it will tell you exactly which services were compromised. The moment you find a match, you need to change the password for that account and for any other site where you might have reused it.
Is It Possible to Stop All Junk Email Completely?
Let's be realistic: stopping 100% of junk mail is a bit of a pipe dream. Spammers are relentless and are always cooking up new ways to sneak past filters. The real goal, and a very achievable one, is to reduce the flood to a tiny, manageable trickle.
This is where you combine smart habits with the right technology. An effective defence isn't just one thing; it's a layered strategy.
- Start with a strong foundation: Use an email service with powerful, built-in spam filters.
- Isolate the source: Use email aliases for signing up to different newsletters or online shops. If one alias gets spammed, you know who the culprit is and can just delete it.
- Guard your main address: Be selective about where you share your primary email.
- Choose privacy-focused tools: A good private email provider will automatically block trackers and spot phishing attempts before they even hit your inbox.
The idea is to make your inbox a difficult and unappealing target. The threat isn’t going away—in fact, research shows that over one-third of Canadians have been hit by scammers, with 34 percent receiving phishing emails. If you're curious about how sophisticated these attacks are becoming, you can read the full research on these Canadian scammer tactics.
Ready to take back your inbox? A private, secure, and ad-free email solution is the best defence. Typewire is built in Canada to protect your privacy with powerful anti-spam filters, tracker blocking, and zero-access encryption. Start your 7-day free trial today.