Email phishing is a particularly nasty type of cybercrime where attackers pose as someone you trust—think your bank, a colleague, or a popular brand—and send you fraudulent emails. Their goal is to trick you into revealing sensitive information. It’s less of a technical hack and more of a psychological game, preying on human nature to get you to willingly hand over passwords, credit card numbers, or personal data.
The Digital Con Artist in Your Inbox
Imagine a con artist who doesn't need a disguise in the real world. Instead, they operate from the shadows, crafting the perfect digital mask. They use convincing logos, familiar language, and a powerful sense of urgency to look completely legitimate.
Their whole operation is designed to earn your trust for just a few seconds—long enough for you to click a malicious link or open a dangerous attachment. This isn't some random, brute-force attack; it’s a carefully planned act of impersonation. They might pretend to be from your bank with a "security alert," a delivery service about a "missed package," or even your own IT department warning of a "password expiry." The scenarios feel just plausible enough to bypass our natural skepticism.
Why Your Email Is Such a Prime Target
Think about it: your inbox is the command centre for your entire digital life. It holds the keys to almost every other online account you have, from social media and shopping sites to your financial services. If someone gets into your email, they can reset the passwords for everything else. This makes protecting your email one of the most critical parts of your overall email security.
A compromised email account can set off a disastrous domino effect. An attacker can gain access to a treasure trove of your personal and financial information, and the damage can spread far beyond just that one account.
An attacker doesn’t need to break down your digital door if they can convince you to hand over the key. Phishing works by exploiting human psychology—our innate trust, fear, and curiosity—rather than complex technical vulnerabilities.
The Real-World Impact of Phishing
When a phishing attack succeeds, the consequences can be devastating. For an individual, it could mean identity theft, significant financial loss, or having personal photos and documents stolen. For businesses, the fallout from a single employee falling for a scam can be catastrophic, leading to massive data breaches, financial fraud, and irreparable damage to the company’s reputation.
The sheer scale of this threat is staggering; phishing is consistently one of the top causes of data breaches worldwide. This reality makes it clear we need a better approach to email security. Instead of just reacting to threats after the fact, the best defence is a proactive one.
It all starts with a foundation built on email privacy and email security from the ground up. Choosing a secure hosted email platform that prioritizes protecting its users over collecting their data is your strongest shield. These services offer advanced filtering and privacy features that are designed to stop phishing attacks before they even have a chance to land in your inbox, safeguarding your most critical digital asset.
How to Recognize a Phishing Email
Think of a phishing email as a counterfeit bill. At a quick glance, it looks real enough to pass, but when you know what to look for, the tiny flaws give it away. These emails aren't just random spam; they're carefully designed social engineering traps meant to trick you into acting before you have a chance to think.
Scammers are masters of psychological manipulation. They create a false sense of urgency, fear, or even opportunity, knowing that a panicked mind is less likely to spot the red flags. That’s why so many phishing attempts come disguised as urgent "security alerts," fake "account suspensions," or too-good-to-be-true "prize notifications."
To get a better handle on this, the concept map below illustrates the core parts of a phishing attack, showing how deception is used to hook a target and achieve the scammer's goal.
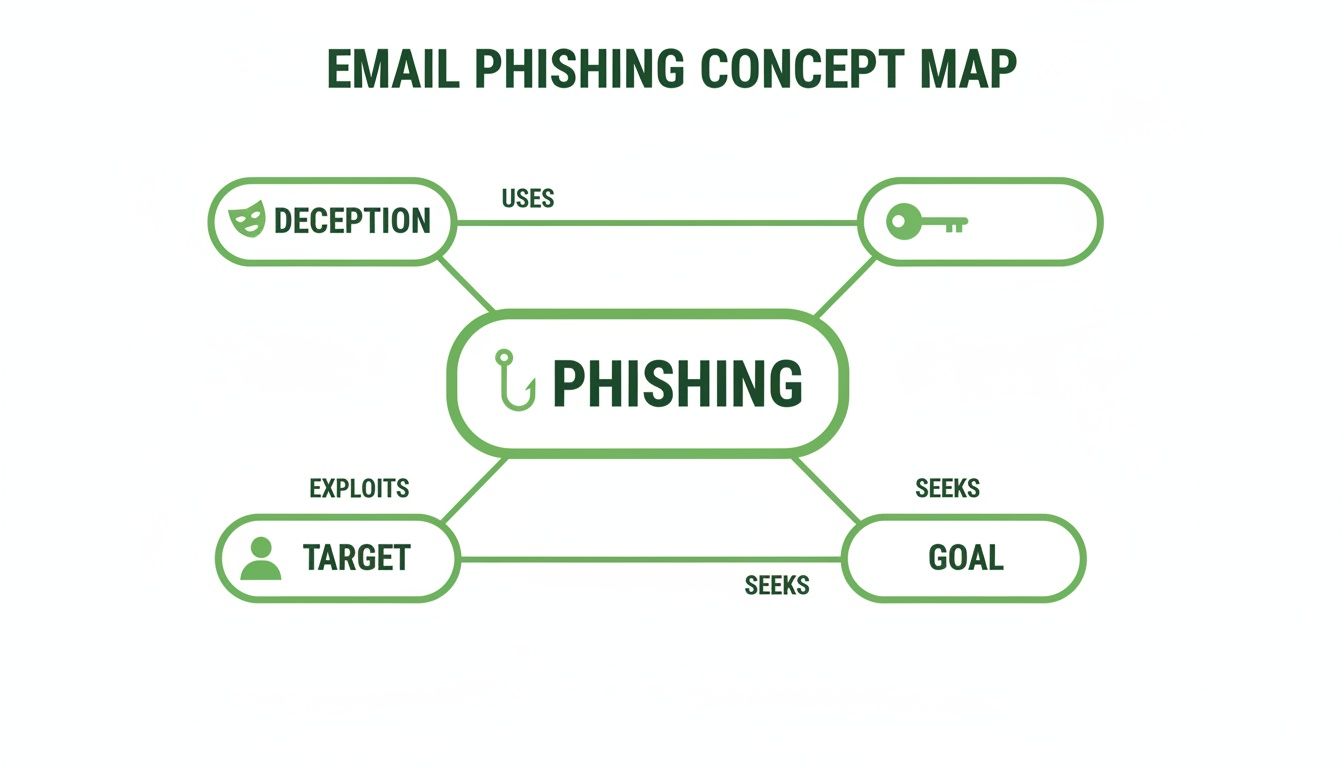
This map really drives home that every phishing attempt is a calculated process. It starts with a believable disguise and ends with pressuring someone to act against their own best interests.
Breaking Down the Anatomy of a Phish
To keep your inbox safe, it helps to develop a mental checklist for spotting fakes. Let’s dissect the common tells of a phishing email so you can see the trap before you fall for it. Often, scammers will combine several of these elements to create a more convincing, but ultimately fraudulent, message.
1. The Deceptive 'From' Address
At first glance, the sender’s name might look totally legitimate—think "Your Bank" or "Microsoft Security Team." But the actual email address hiding behind that name usually tells a different story. Scammers have a couple of go-to tricks here:
- Spoofing: They create an address that’s almost identical to the real one, hoping you won't notice the difference. This could be something subtle like "support@microsott.com" (with two 't's) or using a public domain like "@gmail.com" when it should be an official company one.
- Display Name Deception: This is especially sneaky on mobile devices where the full email address is often hidden. Attackers will use a trusted display name, banking on the fact that you won't take the extra step to reveal the suspicious address underneath.
2. An Urgent and Alarming Subject Line
Phishing subject lines are pure clickbait, engineered to spark an immediate emotional reaction. The goal is to make you panic and click without a second thought. You've probably seen these before:
- "Action Required: Your Account Has Been Suspended"
- "Unusual Sign-in Activity Detected"
- "You Have a Pending E-Transfer"
- "Your Invoice [Number] is Overdue"
These messages manufacture a crisis, pushing you to bypass your usual caution. It's this psychological game that makes phishing so dangerously effective.
The Hidden Dangers in the Email Body
The body of the email is where the real trap is sprung. Scammers will meticulously copy the logos, fonts, and overall design of legitimate companies to earn your trust. But hidden within this familiar-looking package are the malicious elements you need to be on the lookout for.
Even seasoned security experts can fall for a well-crafted phish when they're tired or distracted. The attack that compromised Troy Hunt's Mailchimp list was successful because it created just the right amount of urgency without being over-the-top, catching him at a moment of weakness.
This is a powerful reminder that vigilance is crucial for everyone, no matter how tech-savvy you are.
Here’s what to look for inside the email:
- Suspicious Links: Always hover your mouse over any buttons or hyperlinked text before you click. The true destination URL will pop up either next to your cursor or at the bottom of your browser window. If that URL looks sketchy or doesn't match the company's real website, it's a huge red flag.
- Dangerous Attachments: Be extremely wary of unexpected attachments, especially from senders you don't know. Phishing emails often use seemingly harmless files like invoices (PDFs) or shipping notices (Word documents) to sneak in malware. While many hosted email platforms have built-in virus scanners, you are always the final line of defence.
- Generic Greetings and Poor Grammar: Although some attacks are highly personalized, many still rely on generic greetings like "Dear Valued Customer." A real company will almost always use your name. Obvious spelling mistakes and clunky, unnatural phrasing are also classic giveaways of a scam.
By learning to spot these individual red flags, you build a powerful defence against these attacks. For a deeper look into specific examples, you can learn more by checking out our guide on how to identify phishing emails.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
While every phishing attack runs on deception, scammers have a whole playbook of different strategies to trick you. Knowing what you're up against is half the battle. Think of it like a game of chess—if you can spot your opponent's opening moves, you're in a much better position to defend yourself.
Not all phishing is a wide-net, spray-and-pray operation. Many attacks are incredibly specific, using information about you to make their bait almost impossible to resist. This is why just having a basic spam filter isn't enough; you need a more robust defence, like the kind built into a secure hosted email platform.

Let's break down the most common phishing attacks you're likely to see. Learning to recognise these patterns is the first step to keeping your digital life safe.
Spear Phishing: The Highly Personalised Attack
If a generic scam is a shotgun blast, spear phishing is a sniper rifle. Attackers don't just blast out thousands of emails; they pick a specific target—a single person or a small group—and do their homework. They'll scour your social media, your company's website, and any other public information to find personal details.
With that research, they can craft an email that feels incredibly real. It might mention a colleague by name, reference a project you just finished, or talk about a conference you recently attended. Because it contains details that seem private, your natural defences go down, undermining your personal email privacy.
Spear phishing works because it preys on our trust in the familiar. When an email contains specific, personal details, our brain is wired to see it as authentic, bypassing the usual skepticism we might have for a generic message.
This targeted approach makes spear phishing one of the most dangerous threats out there, for both individuals and entire organisations. A single, well-crafted email can be all it takes to cause a massive data breach. To learn more about this specific threat, check out our guide on what is spear phishing and how to stop it.
Whaling: Targeting the Big Fish
Whaling is a special kind of spear phishing that goes after the biggest targets in an organisation. Scammers set their sights on the "big fish"—CEOs, CFOs, and other senior executives—because compromising their accounts gives them access to the most sensitive data and financial controls.
A whaling email might look like it’s from the company's lawyer demanding an urgent wire transfer, or a board member asking for confidential financial reports. The combination of authority and urgency is designed to pressure the executive (or their assistant) into acting immediately, without thinking to verify the request. A successful whaling attack can lead to millions in direct financial losses or the theft of priceless intellectual property.
It’s a powerful reminder that every sensitive request needs strict verification, no matter who it appears to be from.
Clone Phishing: The Art of the Perfect Copy
Clone phishing is a nasty trick that uses a legitimate email you've already received against you. A scammer will take a real email—like a shipping confirmation from Amazon or a notification from Dropbox—and create an almost identical copy, or "clone."
They then swap the real links or attachments with malicious ones and send the email from an address that looks almost exactly like the original. Because the email looks so familiar, you’re far more likely to trust it and click the new, dangerous link without a second thought. It's a clever tactic because it hijacks the trust you've already built with a brand you know.
Phishing Attack Types and Their Targets
Each phishing method uses a different angle to try and get past your guard. This quick-reference table breaks down the key differences to help you spot them in the wild.
| Attack Type | Primary Target | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Generic Phishing | A large, random group of people | A wide-net approach using common bait like fake invoices or password resets. |
| Spear Phishing | A specific individual or small group | Highly personalised content based on research of the target's public information. |
| Whaling | High-level executives (CEOs, CFOs) | Impersonates authority to trick senior staff into making financial transfers or revealing data. |
| Clone Phishing | Anyone who has received a legitimate email | Copies a real email the target has already seen and replaces safe links with malicious ones. |
Ultimately, the variety of these tactics shows that scammers are always evolving. A private, secure hosted email platform can give you a critical layer of defence, using advanced algorithms and privacy-focused design to catch and block these threats before they ever land in your inbox.
Why Phishing Attacks Are So Successful
Phishing continues to work so well, not because of some brilliant, unbreakable code, but because it targets the one vulnerability no software can patch: human nature. Attackers have figured out that it's much easier to trick someone into unlocking the door than it is to break it down themselves.
They’ve become masters of psychological manipulation, blending their social engineering with just enough technical trickery to make their scams look completely real. An email can appear pixel-perfect, but it's often a carefully constructed trap. To really understand why these attacks keep succeeding, we need to look at both the human and the technical sides of the coin.
Exploiting Human Nature
The most effective phishing messages are designed to short-circuit our rational thinking by triggering a powerful emotional response. Scammers know we're busy and often process emails on autopilot, and they use this to their advantage. A distracted mind is their best friend.
They rely on a few predictable psychological triggers:
- Urgency and Fear: "Your account has been suspended." "We've detected an unusual login." These messages create instant panic, pushing you to act now before you have a chance to question it.
- Authority: We’re naturally conditioned to trust authority figures. So, when an email looks like it’s from your CEO, the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), or your bank, our first instinct is to comply.
- Curiosity and Greed: Who doesn't love a good deal? The promise of a prize, a surprise package, or an exclusive discount is often too tempting to ignore, baiting you to click a link you'd otherwise be wary of.
These tactics aren't random; they're fine-tuned to prey on deeply rooted human behaviours. They exploit our instinct to resolve problems quickly, our trust in familiar names, and our simple curiosity.
The Technical Loopholes They Use
Beyond the mind games, attackers take advantage of technical weaknesses baked into many email systems. The most common tactic by far is email spoofing. This is where they forge the "From" address to make an email look like it came from a legitimate source, like your bank or a colleague. It's surprisingly easy for a scammer to make an email look like it’s from "yourbank.ca" when it was actually sent from their own malicious server.
This is where the email service you choose really matters. A lot of the big, ad-supported email providers offer basic protection, but their business models are often built around collecting data, not providing ironclad security. They can lack the advanced, privacy-focused protocols needed to reliably spot and block sophisticated spoofing attempts.
A secure, hosted email platform acts as a critical line of defence. By prioritizing email privacy and email security above all else, these services can catch and neutralize threats that simpler systems might let slip through, keeping your inbox—and your sensitive data—safe.
In Canada, this is a massive issue. A recent poll found that 38% of Canadians have received phishing emails in the last three years. Scammers frequently pose as banks, the CRA, and delivery services to get their hands on personal information. This is made worse by our own habits, as the same study found 52% of people admit to checking their email on unsecured public Wi-Fi. You can dive deeper into these Canadian cybersecurity trends to see just how widespread the problem is.
When you combine this constant exposure with clever psychological and technical tricks, you create a perfect storm where one moment of inattention can lead to a serious security breach.
Building Your Defence Against Phishing
Knowing what email phishing is and spotting the red flags are your first line of defence. But real email security isn’t about just dodging attacks as they come—it's about building a fortress that stops them from ever reaching you in the first place. This means blending smart personal habits with the powerful tools offered by a secure, private hosted email platform.

Your defence plan starts with discipline. Get in the habit of being skeptical of any unexpected email that tries to rush you into action. Before you even think about clicking, hover your mouse over the link to see the actual destination URL. Look closely at the sender’s full email address, not just their display name, for anything that seems off. Think of these habits as your personal firewall.
Relying on vigilance alone, however, is a gamble. A truly solid defence needs a foundation of strong email security and email privacy built right into your email service. This is where choosing the right provider becomes your single most powerful move.
The Power of a Privacy-First Email Platform
Many free, ad-supported email services treat you like the product. Their business model is built on collecting your data, which can open up security holes. A privacy-focused hosted email platform, on the other hand, works on a completely different premise: its only job is to protect you and your communications.
These platforms give you a multi-layered defence that’s always on, actively working to keep phishing attempts out. Key features that form this protective shield include:
- Advanced Anti-Phishing Filters: These sophisticated systems scan incoming emails for signs of spoofing, dodgy links, and other classic phishing tactics, blocking them before you see them.
- Default Spy Pixel Blocking: Lots of marketing emails and newsletters contain tiny, invisible tracking pixels that tell the sender when and where you opened their message. A private email provider blocks these by default, shutting down a major data collection channel for spammers and scammers.
- Zero-Access Encryption: This is a crucial one. It means that nobody—not even the provider—can read your stored emails. Your data is protected from both outside attacks and internal prying eyes, making it worthless to hackers even if they managed to breach a server.
By having these features active from the get-go, a secure hosted email platform drastically cuts down your exposure to phishing.
Strategic Tools for Protecting Your Identity
Beyond these core security layers, a private email service gives you smart tools to shrink your digital footprint and shield your real email address. One of the most effective is the use of email aliases.
An email alias is basically a disposable forwarding address that sends emails to your main inbox. Think of it as a mask for your real identity. You can create a unique alias for every website or service you sign up for—one for social media, another for shopping, and a third for newsletters.
By using aliases, you build compartments in your digital life. If one alias starts receiving spam or phishing attempts, you know exactly which service was breached or sold your data, and you can simply delete the alias without affecting your main account.
This simple practice is incredibly effective. It keeps your primary email address from being exposed in public data breaches, making it much harder for criminals to target you with personalized spear-phishing attacks. For more actionable advice on safeguarding your inbox, explore our essential security tips on how to avoid phishing emails.
The Canadian Advantage: Data Residency and PIPEDA
For anyone in Canada, choosing a hosted email platform based here adds another powerful layer of protection. When your data is stored on Canadian soil, it falls under the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA). This is a federal privacy law that lays down strict rules for how your personal information must be handled.
PIPEDA provides a strong legal framework that puts your privacy rights first, ensuring your data isn't subject to the broader surveillance laws of other countries. This principle of data residency is a cornerstone of digital sovereignty, giving you peace of mind that your private communications are legally protected.
The financial stakes are incredibly high. In a single recent year, Canadians lost around $100 million to online fraud, with phishing being a major gateway. The shift to remote work only made things worse; during the first six months of the pandemic, a staggering 34% of Canadians reported receiving phishing emails.
Ultimately, building a tough defence against phishing means attacking the problem from two sides. You need to combine your own vigilant habits with the superior technology of a private, hosted email platform. For a comprehensive look at online safety, reviewing the best practices for securing your Google Workspace can offer foundational knowledge that applies to any email defence. This combined approach empowers you to take back control of your inbox and secure your digital life.
A Few Lingering Questions About Email Phishing
Even with a solid understanding of phishing, a few practical questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones with clear, straightforward answers.
What Should I Do If I Just Clicked a Phishing Link?
Okay, first things first: don't panic. The critical thing is to act fast to limit the damage. Your immediate goal is to cut off any connection that malicious link might have opened.
Get your device offline immediately. Turn off your Wi-Fi, unplug the ethernet cable—whatever it takes. This can stop malware in its tracks before it phones home to the attacker. Once you're disconnected, run a full, deep scan with a trusted antivirus program to hunt down and quarantine anything nasty it finds.
Next, change the password for the account you believe was targeted. And if you’ve reused that password anywhere else (we all know we shouldn't, but it happens), you need to change those passwords too, right now. As a final, crucial step, turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) for every important account. It's one of the single best upgrades you can make to your email security.
How Is Phishing Different From Spam?
While both are inbox clutter, their intent is what really separates them. Think of spam as digital junk mail—annoying flyers and unsolicited catalogues trying to sell you something. It’s a nuisance, but usually harmless.
Phishing, on the other hand, is a targeted act of fraud. It's a con job designed with one goal in mind: to trick you into handing over sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or other personal details.
A spam filter is like a mail sorter, automatically binning the promotional junk. But an anti-phishing system, like those built into secure hosted email platforms, is more like a dedicated security guard, actively spotting and neutralizing criminals trying to get past the gate.
Can I Get Phished on My Phone?
Absolutely. In fact, it's often more dangerous. The smaller screens on our phones and tablets make it incredibly difficult to spot the tell-tale signs of a phishing attempt, like a cleverly disguised URL or a slightly off sender address.
Plus, we often check our email on the go—while distracted, multitasking, or in a rush. This is precisely the mindset attackers bank on, making us far more likely to tap a link without a second thought.
We're also seeing a rise in mobile-specific attacks like "smishing" (phishing via SMS) and "vishing" (voice phishing over phone calls). The same rules apply here: stay skeptical, always verify who's contacting you, and use a secure email app with built-in protections. Robust email privacy settings are your best line of defence, no matter the device.
Are Free Email Services Less Secure?
While the big-name free email providers have basic protections, their business model can create some real security and privacy gaps. Let's be blunt: for many of these services, their revenue comes from scanning your data to sell ads. You aren't the customer; you're the product.
Privacy-first hosted email platforms work on a completely different model. You pay a subscription, and in return, their entire business revolves around protecting you and your data. It's a straightforward exchange.
Because their reputation is built on trust, these providers invest heavily in superior security. You'll find features like end-to-end encryption, more sophisticated phishing detection, and spy-pixel blocking turned on by default—things that go way beyond the free offerings. This makes a private email service a fundamentally stronger foundation for keeping your digital life safe from sophisticated attacks.
Ready to put a stop to phishing attempts and reclaim your privacy? Typewire offers a secure, Canadian-hosted email platform with advanced anti-phishing protection, zero-access encryption, and a strict no-tracking policy. Start your free 7-day trial and experience a safer inbox today.


